Install a New Instance of SQL Server
Installation procedures will vary based on your version of SQL Server. The following procedures are specific to Microsoft SQL Server 2022.
The following instructions assume you are installing a single instance of SQL Server on a Windows Server host with no Azure integration.
-
Double-click
setup.exefrom the Microsoft SQL Server ISO. -
Click Installation on the SQL Server Installation Center page.
-
Select New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.

-
Complete the following procedures in the SQL Server Setup wizard:
-
Edition: Select the SQL Server edition, enter the product key, and select the license option, then click Next.
-
License Terms: Accept the license terms and click Next.
-
Global Rules: View the results, then click Next.
-
Microsoft Update: Click Use Microsoft Update to check for updates, then click Next.
-
Install Rules: Review the results, then click Next.
-
Azure Extension for SQL Server: Uncheck Azure Extension for SQL Server, then click Next.
-
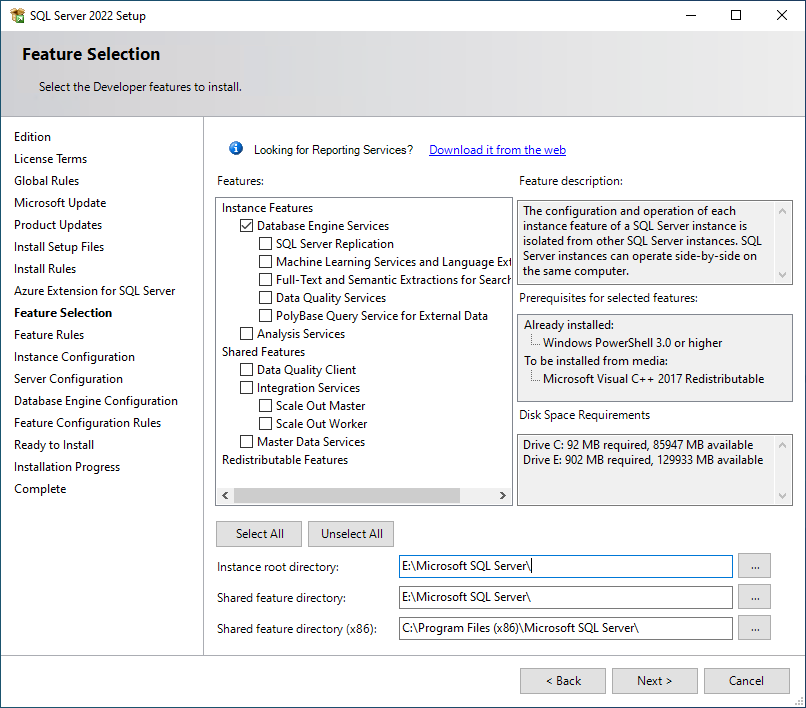
Feature Selection: Check Database Engine Services.
-
Review the installation paths, then click Next.
NOTE: For larger installations, consider installing the SQL Server instance on a separate volume by changing the Instance Root Directory path parameter.
-
Feature Rules: Review the results then click Next.
-
Instance Configuration - Select the appropriate instance type, modify the Instance ID if desired, then click Next.
