Micro Focus COBOL™
Language Reference - Additional Topics
Micro Focus®
Issue 20
September
2001
Copyright © 2001 Micro Focus International Limited.
All rights reserved.
Micro Focus International Limited has made every effort to ensure that this
book is correct and accurate, but reserves the right to make changes without
notice at its sole discretion at any time. The software described in this document
is supplied under a license and may be used or copied only in accordance with the
terms of such license, and in particular any warranty of fitness of Micro Focus
software products for any particular purpose is expressly excluded and in no event
will Micro Focus be liable for any consequential loss.
Animator®,
COBOL Workbench®,
EnterpriseLink®,
Mainframe Express®,
Micro Focus®,
Net Express®,
REQL® and
Revolve® are registered trademarks, and
AAI™,
Analyzer™,
Application to Application Interface™,
AddPack™,
AppTrack™,
AssetMiner™,
CCI™,
DataConnect™,
Dialog System™,
EuroSmart™,
FixPack™,
LEVEL II COBOL™,
License Management Facility™,
License Server™,
Mainframe Access™,
Mainframe Manager™,
Micro Focus COBOL™,
Object COBOL™,
OpenESQL™,
Personal COBOL™,
Professional COBOL™,
Server Express™,
SmartFind™,
SmartFind Plus™,
SmartFix™,
SourceConnect™,
Toolbox™,
VS COBOL™,
WebSync™, and
Xilerator™
are trademarks of Micro Focus International Limited. All other trademarks
are the property of their respective owners.
No part of this publication, with the exception of the software product
user documentation contained on a CD-ROM, may be copied, photocopied,
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, or reduced to any electronic medium or
machine-readable form without prior written consent of Micro Focus
International Limited.
Licensees may duplicate the software product user documentation
contained on a CD-ROM, but only to the extent necessary to support the users
authorized access to the software under the license agreement. Any reproduction
of the documentation, regardless of whether the documentation is reproduced in
whole or in part, must be accompanied by this copyright statement in its
entirety, without modification.
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. It is acknowledged that the Software
and the Documentation were developed at private expense, that no part is in the
public domain, and that the Software and Documentation are Commercial Computer
Software provided with RESTRICTED RIGHTS under Federal Acquisition Regulations
and agency supplements to them. Use, duplication or disclosure by the U.S.
Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii)
of The Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFAR
252.227-7013 et. seq. or subparagraphs (c)(1) and (2) of the Commercial
Computer Software Restricted Rights at FAR 52.227-19, as applicable. Contractor
is Micro Focus International Limited, 9420 Key West Avenue, Rockville,
Maryland 20850. Rights are reserved under copyright laws of the United States
with respect to unpublished portions of the Software.
Preface
This book
describes the support for those COBOL language features that are additional to
the ANSI COBOL standards X3.23-1985, X3.23a-1989 and X3.23b-1993. These COBOL
language extensions are supported by a number of COBOL systems.
Audience
This book is
intended for programmers already familiar with the COBOL language.
Related Publications
Other books to which you may need to refer include the Getting
Started book and User's Guide for your COBOL system, and:
- Language Reference
- Error Messages
- Compatibility Guide
Using this
book
This book
describes the support provided for additional language features such as
DBCS, Report Writer and
Segmentation. These features are less commonly used. Your Language
Reference should be used as the companion
book to this one.
It describes the support we
provide for the base COBOL language.
Notation
Throughout this book, the following notation is used to
describe the format of COBOL statements:
- Words printed in capital letters which are underlined must always be
present when the functions of which they are a part are used. An error will be
reported by your COBOL system if the underlined words are absent or incorrectly
spelled. The underlining is not necessary when writing a COBOL source program.
- Words printed in capital letters which are not underlined are used in
the COBOL source program for readability only. They may be written, or not, as
the programmer wishes, but if written, must be correctly spelled.
- All words printed in small letters are generic terms representing
names which will be devised by the programmer.
- When material is enclosed in braces { }, a choice must be made from
the options within them.
- When material is enclosed in choice indicators { | | }, one or more
of the unique options must be specified, but a single option may be specified
only once.
- When material is enclosed in square brackets [ ] , it is an
indication that the material is an option which may be included or omitted as
required.
- When material is enclosed in boxed, square brackets:

it is an indication that the material is mandatory for ANSI'74 COBOL
(American National Standards Institute publication X3.23-1974) but may be
optionally omitted as an extension to that language specification. The symbol
adjacent to the box or appearing in the margin indicates the dialects of COBOL
in which that material is optional. See rule 11 for further details on dialect
features.
- In text, the ellipsis (...) shows the omission of a portion of a
source program or a sequence. This meaning becomes apparent in context.
In the General Formats, the ellipsis represents the position at
which repetition may occur at the user's option. The portion of the format that
may be repeated is determined as follows:
Given ... in a clause or statement format, scanning right to left,
determine the } or ] immediately to the left of the ...; continue scanning
right to left and determine the logically matching { or [; the ... applies to
the words between the determined pair of delimiters.
