Understand the Event Integrity Check
Depending on how you have configured your SmartConnectors and Transformation Hub, the Event Integrity Check can verify raw event data and the parsed fields within an event, respectively. The check looks for events referenced by verification events in the database. The SmartConnectors group several events and compute a hash for each raw event in the batch. If you use Transformation Hub as a destination, it also groups events then generates a hash for the parsed fields within each event. The SmartConnector and Transformation Hub each generates a hash of the individual hashes to create a verification event. The number of events in a batch depends on how you configure the batch size setting for each connector. Note that SmartConnectors do not store the hashes for individual events.
Figure 1 (below) shows how events flow from your data sources to the SmartConnectors, which generate the verification events for the raw events. Then Transformation Hub generates verification events for parsed fields within each event.
Figure 1. Process for generating verification events for an Event Integrity Check
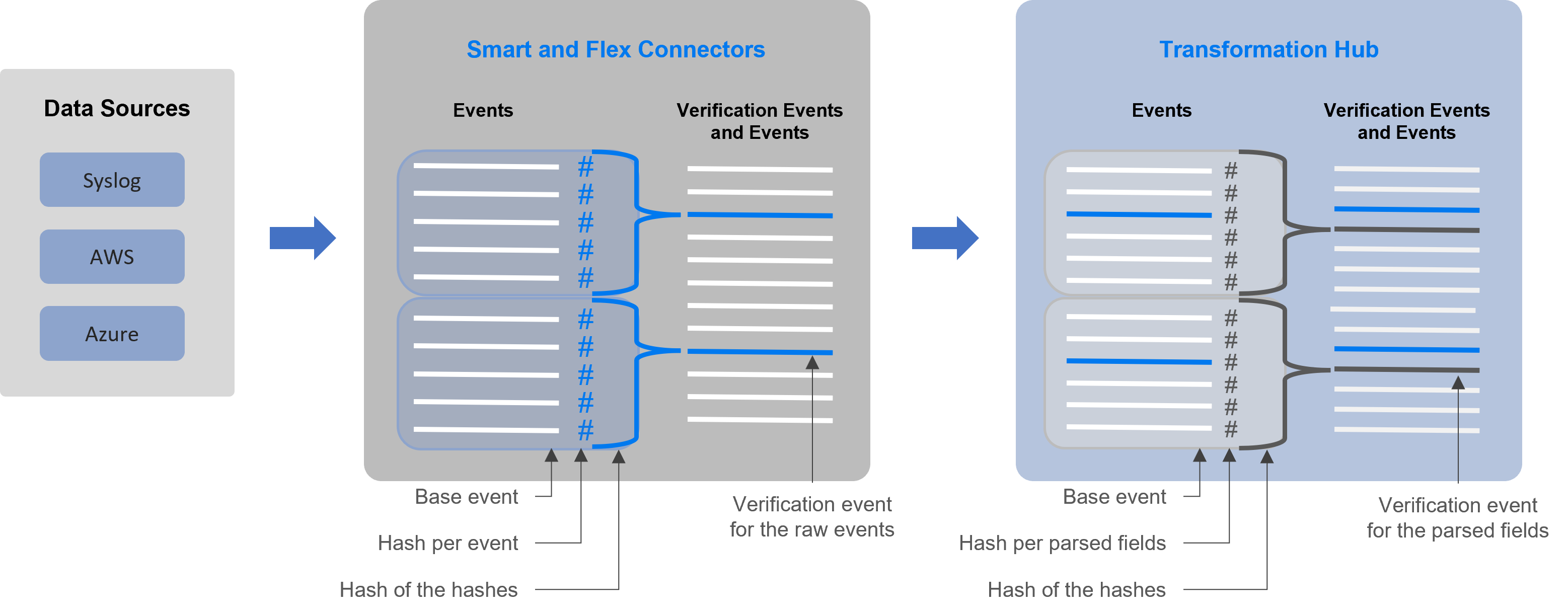
Each verification event includes the following items:
- a group of events with raw data or events with parsed fields
- an ordered list of the event IDs within the batch
- a crypto signature field representing the computed hash for that batch (the hash of hashes)
When you run an Event Integrity Check, the system performs the following actions for each verification event in the specified time range:
- Looks for the globally unique event ID (GEID) of each event referenced with the verification event.
- Generates hashes for the events within the base event.
- Generates a hash to represent the base events’ hashes in the sequence provided by the verification event. You might call this the generated hash of hashes.
- Compares the generated hash of hashes to the hash of hashes in the crypto signature field that the SmartConnector or Transformation Hub created for the verification event.