-
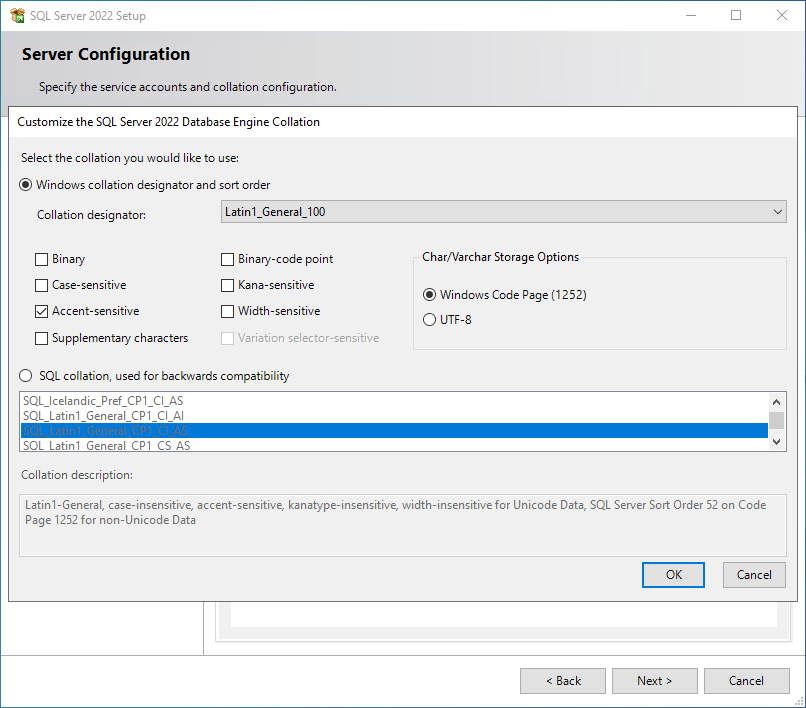
Server Configuration: Select the Collation tab, then click Customize.
-
Select Windows collation designator and sort order in the Customize the SQL Server 2022 Database Collation dialog, then select your desired collation from the drop-down menu, preferably one that aligns with the Windows Server hosting the 24.3 Engine.
If you are unsure which collation to use, select Latin1_General_100, which is a safe option for File Dynamics CEDM.
NOTE: Select one of the *_100 or later collations, as these offer the best compatibility for advanced options such as Supplementary characters.
Refer to the following Microsoft document for more information on collation and locales:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/collations/collation-and-unicode-support.IMPORTANT: 24.3 requires the use of a Windows collation. Legacy SQL collations are not supported.
-
[Optional] Select Accent-sensitive and Supplementary characters.
-
[Optional] Select options for Kana-sensitive, Width-sensitive, and Variation selector-sensitive if you understand their impact with specific Asian character sets.
-
Deselect all other options.
-
Select Windows Code Page (1252) for the Char/Varchar Storage Options.
IMPORTANT: File Dynamics CEDM does not currently support the use of UTF-8 as a character storage option.
-
Click OK to close the customization dialog, then click Next.
-
-
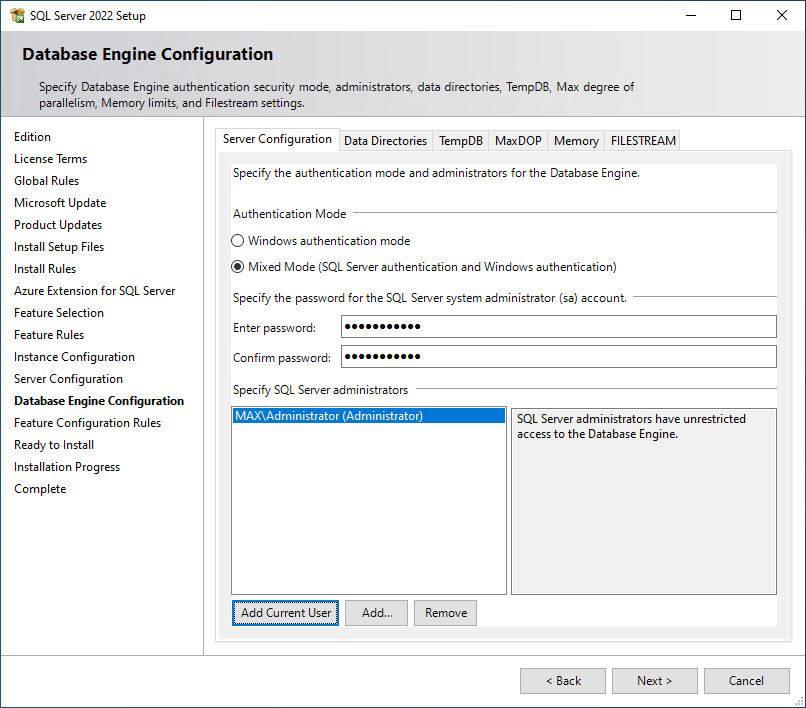
Database Engine Configuration: Complete the following procedures in this panel:
-
Feature Configuration Roles: Review any messages, then click Next.
