 | Procedure Division - ACCEPT - DIVIDE |
| Procedure Division - MERGE - OPEN |  |
The ENTER statement provides a means of allowing the use of more than
one language in the same pr
ogram.
 The ENTER statement is
classed as an obsolete element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to
be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI Standard.
The ENTER statement is
classed as an obsolete element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to
be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI Standard.
 All dialects in this COBOL
implementation support this syntax for documentation purposes only. The
FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect all occurrences of this
syntax.
All dialects in this COBOL
implementation support this syntax for documentation purposes only. The
FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect all occurrences of this
syntax.
 Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, this feature is explicitly excluded from the
X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in an X/Open
COBOL conforming source program.
Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, this feature is explicitly excluded from the
X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in an X/Open
COBOL conforming source program.
General Format

Syntax Rules
- Language-name and routine-name can be any user-defined word or
alphanumeric literal.
General Rules
- This statement is treated as for documentation purposes only. Access
to other languages can be achieved by means of the CALL statement.
The ENTRY statement establishes an alternate entry point into a called
COBOL program.
General Formats
Format 1
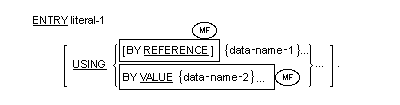
Format 2
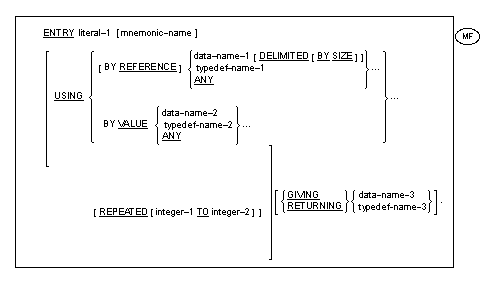
Directives
- In addition to Compiler directives which provide flagging and modify
the reserved word list, the following directive may impact either the
syntax or semantics described in this section.
- STICKY-LINKAGE - controls whether addressability to Linkage
Section items is maintained between calls to different entry points
in the same program.
- LITLINK - controls the number of significant characters in an
entry-name when .obj files are generated.
Syntax Rules
All Formats
- The ENTRY statement cannot be used in a program that is nested within
another program.
- Literal-1 must be non-numeric
and must not be a figurative constant. In some environments, only the
first 8 characters are significant.
Format 1
- Format 1 must be specified only within program definitions.
- Data-name-1 must be defined as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the
Linkage Section,
 File Section or
File Section or
 Working-Storage Section.
Working-Storage Section.
-
 Data-name-2 must be defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the Linkage Section, File Section
or Working-Storage Section. Data-name-2 can be of any class, but the
length must be no greater than 8 bytes.
Data-name-2 must be defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the Linkage Section, File Section
or Working-Storage Section. Data-name-2 can be of any class, but the
length must be no greater than 8 bytes.
Format 2
-
 Format 2 can only be used
in a program in which the EXTERNAL clause is specified in the PROGRAM-ID
paragraph, that is a call prototype.
Format 2 can only be used
in a program in which the EXTERNAL clause is specified in the PROGRAM-ID
paragraph, that is a call prototype.
-
 Data-name-1 and
data-name-2 must be defined as 01 level records in the LINKAGE SECTION.
Data-name-1 and
data-name-2 must be defined as 01 level records in the LINKAGE SECTION.
-
 Typedef-name-1,
typedef-name-2, and typedef-name-3 must be previously defined in the
same source file as a programmer-defined usage by means of a TYPEDEF
clause.
Typedef-name-1,
typedef-name-2, and typedef-name-3 must be previously defined in the
same source file as a programmer-defined usage by means of a TYPEDEF
clause.
General Rules
All Formats
- The content of literal-1 gives the entry-name, a name which
identifies an entry point into the program that is an alternative to the
default COBOL entry point at the start of the PROCEDURE DIVISION. The
program-name given in the PROGRAM-ID paragraph can be considered to
identify the default COBOL entry point.
Note that program files containing executable COBOL code typically
have names that are essentially the same as the program-name. When a
CALL is made and the program-name or entry-name is not already loaded
into memory, program files are located by filename but can appear to
be located by program-name. In such circumstances, a CALL that
references a program-name may succeed but a CALL that references an
entry-name may fail.
The entry-name is largely equivalent to a program-name and the two
are subject to common rules for formation of the name as indicated in
the section The Program-ID Paragraph and Nested Source Programs.
Literal-1 corresponds to literal-1 of the general format for the
PROGRAM-ID paragraph.
- When the calling program invokes the called program by a CALL
statement naming the entry-name given by literal-1, control is
transferred to the next executable statement following the ENTRY
statement.
- Data items that are declared in the Linkage Section but are not
declared in the USING phrase of the ENTRY statement can only be
referenced if they have been linked to a data item by executing a SET
statement or if the STICKY-LINKAGE Compiler directive is used.
