This part describes the base COBOL language definition.
The structure of the entire compilation group is described first. Each component of the compilation group is divided into four divisions.
Material is thus presented on the four divisions - the Identification Division, Environment Division, Data Division and Procedure Division. Within these divisions, material is presented according to COBOL sections, shown by the headers. Clauses, including intrinsic functions and COBOL verbs, are listed in alphabetical order, for ease of use.
Additional language features such as DBCS and Report Writer are supported, and are described in your companion manual, Language Reference - Additional Topics.
![]() A compilation group is the entire source file that
is submitted to the compiler. A compilation group consists of a series of
source units. A source unit may contain other source units and these contained
source units may reference some of the resources of the source units within
which they are contained.
A compilation group is the entire source file that
is submitted to the compiler. A compilation group consists of a series of
source units. A source unit may contain other source units and these contained
source units may reference some of the resources of the source units within
which they are contained.
![]() A compilation group may contain zero, one, or more
source units.
A compilation group may contain zero, one, or more
source units.
A source unit begins with an identification division and includes any
![]() contained source units.
contained source units.
With the exception of
![]() compiler directives,
compiler directives,
source text manipulation
statements, and
![]() end markers,
end markers,
the statements, entries,
paragraphs, and sections of a source unit are grouped into four divisions that
are sequenced in the following order:
The beginning of a division in a source unit is indicated by the
appropriate division header. The beginning of the
![]() identification division may also be indicated by
one of the paragraph headers permitted in the identification division.
identification division may also be indicated by
one of the paragraph headers permitted in the identification division.
The end of a division in a source unit is indicated by one of the following:
The end of a source unit is indicated by an
![]() end marker, if specified, or by the absence of
additional source lines in the compilation group.
end marker, if specified, or by the absence of
additional source lines in the compilation group.
When a source unit, B, is
![]() contained in another source unit, A, it may be
directly or indirectly contained. Source unit B is directly contained in source
unit A if there is no source unit contained in A that also contains B. Source
unit B is indirectly contained in source unit A if there exists a source unit
contained in A that also contains B.
contained in another source unit, A, it may be
directly or indirectly contained. Source unit B is directly contained in source
unit A if there is no source unit contained in A that also contains B. Source
unit B is indirectly contained in source unit A if there exists a source unit
contained in A that also contains B.
A source unit that is directly or indirectly contained within another source unit is considered in these specifications as a separate source unit that may additionally reference certain resources defined in the containing source unit.
The object code resulting from compiling a source unit contained within another source unit is considered in these specifications to be inseparable from the object code resulting from compiling the containing source unit.
![]() A compilation unit is a source unit that is not
contained within another source unit. It may be preceded or followed by other
compilation units in a compilation group.
A compilation unit is a source unit that is not
contained within another source unit. It may be preceded or followed by other
compilation units in a compilation group.
A source element is a source unit excluding any nested source units.
A runtime element is the result of compiling a source element.
A runtime module is the result of compiling a compilation unit.
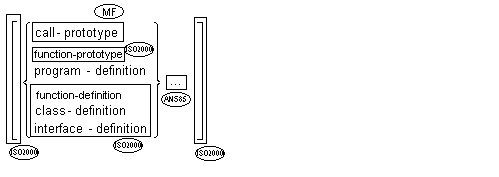
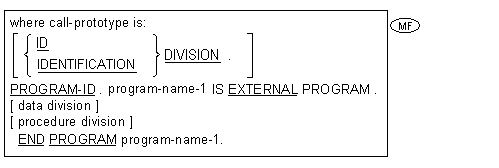
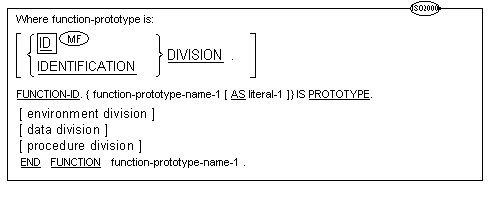
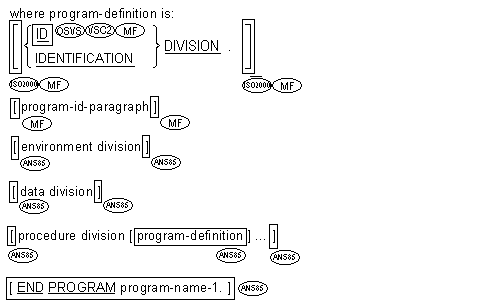
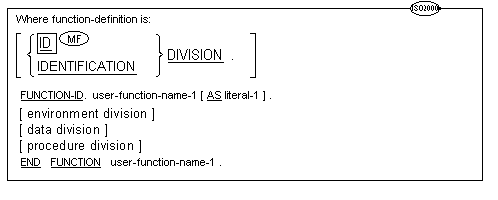
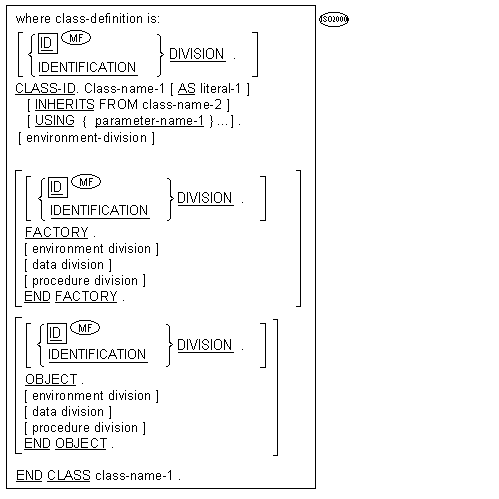
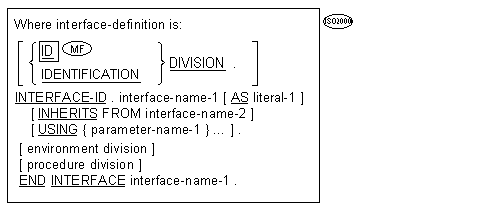
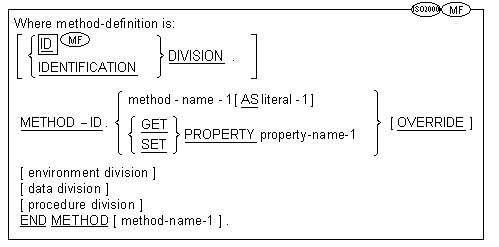
![]() call-prototypes and
call-prototypes and
![]() function-prototypes
function-prototypes
must precede all other types of source units.
![]()
End markers indicate the end of a definition
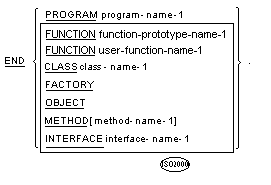
![]() If the PROPERTY phrase is specified in the
METHOD-ID paragraph, method-name-1 shall be omitted.
If the PROPERTY phrase is specified in the
METHOD-ID paragraph, method-name-1 shall be omitted.
Copyright © 2001 Micro Focus International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.