- This Reference presents the syntax of IBM SAA AD/Cycle COBOL370
(COBOL/370) statements and the rules for writing source programs that are to be
compiled by the COBOL/370 compiler.
The only distinction
we make between
COBOL/370 and IBM VS COBOL II is that for the Procedure-Pointer format, the
default length is eight bytes rather than four bytes.
- This Reference presents the syntax of Multivendor Integration
Architecture (MIA) - Technical Requirements for the programming language COBOL.
No boxes or dialect symbols for MIA are used in this
book.
- The COBOL language accepted by most COBOL compilers includes
extensions to the COBOL language defined in American National Standard
X3.23-1974. Different compilers allow different extensions to this standard
which means that different versions, called `dialects', of COBOL exist. This
COBOL product is designed for use in cross-development; it can be used for
developing not only programs for use on your COBOL system itself but also
programs for use with IBM OS/VS COBOL,
IBM VS COBOL II, IBM COBOL/370
or IBM COBOL for OS/390 & V2R2, or programs that conform entirely to ANS
X3.23-1974 or its successor ANS X3.23-1985. It allows most extensions that are
in the IBM COBOLs, and all the features from ANS X3.23-1985 and
X3.23a-1989.
To help you keep to the appropriate dialect - that of your target
system - this book
shows the dialects in which each feature appears. In the text, features outside
ANS X3.23-1974 are in separate paragraphs, with a symbol indicating the dialect
at the start of the paragraph. Where a complete section is a separate dialect,
the heading of the section is followed by a symbol in a paragraph by itself. A
phrases which is part of a separate dialect is separated out into a paragraph
on its own, marked as indicated above. In syntax diagrams, features outside ANS
X3.23-1974 are enclosed in boxes, with symbols adjacent to the boxes or in the
margin.
The symbols used are as follows:
 |
These features are extensions to ANS X3.23-1974
that appear in IBM OS/VS COBOL. |
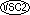 |
These features are extensions to ANS X3.23-1985
that appear in IBM VS COBOL II. |
 |
These features are extensions to ANS X3.23-1985
that are supported in IBM SAA AD/Cycle COBOL/370, but not in IBM VS COBOL
II. |
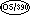 |
These features are extensions to ANS X3.23-1985 that are supported
in IBM COBOL for OS/390 V2R2, but not in IBM SAA AD/Cycle
COBOL/370. |
 |
These features are new features defined in ANS
X3.23-1985 which are not supported under ANS X3.23-1974. |
 |
These features are extensions to ANS X3.23-1985
that appear in the X/Open CAE Specification, COBOL language (XPG-4). |
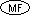 |
These features are extensions to ANS X3.23-1985
that are specific to Micro Focus COBOL. |
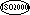 |
These features are features defined in ISO/IEC
1989:2000 which are not supported under ANS X3.23-1985. |
Notes:
- The Micro Focus, VS COBOL II, COBOL/370,
OS/390 and X/Open dialects
are all based on the ANS X3.23-1985 COBOL Standard. Therefore, any syntax (or
rules) which are marked as valid for ANS85 are also valid for Micro Focus, VS
COBOL II, COBOL/370, OS/390 and X/Open unless explicitly
designated otherwise.
- The COBOL/370 dialect includes all of the syntax included in VS
COBOL II which is marked with a VSC2 bubble in this
book. The only time
that a COB370 bubble appears in this
book are cases
where COBOL370 (with the NOCMPR2 compiler option) includes additional or
different text than that included with VS COBOL II (with the NOCMPR2 compiler
option).
These bubbles reflect support only for a particular syntax and its
semantics. You have to use Compiler directives to effect a set of reserved
words associated with a particular dialect. See the appendix Reserved
Words in this book and your Compatibility
Guide for a list of the reserved words affected by various dialects.
Thus, for example, if you are developing a program for use on IBM
OS/VS COBOL, you can use the unmarked features plus any marked OSVS; while if
developing solely for your COBOL environment you can use any feature. If you
supply the FLAG Compiler directive when you invoke the system software, your
COBOL system software flags any features outside the given dialect. You can
also use the FLAGAS Compiler directive to turn flagging messages into error
messages.
- Some features have different effects in different dialects; you
specify a dialect-control directive to select the dialect with which you want
compatibility. The boxes around such features are double-ruled.
Extra reserved words needed by features outside ANS X3.23-1985 are
reserved only when the appropriate dialect-control directive is present; this
means you can ensure that the only words reserved in the specified dialect are
reserved on your target system. If you use only features that need no extra
reserved words, and whose effects are the same in all dialects, you need not
specify a dialect-control directive.
The dialect-control directive specifying the ANS X3.23-1985 dialect
also causes the few ANS 3.23-1974 features not allowed in ANS X3.23-1985 to be
flagged with a warning message.
- The phrase "is documentary only" in the text of this
book means that the
associated coding is accepted syntactically by your COBOL system software, but
is ignored when producing the object program.
- Hexadecimal values are enclosed in quotation marks and preceded by a
lowercase x for nonnumeric values and by a lowercase h for numeric values; for
example, x"9D".
![]()