- Up to sixty-two data-names are permitted in the USING phrase.
- Both the BY REFERENCE and the BY VALUE phrases are transitive across
the parameters that follow them until another BY REFERENCE or BY VALUE
phrase is encountered. If neither the BY REFERENCE nor the BY VALUE
phrase is specified prior to the first parameter, the BY REFERENCE
phrase is assumed.
Format 1
-
 If data-name-1 is defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the File Section or Working-Storage
Section then the object program operates as if a data item had been
declared in the Linkage Section with the same data declaration as
data-name-1 and the contents of that data item were moved to data-name-1
prior to executing the first statement in the called program. In an
initial program, these values are overwritten by the initialization of
the program's Working-Storage data and are therefore not available to
the called program.
If data-name-1 is defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the File Section or Working-Storage
Section then the object program operates as if a data item had been
declared in the Linkage Section with the same data declaration as
data-name-1 and the contents of that data item were moved to data-name-1
prior to executing the first statement in the called program. In an
initial program, these values are overwritten by the initialization of
the program's Working-Storage data and are therefore not available to
the called program.
- If the activating runtime element is COBOL the following rules
apply. If the activating runtime element is not COBOL, see your COBOL
system documentation on interfacing for details of when you need to use
the BY REFERENCE or BY VALUE clauses.
- The USING phrase identifies the names of the formal parameters used
by the program or for any arguments passed to it. The arguments passed
to it are identified in the activating source element by the USING
phrase of a CALL statement. The correspondence between the two lists of
names is established on a positional basis.
- If the argument is passed by content, the called program operates as
if the record in the linkage section were allocated by the calling
runtime element during the process of initiating the call and as if this
record does not occupy the same storage area as the argument in the
calling runtime element. This allocated record is exactly the same
number of alphanumeric character positions in length as the argument.
That argument is moved to this allocated record without conversion. This
record is then treated by the called program as if it were the argument
and as if it were passed by reference.
- If the argument is passed by reference, the called program operates
as if the formal parameter occupies the same storage area as the
argument.
-
 If the argument is passed
by value, the called program operates as if the record in the linkage
section were allocated by the calling runtime element during the process
of initiating the call and as if this record does not occupy the same
storage area as the argument in the calling runtime element. This
allocated record is exactly the same number of alphanumeric character
positions in length as the argument. That argument is moved to this
allocated record without conversion. This record is then treated by the
called program as if it were the argument and as if it were passed by
reference.
If the argument is passed
by value, the called program operates as if the record in the linkage
section were allocated by the calling runtime element during the process
of initiating the call and as if this record does not occupy the same
storage area as the argument in the calling runtime element. This
allocated record is exactly the same number of alphanumeric character
positions in length as the argument. That argument is moved to this
allocated record without conversion. This record is then treated by the
called program as if it were the argument and as if it were passed by
reference.
- At all times in the activated element, references to data-name-1,
 data-name-2 and
data-name-2 and
 data-name-3 are resolved in
accordance with their description in the Linkage Section. If this
description defines a greater number of character positions than the
corresponding data item in the activating element, unpredictable results
can occur. Failure to comply with this rule or exceeding the maximum
allowed size of the system area for a particular run time environment
may result in the system becoming catastrophically corrupt.
data-name-3 are resolved in
accordance with their description in the Linkage Section. If this
description defines a greater number of character positions than the
corresponding data item in the activating element, unpredictable results
can occur. Failure to comply with this rule or exceeding the maximum
allowed size of the system area for a particular run time environment
may result in the system becoming catastrophically corrupt.
-
 When a program is called
and a BY REFERENCE operand in the USING phrase corresponds to a
parameter in the calling program, a referential connection is
established and endures until control is returned to the calling
program. If the program is called a second time, without any intervening
cancel of the program, and that same BY REFERENCE operand does not
correspond to a parameter in the calling program, then you must not
reference that operand unless the STICKY-LINKAGE Compiler directive is
specified.
When a program is called
and a BY REFERENCE operand in the USING phrase corresponds to a
parameter in the calling program, a referential connection is
established and endures until control is returned to the calling
program. If the program is called a second time, without any intervening
cancel of the program, and that same BY REFERENCE operand does not
correspond to a parameter in the calling program, then you must not
reference that operand unless the STICKY-LINKAGE Compiler directive is
specified.
- If the USING phrase is specified, the INITIAL clause must not be
present in any CD entry. (See the section The Communication
Description - The Complete Entry Skeleton in the chapter Communication
in your Language Reference - Additional Topics.)

The EVALUATE statement describes a m
ulti-branch, m
ulti-join structure. It can cause mu
ltiple conditions to be evaluated. The subsequent action of the
runtime element
depends on the results of these
evaluations.
