Patching the Load Balancer
Before proceeding with annotating and patching the load balancer, execute the following command:kubectl get svc -A
In the resulting output, ensure that frontend-ingress-controller-svc has an IP address assigned.
If the command is processing for a long time, it indicates that Kubernetes is unable to create an internal load balancer and assign an IP to it. The usual cause is missing necessary rights. Refer to the Prerequisites section and make sure all prerequisites are met before proceeding any further.
To annotate and patch the load balancer:
On the jump host, run the following commands.
kubectl annotate service -n core frontend-ingress-controller-svc service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal=true
kubectl patch services frontend-ingress-controller-svc -p '{"spec":{"type":"LoadBalancer","loadBalancerIP": "PUBLIC_IP"}}' -n core
Where PUBLIC_IP is the value of the public IP you assigned previously.
Configuring the Load Balancer
As part of load balancer configuration, to permit access to the 5443 port for product deployment, you need to add the following to the AKS load balancer:
- A health probe and load balancing rule for port 5443
- A health probe and load balancing rule for port 433
These steps are explained below.
To add a health probe for port 5443 using the Azure Portal:
- On your jump host, run the following command to get the value of
portal-ingress-controller-svcfor port 5443:kubectl get svc -n core | grep portal-ingress-controller-svc
portal-ingress-controller-svc NodePort 10.0.146.63 5443:31249/TCP,5444:31036/TCP 21m- Open the Azure Portal and locate the Azure Kubernetes resource group. (The AKS resource group name is in format MC_<your_resource_group>_<aks_name>_<location>.)
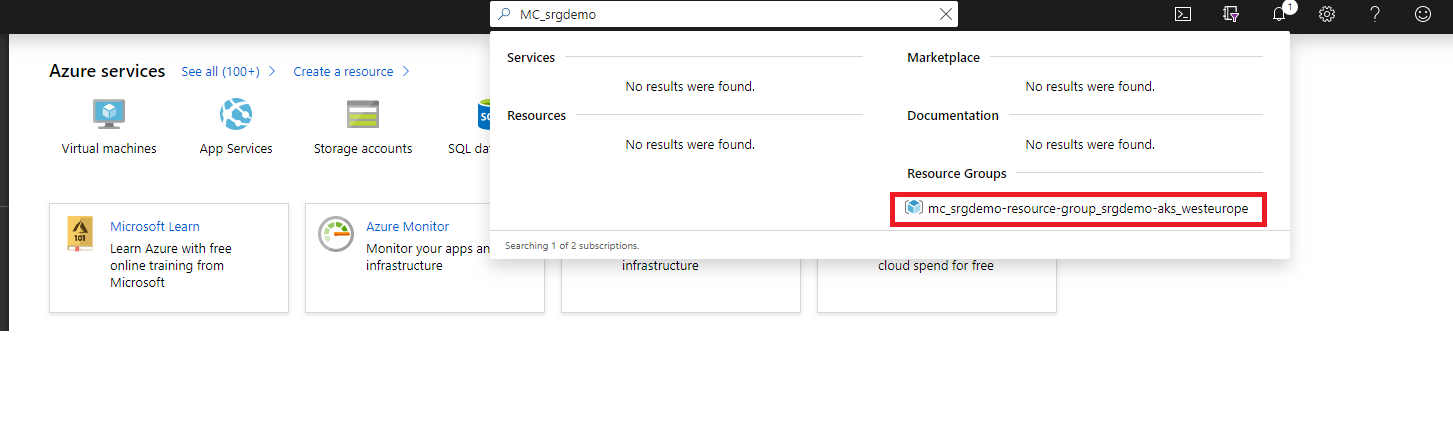
- Open the Kubernetes resource group.
- Locate the Kubernetes load balancer, and then open it.

