 | Assigning Scope with Subprojects | Analyzing Data Impacts |  |
Revolve helps you improve the quality of your project's source code by employing workbench capabilities to the facilitation of code modification. Revolve determines which statements, paragraphs, variables, and copybooks are unused in the system and alerts you to their status, in the event that the unused components should be extracted from the system. Revolve also provides a variety of vantage points from which code analysis can be observed. This feature ensures that your code modification efforts are necessary and correct.
You need to have read the chapter Start Here for the Tutorials! and worked through the first session, Creating and Loading Projects, before you do this session.
In this session, we assume that you have created Sample.prj.
Revolve determines which statements, paragraphs, variables, and copybooks are unused in the system and alerts you to their status, in the event that the unused components should be extracted from the system. Revolve also provides a variety of vantage points from which code analysis can be observed. This feature ensures that your code modification efforts are necessary and correct.
In this session you will identify an unused paragraph in the project's source code and learn how to remove it's source. You will also become familiar with the Split Screen Editor and how to use it to edit source.
You will apply the procedures in this session to the sample project created in Creating and Loading Projects. If Revolve and sample.prj are closed, open them like before.
In this session you:
To do this:
The expanded folder displays dynamic scripts that generate specific source code reports.
A progress bar displays the advancement of the script. A text report containing the results of the script is also displayed.
The report indicates that there is are several unused paragraphs in BATCH2.CBL.
C100-CONVERT-SALES-DATE
The line for C100-CONVERT... is not "selected" in a color as in other Revolve windows. However, notice that the status bar at the bottom of the Report shows that it is the selected element.
The Split Screen Editor opens to show the contents of BATCH2.CBL with paragraph C100-CONVERT-SALES-DATE selected.
Notice C100-CONVERT-SALES-DATE's source is highlighted in yellow. When yellow appears in the editor, it indicates unneeded source code was identified with a script.
Notice all of the unused paragraphs that were identified with the script are highlighted in yellow. Highlighting is applied to the source for these elements across the project. If you were to open this source file in another tool or browser, these highlights would be shown.
The Split Screen Editor returns to the source for C100-CONVERT-SALES-DATE. Since this paragraph is not needed, all of its contents are selected and can be removed.
The source for the unused paragraph has been removed.
The source for BATCH2.CBL is displayed in the Split Screen Editor. Let's find our unused paragraph named C100-CONVERT-SALES-DATE.
The Search and Replace interface is invoked.

Figure 7-1: Search and Replace for the Unused Paragraph
The unused paragraph is shown still highlighted in yellow. You can modify the paragraph, replace it with something else by using the Search and Replace interface, or leave it alone in the source because it is not causing problems. If you do want to leave the unused paragraphs, you may want to remove highlights to avoid confusion.
The Shell tool is invoked. This is a command line interface that employs REQL for some analysis and administrative tasks.
clear all;in the Shell.
This removes highlighting from all highlighted source.
Notice the highlights have been removed from the source code of the unused paragraphs. To re highlight the paragraphs, run the script that was executed at the beginning of this section.
You have just learned how to use Revolve's scripts to identify areas in your project that should be improved. You also worked with the Split Screen Editor, the Highlight feature, and the Shell tool.
In addition to facilitating individual changes, Revolve also combines multiple changes into a single operation. Names of variables and paragraphs can be replaced throughout an entire application. Consistency and standards are improved or enforced by the normalization of names. In this session let's replace the string "GAME" with "ACTIVITY" in eligible variables.
To do this:
The Project Manager is opened in the Desktop.
The COBOL files loaded in the project are displayed. You may need to resize the window to see the entire list.
The source code of BATCH1.CBL is displayed and selected in the Split Screen Editor.

Figure 7-2: Source code for BATCH1.CBL in the Split Screen Editor
The Search and Replace interface is invoked.
Be sure that Proper Name is not checked.
WORKING-STORAGE is selected in the editor.
The Replace With field is enabled.
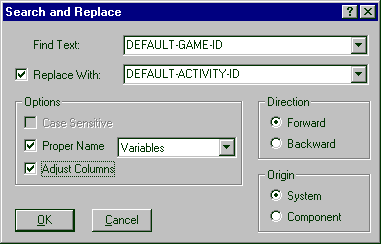
Figure 7-3: Search and Replace Dialog
A Proper Name Replace prompt asks, "Replace this occurrence?" The occurrence is highlighted in the Split Screen Editor window.
The first highlighted item is the definition. The subsequent items are usages.
You are notified that the one definition was replaced and that all four subsequent usages were also replaced. The columns should all be aligned because of step 12.
You can close Revolve, if you want to stop for now. The project that you have created and loaded is automatically saved.
You can continue with the next tutorial later, by simply reopening the project.
Copyright © 1999 MERANT International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.
 | Assigning Scope with Subprojects | Analyzing Data Impacts |  |