General Format
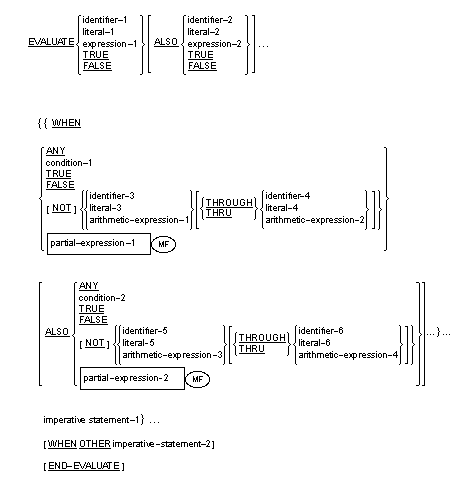
Syntax Rules
- The operands or the words TRUE and FALSE which appear before the
first
WHEN phrase of the EVALUATE statement are referred to individually
as
selection subjects and collectively, for all those specified, as
the set of selection subjects.
- The operands or the words TRUE, FALSE, and ANY which appear in a WHEN
phrase of an EVALUATE statement are referred to individually as
selection objects and collectively, for all those specified in a
single WHEN phrase, as the set of selection objects.
- The words THROUGH and THRU are equivalent.
- Two operands connected by a THROUGH phrase must be of the same class.
The two operands thus connected constitute a single selection object.
- The number of selection objects in each set of selection objects must
be equal to the number of selection subjects.
- Each selection object in a set of selection objects must correspond
to the selection subject having the same ordinal position in the set of
selection subjects according to the following rules:
- Identifiers, literals, or arithmetic expressions appearing in a
selection object must be valid operands for comparison to the
corresponding operand in the set of selection subjects. (See the
section Relation Condition earlier in this chapter.)
- Condition-1, condition-2, or the words TRUE or FALSE appearing as
a selection object must correspond to a conditional expression or
the words TRUE or FALSE in the set of selection subjects.
- The word ANY can correspond to a selection subject of any type.
-
 Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference floating-point data items.
Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference floating-point data items.
-
 Where numeric literals
are permitted, floating-point literals are permitted.
Where numeric literals
are permitted, floating-point literals are permitted.
-
 Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference pointer data items.
Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference pointer data items.
-
 If partial-expression-1 or
partial-expression-2 is specified as a selection object, it must
correspond to a selection subject that is an identifier, a literal or an
arithmetic expression. Partial-expression-1 and partial-expression-2
must be a sequence of COBOL words which, when following the
corresponding selection subject, make the resultant text a valid
conditional expression.
If partial-expression-1 or
partial-expression-2 is specified as a selection object, it must
correspond to a selection subject that is an identifier, a literal or an
arithmetic expression. Partial-expression-1 and partial-expression-2
must be a sequence of COBOL words which, when following the
corresponding selection subject, make the resultant text a valid
conditional expression.
General Rules
- The execution of the EVALUATE statement operates as if each selection
subject and selection object were evaluated and assigned a numeric or
nonnumeric value, a range of numeric or nonnumeric values, or a truth
value. These values are determined as follows:
- Any selection subject specified by identifier-1, identifier-2,
and any selection object specified by identifier-3, identifier-5,
without either the NOT or the THROUGH phrases, are assigned the
value and class of the data item referenced by the identifier.
- Any selection subject specified by literal-1, literal-2, and any
selection object specified by literal-3, literal-5, without either
the NOT or the THROUGH phrases, are assigned the value and class of
the specified literal. If literal-3, literal-5, is the figurative
constant ZERO, it is assigned the class of the corresponding
selection subject.
- Any selection subject in which expression-1, expression-2, is
specified as an arithmetic expression and any selection object,
without either the NOT or the THROUGH phrases, in which
arithmetic-expression-1, arithmetic-expression-3, is specified are
assigned a numeric value according to the rules for evaluating an
arithmetic expression. (See the section Arithmetic Expressions
earlier in this chapter.)
- Any selection subject in which expression-1, expression-2 is
specified as a conditional expression and any selection object in
which condition-1, condition-2, is specified are assigned a truth
value according to the rules for evaluating conditional expressions.
(See the section Conditional Expressions earlier in this
chapter.)
- Any selection subject or any selection object specified by the
words TRUE or FALSE is assigned a truth value. The truth value "true"
is assigned to those items specified with the word TRUE, and the
truth value "false" is assigned to those items specified
with the word FALSE.
- Any selection object specified by the word ANY is not further
evaluated.
- If the THROUGH phrase is specified for a selection object,
without the NOT phrase, the range of values is all values which,
when compared to the selection subject, are greater than or equal to
the first operand and less than or equal to the second operand
according to the rules for comparison. (See the section Relation
Condition in this chapter.) If the first operand is greater than
the second operand, no values are in the range.
- If the NOT phrase is specified for a selection object, the values
assigned to that item are all values not equal to the value, or
range of values, which would have been assigned to the item had the
NOT phrase not been specified.