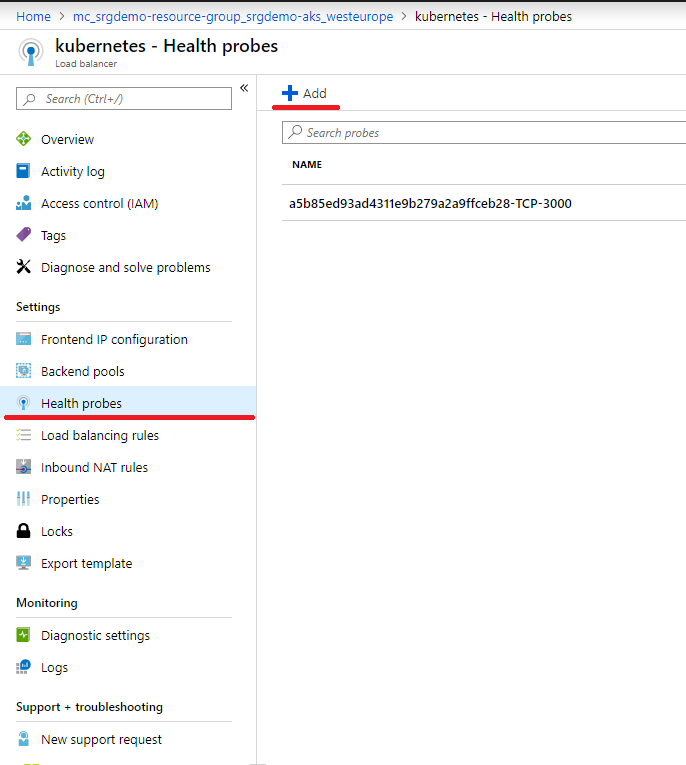
- On the Kubernetes load balancer resource, click Health probes.
- Add a health probe for 5443. Port Value should be the value obtained for the service NodePort in step 1.
To add a health probe for port 5443 using the Azure Cloud Shell:
- Get the AKS resource group and store it in an environment variable for later usage:
CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP=$(az aks show --resource-group <RESOURCE GROUP> --name <AKS NAME> --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv)
For example, for AKS srg-demo-aks from resource group srg-demo:
CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP=$(az aks show --resource-group srg-demo --name srg-demo-aks --query nodeResourceGroup -o tsv)
- Create the health probe by running the command:
az network lb probe create -g $CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 5443-hp --protocol tcp --port <NODE PORT>
Example:
az network lb probe create -g $CLUSTER_RESOURCE_GROUP --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 5443-hp --protocol tcp --port 31249
To add a load balancing rule for port 5443 using the Azure Portal:
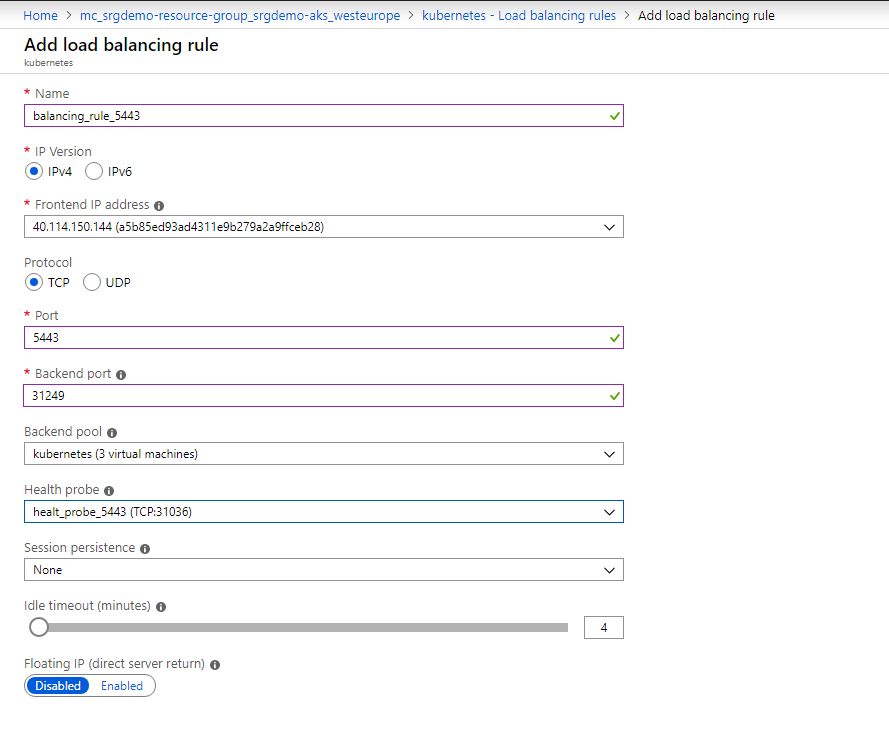
- Open the Kubernetes load balancer, and then click Load balancing rules.

- Add a rule for port 5443. The backend port is the value for
portal-ingress-controller-svcobtained previously and the health probe you just created.
To add a load balancing rule for port 5443 using the Azure Cloud Shell:
- Run the following command:
az network lb rule create -g <AKS RESOURCE GROUP> --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 5443-lb-rule --protocol Tcp --frontend-port 5443 --backend-port <SERVICE PORT> --probe-name 5443-hp --backend-pool-name kubernetes
For example:az network lb rule create -g mc_srg-demo_srg-demo-aks_westeurope --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 5443-lb-rule --protocol Tcp --frontend-port 5443 --backend-port 31249 --probe-name 5443-hp --backend-pool-name kubernetes
To add a health probe for port 443 using the Azure Portal:
- In the Azure portal, locate the Azure Kubernetes resource group. (The AKS resource group name is in the format
MC_<your_resource_group>_<aks_name>_<location>.)

- Open the Kubernetes resource group.
- On the Kubernetes load balancer resource, click Health probes.
- Click + Add for Kubernetes load balancer health probes and specify values for the following:
- Name: Assign a name to the probe.
- Protocol: Select TCP.
- Port: Specify 443.
To add a health probe for port 443 using the Azure Cloud Shell:
- Run the following command:
az network lb probe create -g <AKS RESOURCE GROUP> --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 443-hp --protocol tcp --port 443
For example:az network lb probe create -g mc_srg-demo_srg-demo-aks_westeurope --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 443-hp --protocol tcp --port 443
To add a load balancing rule for port 443 using the Azure Portal:
- Open the Kubernetes load balancing rule and click Load balancing rules.
- Click + Add for the Kubernetes load balancer load balancing rules and specify values for the following:
- Name: assign a name to the probe.
- Port: Specify 443.
- Backend port: Specify 443.
- Health probe: Select the probe you previously created for port 443.
- Session Persistence: select Client IP and Protocol.
- Open the Kubernetes resource group.

To add a load balancing rule for port 443 using the Azure Cloud Shell:
- Run the following command:
az network lb rule create -g <AKS RESOURCE GROUP> --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 443-lb-rule --protocol Tcp --frontend-port 443 --backend-port 443 --probe-name 443-hp --backend-pool-name kubernetes --load-distribution SourceIPProtocol
For example:az network lb rule create -g mc_srg-demo_srg-demo-aks_westeurope --lb-name kubernetes-internal -n 443-lb-rule --protocol Tcp --frontend-port 443 --backend-port 443 --probe-name 443-hp --backend-pool-name kubernetes --load-distribution <SourceIPProtocol>