-
Ready to Install: Perform a final review of all installation options, then click Install.
-
Complete: Click Close once the installation is complete to exit the setup wizard.
-
-
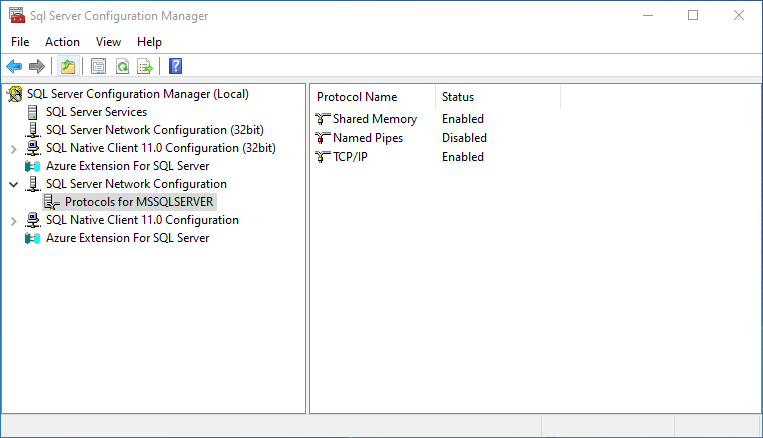
From the Windows Start Menu launch SQL Server Configuration Manager.
-
Expand SQL Server Network Configuration in the left-hand pane.
-
Click Protocols for MSSQLSERVER (or the name of the database instance you chose earlier).
-
Right-click TCP/IP and select Properties.
-
Click the Protocol tab.
-
Set the Enabled field to Yes.
-
Set the Listen All field to Yes.
-
Click the IP Addresses tab.
-
Set the TCP Port field to
1433under the IPAll heading at the bottom. -
Click OK.
-
Close the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
-
-
Launch Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
-
Click Inbound Rulesfrom the left-hand column.
-
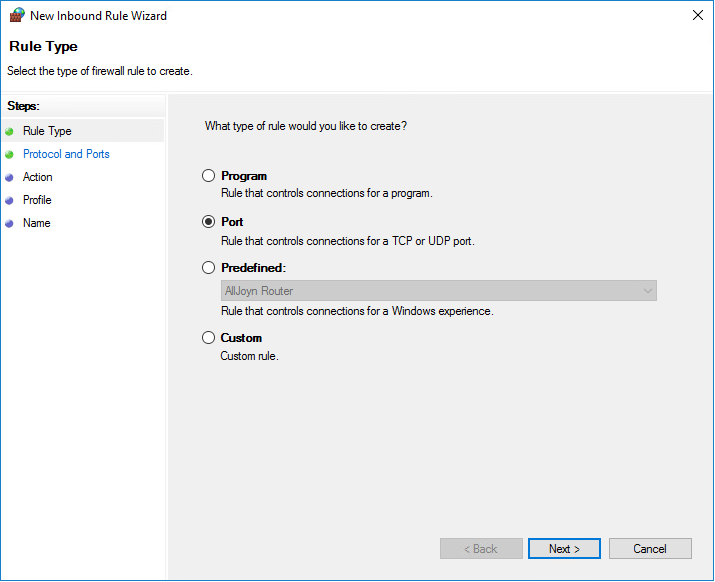
Click New Rule from the Actions column.
-
Click Next.
-
Enter
1433in the Specific local ports field on the Protocol and Ports page, then click Next. -
Click Next on the Action page to accept the default setting.
-
Click Next on the Profile page to accept the default settings.
-
Specify a name (e.g.,
SQL Server) for the new inbound rule in the Name field on the Name page . -
Click Finish.
-