- The execution of the EVALUATE statement then proceeds as if the
values assigned to the selection subjects and selection objects were
compared to determine if any WHEN phrase satisfies the set of selection
subjects. This comparison proceeds as follows:
- Each selection object in the set of selection objects for the
first WHEN phrase is compared to the selection subject having the
same ordinal position in the set of selection subjects.
- If the items being compared are assigned numeric or
nonnumeric values, or a range of numeric or nonnumeric values,
the comparison is satisfied if the value, or one of the range of
values, assigned to the selection object is equal to the value
assigned to the selection subject according to the rules for
comparison. (See the section Relation Condition in this
chapter.)
- If the items being compared are assigned truth values, the
comparison is satisfied if the items are assigned the identical
truth value.
- If the selection object being compared is specified by the
word ANY, the comparison is always satisfied regardless of the
value of the selection subject.
- If the above comparison is satisfied for every selection object
in the set of selection objects being compared, the WHEN phrase
containing that set of selection objects is selected as the one
satisfying the set of selection subjects.
- If the above comparison is not satisfied for one or more
selection objects in the set of selection objects being compared,
that set of selection objects does not satisfy the set of selection
subjects.
- This procedure is repeated for subsequent sets of selection
objects, in the order of their appearance in the source
element,
until either a WHEN phrase satisfying the set of selection subjects
is selected or until all sets of selection objects are exhausted.
- After the comparison operation is completed, execution of the
EVALUATE statement proceeds as follows:
- If a WHEN phrase is selected, execution continues with the first
imperative-statement-1 following the selected WHEN phrase.
- If no WHEN phrase is selected and a WHEN OTHER phrase is
specified, execution continues with imperative-statement-2.
- The scope of execution of the EVALUATE statement is terminated
when execution reaches the end of the scope of the selected WHEN
phrase or WHEN OTHER phrase or when no WHEN phrase is selected and
no WHEN OTHER phrase is specified. (See the section Explicit And
Implicit Scope Terminators in the chapter Concepts of the
COBOL Language.)
-
 If the selection object is
specified by partial-expression-1 or partial-expression-2, the
corresponding selection subject is considered to be the word TRUE. The
selection object is considered to be condition-1 or condition-2
respectively, where condition-1 or condition-2 is the conditional
expression resulting from partial expression-1 or partial-expression-2
following the original corresponding selection-subject-1 or
selection-subject-2 respectively.
If the selection object is
specified by partial-expression-1 or partial-expression-2, the
corresponding selection subject is considered to be the word TRUE. The
selection object is considered to be condition-1 or condition-2
respectively, where condition-1 or condition-2 is the conditional
expression resulting from partial expression-1 or partial-expression-2
following the original corresponding selection-subject-1 or
selection-subject-2 respectively.

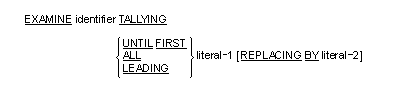
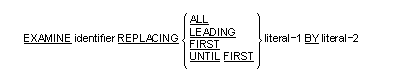
The EXAMINE statement replaces or counts the number of occurrences of a
given character in a data item.
General Formats
Format 1
Format 2
Syntax Rules
All Formats
- The identifier must be described, explicitly or implicitly, as USAGE
IS DISPLAY.
- Each literal must consist of a single character. If identifier is a
numeric item, the literals must be numeric literals, nonnumeric literals
whose value is a single numeric digit, or the figurative constant ZERO.
If identifier belongs to any other class, then the literals can be
numeric or nonnumeric, or any figurative constant without the word ALL.
General Rules
All Formats
- Examination proceeds as follows:
- For nonnumeric data items, examination starts at the leftmost
character and proceeds to the right. Each character in the data item
specified by the identifier is examined in turn.
- If a data item referred to by the EXAMINE statement is numeric,
it must consist of numeric characters and can possess an operational
sign. Examination starts at the leftmost character (excluding the
sign) and proceeds to the right. Each character except the sign is
examined in turn. Regardless of where the sign is physically
located, it is completely ignored by the EXAMINE statement.
- The T
ALLYING option creates an integral count which replaces the value
of a spe
cial register called TAL
LY. The count represents the number of:
- Characters not equal to literal-1 encountered before the first
occurrence of literal-1 when the UNTIL FIRST option is used.
- Occurrences of literal-1 when the ALL option is used.
- Occurrences of literal-1 prior to encountering a character other
than literal-1 when the LEADING option is used.
- When either of the REPLACING options is used, the replacement rules
are as follows:
- When the ALL option is used, then literal-2 is substituted for
each occurrence of literal-1.
- When the LEADING option is used, the substitution of literal-2
terminates as soon as a character other than literal-1 or when the
right-hand boundary of the data item is encountered.
- When the FIRST option is used, the first occurrence of literal-1
is replaced by literal-2.
- When the UNTIL FIRST option is used, the substitution of
literal-2 terminates as soon as literal-1 or the right-hand boundary
of the data item is encountered.

The
EXEC(UTE) statement is provided as a linkage mechanism to allow
control to be passed to non-COBOL subsystems.
General Format

Syntax Rules
- Text-data can be any textual data not containing the string END-EXEC.
General Rules
- The statement will be compiled as a CALL "text-name" USING
text-data-buffer statement (see the section The CALL Statement
earlier in this chapter), where text-data-buffer contains all the
text-data from the EXEC statement (space compressed) for further parsing
by the CALLed program text-name.
This means that the called subprogram (text-name) will be passed a
text string which includes the entire COBOL statement beginning with
the EXEC(UTE) verb and ending with the END-EXEC phrase. The called
program must parse and then process all of the included information.
If an identifier-name is included in text-data, then it is the name
of the identifier, not the value of the data in the identifier that is
passed to the subprogram.
- The special case EXEC SQL is normally treated differently by the
compiler. If you wish EXEC SQL statements to be treated as described
here you must ensure that the Compiler directive NOSQL is explicitly
set.
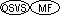
The EXHIBIT statement causes an (optionally conditional) display of the
literals, and/or identifiers (optionally preceded by the identifier name)
specified in the statement.
General Format
Syntax Rules
- Each identifier specified in the EXHIBIT statement can be any class
of data.
TALLY and
RETURN-CODE are the only
special
registers that can be used as identifiers.
- CHANGED and NAMED can both be omitted.
General Rules
- Literals and identifiers displayed by the EXHIBIT statement are
separated by a space on the displayed line.
- Each literal can be any figurative constant other than ALL.
- If the literal is numeric, it must be an unsigned integer.
- Each execution of an EXHIBIT NAMED statement displays each identifier
or literal specified, with each identifier (including any qualifiers and
subscripts) followed by an "=" (equal sign) and its current
value. They all appear on a single line in the order in which they
appear in the statement.
- Each execution of an EXHIBIT CHANGED NAMED statement displays each
identifier or literal specified, with each identifier (including any
qualifiers and subscripts) followed by an "=" (equal sign) and
its current value. They all appear on a single line in the order in
which they appear in the statement. However, the display for each
identifier (name and value) is conditional on the value of that
identifier having changed since the last execution of the current
EXHIBIT statement. If one or more of the identifier values have not
changed, neither the name nor the value is printed for those
identifiers. If none of the identifier values has changed, and no
literals are specified, no display takes place (display of a blank line
is suppressed).
- Each execution of an EXHIBIT CHANGED statement displays the current
value of each identifier or literal specified. They all appear on a
single line in the order in which they appear in the statement. However,
the value display for each identifier is conditional on the value of
that identifier having changed since the last execution of the current
EXHIBIT statement. If one or more of the identifier values have not
changed, the value for those identifiers is not printed; spaces are
inserted instead. If none of the identifier values has changed, and no
literals are specified, a blank line is displayed (display of a blank
line is not suppressed).
- Each execution of an EXHIBIT statement with neither the CHANGED nor
the NAMED option displays each identifier or literal specified. They all
appear on a single line in the order in which they appear in the
statement.
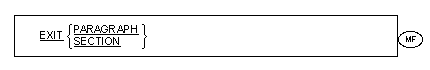
The EXIT statement provides a common en
d point for a series of procedures.
 The EXIT statement can also
exit an inline PERFORM, a paragraph or a section.
The EXIT statement can also
exit an inline PERFORM, a paragraph or a section.
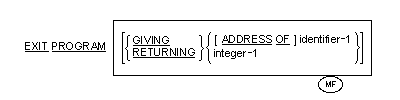
The EXIT PROGRAM statement marks the logical end of a called program.
 You can also return values to
activating runtime
elements written in any language.
You can also return values to
activating runtime
elements written in any language.
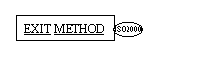
 The EXIT METHOD statement
marks the logical end of an invoked method.
The EXIT METHOD statement
marks the logical end of an invoked method.
General Formats
Format 1

Format 2

Format 3
Format 4
Format 5
Syntax Rules
Format 1
- The EXIT statement should appear in a sentence by itself.
 This rule is not enforced.
This rule is not enforced.
- The EXIT sentence should be the only sentence in the paragraph.
 This rule is not enforced.
This rule is not enforced.
Format 2
- A Format 2 EXIT statement can be used only within an inline PERFORM.
Format 4
- If an EXIT PROGRAM statement appears in a consecutive sequence of
imperative statements within a sentence, it must appear as the last
statement in that sequence.
 This rule is not
enforced.
This rule is not
enforced.
- There must be no sentence other than the EXIT PROGRAM sentence in the
paragraph.
 This rule is not
enforced.
This rule is not
enforced.
-
 Integer-1 may be signed.
Integer-1 may be signed.
-
 GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
-
 If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, identifier-1 must be no larger than 8 bytes in size.
If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, identifier-1 must be no larger than 8 bytes in size.
Format 5
-
 An EXIT METHOD statement
may be specified only in a method procedure division.
An EXIT METHOD statement
may be specified only in a method procedure division.
Formats 4 and 5
- The EXIT statement must not be specified in a declarative procedure
for which the GLOBAL phrase is specified in the associated USE
statement.
General Rules
Format 1
- An EXIT statement serves only to enable the user to assign a
procedure-name to a given point in a
procedure division. Such an EXIT statement has no other effect on
the compilation or execution
.
Format 2
-
 The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement without a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to
an implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately following the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.
The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement without a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to
an implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately following the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.
-
 The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement with a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to an
implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately preceding the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.
The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement with a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to an
implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately preceding the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.
Format 3
-
 The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the PARAGRAPH phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the paragraph.
The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the PARAGRAPH phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the paragraph.
-
 The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the SECTION phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the last paragraph in the section.
The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the SECTION phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the last paragraph in the section.
Format 4
- a
 If the EXIT PROGRAM
statement is executed in a program which is not under the control of a
calling runtime element, the EXIT PROGRAM statement causes execution of
the program to continue with the next executable statement.
If the EXIT PROGRAM
statement is executed in a program which is not under the control of a
calling runtime element, the EXIT PROGRAM statement causes execution of
the program to continue with the next executable statement.
-
 The
execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement in a called program which does
not possess the initial attribute causes execution to continue with the
next executable statement following the CALL statement in the calling
runtime element. The state of the calling runtime element is not altered
and is identical to that which existed at the time it executed the CALL
statement except that the contents of data items and the contents of
data files shared between the calling and called runtime elements may
have been changed. The program state of the called program is not
altered except that the ends of the ranges of all PERFORM statements
executed by that called program are considered to have been reached.
The
execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement in a called program which does
not possess the initial attribute causes execution to continue with the
next executable statement following the CALL statement in the calling
runtime element. The state of the calling runtime element is not altered
and is identical to that which existed at the time it executed the CALL
statement except that the contents of data items and the contents of
data files shared between the calling and called runtime elements may
have been changed. The program state of the called program is not
altered except that the ends of the ranges of all PERFORM statements
executed by that called program are considered to have been reached.
-
 Besides the actions
specified in General Rule 7, the execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement
in a called program which possesses the initial attribute is equivalent
to also executing a CANCEL statement referencing that program except
that the statement will not free any memory. See the section The
CANCEL Statement earlier in this chapter.
Besides the actions
specified in General Rule 7, the execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement
in a called program which possesses the initial attribute is equivalent
to also executing a CANCEL statement referencing that program except
that the statement will not free any memory. See the section The
CANCEL Statement earlier in this chapter.
-
 An EXIT PROGRAM statement
must not be executed while executing a declarative procedure in which
the GLOBAL phrase is specified except in a program called while
executing that declarative procedure.
An EXIT PROGRAM statement
must not be executed while executing a declarative procedure in which
the GLOBAL phrase is specified except in a program called while
executing that declarative procedure.
-
 Execution of an EXIT
PROGRAM statement in a program that is under the control of a calling
runtime element,
causes a return value to be set in the system area generally available
for non-COBOL programs to return a value. This system area is never
smaller than 4 bytes in size but may be larger in some environments.
Execution of an EXIT
PROGRAM statement in a program that is under the control of a calling
runtime element,
causes a return value to be set in the system area generally available
for non-COBOL programs to return a value. This system area is never
smaller than 4 bytes in size but may be larger in some environments.
 If the GIVING phrase is
not specified and the calling convention specifies updating the
RETURN-CODE special-register (see the CALL CONVENTION clause in the
earlier section The Special-Names Paragraph) then the object
program operates as if the system area were declared as a COBOL
numeric data item with USAGE COMP-5 and with a size determined by the
operating environment external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE
statement had been executed with the RETURN-CODE as the sending item
and the system area as the receiving item. (See the section
Special Registers in the chapter Concepts of the COBOL
Language for details of RETURN-CODE.)
If the GIVING phrase is
not specified and the calling convention specifies updating the
RETURN-CODE special-register (see the CALL CONVENTION clause in the
earlier section The Special-Names Paragraph) then the object
program operates as if the system area were declared as a COBOL
numeric data item with USAGE COMP-5 and with a size determined by the
operating environment external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE
statement had been executed with the RETURN-CODE as the sending item
and the system area as the receiving item. (See the section
Special Registers in the chapter Concepts of the COBOL
Language for details of RETURN-CODE.)
 If the GIVING ADDRESS OF
phrase is specified, the object program operates as if the system area
were declared as a COBOL data item with USAGE POINTER and as if a SET
statement had been executed with TO ADDRESS OF identifier-1 as the
first operand and the system area as the second operand. The ADDRESS
OF phrase may be used to indirectly pass a value that is larger than
the system area.
If the GIVING ADDRESS OF
phrase is specified, the object program operates as if the system area
were declared as a COBOL data item with USAGE POINTER and as if a SET
statement had been executed with TO ADDRESS OF identifier-1 as the
first operand and the system area as the second operand. The ADDRESS
OF phrase may be used to indirectly pass a value that is larger than
the system area.
 If the GIVING
identifier-1 phrase is specified, identifier-1 must describe the same
number of character positions as is required to hold the return value
in the system area and must be of the type and usage that is expected
by the calling runtime
element. The object program operates as if a MOVE statement had
been executed with identifier-1 as the sending item and the system
area as the receiving item.
If the GIVING
identifier-1 phrase is specified, identifier-1 must describe the same
number of character positions as is required to hold the return value
in the system area and must be of the type and usage that is expected
by the calling runtime
element. The object program operates as if a MOVE statement had
been executed with identifier-1 as the sending item and the system
area as the receiving item.
 If the GIVING integer-1
phrase is specified, integer-1 must not be larger than the value that
can be held in the system area. The object program operates as if the
system area were declared as a COBOL numeric data item with USAGE
COMP-5 and with a size determined by the operating environment
external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE statement had been
executed with integer-1 as the sending item and the system area as the
receiving item.
If the GIVING integer-1
phrase is specified, integer-1 must not be larger than the value that
can be held in the system area. The object program operates as if the
system area were declared as a COBOL numeric data item with USAGE
COMP-5 and with a size determined by the operating environment
external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE statement had been
executed with integer-1 as the sending item and the system area as the
receiving item.
Format 5
-
 The execution of an EXIT
METHOD statement causes the executing method to terminate, and control
to return to the invoking statement. If a RETURNING phrase is present in
the containing method definition, the value in the data item referenced
by the RETURNING phrase becomes the result of the method invocation.
The execution of an EXIT
METHOD statement causes the executing method to terminate, and control
to return to the invoking statement. If a RETURNING phrase is present in
the containing method definition, the value in the data item referenced
by the RETURNING phrase becomes the result of the method invocation.
The GOBACK statement marks the logical end of a called program.
 You can also return values to
calling runtime elements
written in any language or to the operating system environment.
You can also return values to
calling runtime elements
written in any language or to the operating system environment.
General Format

Syntax Rules
- If a GOBACK statement appears in a consecutive sequence of imperative
statements within a sentence, it must appear as the last statement in
that sequence.
This rule is not enforced, although any statements in the sentence
that follow the GOBACK statement will not be executed.
-
 GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
-
 If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, the data item referenced by identifier-1 must be no
larger than 8 bytes in size.
If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, the data item referenced by identifier-1 must be no
larger than 8 bytes in size.
- Integer-1 may be signed.
General Rules
- If a GOBACK statement is executed in a program which is under the
control of a calling runtime
element, the object program operates as if executing an EXIT
PROGRAM statement that has the same clauses as the GOBABCK statement.
See the section The EXIT Statement.
- If a GOBACK statement without the ADDRESS OF clause is executed in a
program which is not under the control of a calling
runtime element,
the object program operates as if executing a STOP RUN statement
that has the same clauses as the GOBACK statement.
- If a GOBACK statement with the ADDRESS OF clause is executed in a
program which is not under the control of a calling
runtime element,
the object program operates as if executing a STOP RUN statement except
that an arbitrary returned value is set in the system area. The GOBACK
statement may result in more compact code than the equivalent EXIT
PROGRAM and STOP RUN statement.
- A GOBACK statement must not be executed while executing a declarative
procedure in which the GLOBAL phrase is specified except in a program
called while executing that declarative procedure.
The GO TO statement causes control to be transferred from one part of
the Procedure Division to another.
 The option of omitting
procedure-name-1 in a Format 1 GO TO statement is classed as an obsolete
element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to be deleted from the
next full revision of the ANSI Standard.
The option of omitting
procedure-name-1 in a Format 1 GO TO statement is classed as an obsolete
element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to be deleted from the
next full revision of the ANSI Standard.
 All dialects in this COBOL
implementation fully support this syntax. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive
can be used to detect all occurrences of this syntax.
All dialects in this COBOL
implementation fully support this syntax. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive
can be used to detect all occurrences of this syntax.
 Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, omitting the procedure-name in Format 1 is
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should
not be used in an X/Open COBOL conforming source program.
Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, omitting the procedure-name in Format 1 is
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should
not be used in an X/Open COBOL conforming source program.
General Formats
Format 1

Format 2

Syntax Rules
All Formats
- Identifier is the name of a numeric elementary item which is an
integer.
- When a paragraph is referenced by an ALTER statement, that paragraph
can consist only of a paragraph header followed by a Format 1 GO TO
statement.
Format 1
- A Format 1 GO TO statement, without procedure-name-1, can only appear
in a single statement paragraph.
 This restriction is not
enforced.
This restriction is not
enforced.
- If a Format 1 GO TO statement appears in a consecutive sequence of
imperative statements within a sentence, it must appear as the last
statement in that sequence.
Format 2
- In Format 2, at least two procedure-names should be specified.
 A Format 2 statement can
be written with only one procedure name.
A Format 2 statement can
be written with only one procedure name.
General Rules
All Formats
- If procedure-name-1 is not specified in Format 1, an ALTER statement,
referring to this GO TO statement, must be executed prior to the
execution of this GO TO statement.
 If an ALTER statement
referring to the paragraph containing this GO TO statement has not
been executed before this GO TO statement is executed, this GO TO
statement is treated like a CONTINUE statement.
If an ALTER statement
referring to the paragraph containing this GO TO statement has not
been executed before this GO TO statement is executed, this GO TO
statement is treated like a CONTINUE statement.
Format 1
- When a GO TO statement represented by Format 1 is executed, control
is transferred to procedure-name-1 or to another procedure-name if the
GO TO statement has been modified by an ALTER statement.
Format 2
- When a GO TO statement represented by Format 2 is executed, control
is transferred to procedure-name-1, procedure-name-2, and so on,
depending on the value of the identifier being 1, 2, ..., n. If
the value of the identifier is anything other than the positive or
unsigned integers 1, 2, ..., n, then no transfer occurs and
control passes to the next statement in the normal sequence for
execution.
The IF statement causes a condition to be evaluated (see the section
Conditional Expressions earlier in this chapter). The subsequent
action of the runtime
element depends on whether the value of the condition is true or
false.
General Format
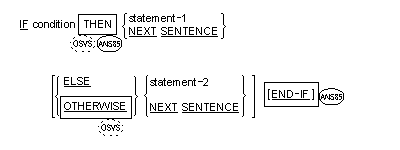
Syntax Rules
- Statement-1 and statement-2 represent either an imperative statement
or a conditional statement optionally preceded by an imperative
statement.
-
 If the END-IF phrase is
specified, the
NEXT SENTENCE phrase must not be specified.
If the END-IF phrase is
specified, the
NEXT SENTENCE phrase must not be specified.
 NEXT SENTENCE can be
specified with END-IF.
NEXT SENTENCE can be
specified with END-IF.
If the NEXT SENTENCE phrase is executed, control will not pass to
the next statement following the END-IF, but instead will pass to the
statement after the closest following period.
General Rules
- The scope of an IF statement can be terminated by any of the
following:
-
 An END-IF phrase at the
same level of nesting.
An END-IF phrase at the
same level of nesting.
- A separator period.
- If nested, by an ELSE phrase associated with an IF statement at a
higher level of nesting.
- When an IF statement is executed, the following transfers of control
occur:
- If the condition is true, statement-1 is executed if specified.
If statement-1 contains a procedure branching or conditional
statement, control is explicitly transferred in accordance with the
rules of that statement. If statement-1 does not contain a procedure
branching or conditional statement, the ELSE phrase, if specified,
is ignored and control passes to the end of the IF statement.
- If the condition is true and the NEXT SENTENCE phrase is
specified instead of statement-1, the ELSE phrase, if specified, is
ignored and control passes to the next executable sentence.
- If the condition is false, statement-1 or its surrogate NEXT
SENTENCE is ignored, and statement-2, if specified, is executed. If
statement-2 contains a procedure branching or conditional statement,
control is explicitly transferred in accordance with the rules of
that statement. If statement-2 does not contain a procedure
branching or conditional statement, control passes to the end of the
IF statement. If the ELSE statement-2 phrase is not specified,
statement-1 is ignored and control passes to the end of the IF
statement.
- If the condition is false, and the ELSE NEXT SENTENCE phrase is
specified, statement-1 is ignored, if specified, and control passes
to the next executable sentence.
- Statement-1 and/or statement-2 can contain an IF statement. In this
case the IF statement is said to be nested.
 IF statements within IF
statements are considered matched IF, ELSE, and END-IF ordered
combinations, proceeding from left to right. Thus, any ELSE
encountered is matched with the nearest preceding IF that has not been
already matched with an ELSE or has not been implicitly or explicitly
terminated. Any END-IF encountered is matched with the nearest
preceding IF that has not been implicitly or explicitly terminated.
IF statements within IF
statements are considered matched IF, ELSE, and END-IF ordered
combinations, proceeding from left to right. Thus, any ELSE
encountered is matched with the nearest preceding IF that has not been
already matched with an ELSE or has not been implicitly or explicitly
terminated. Any END-IF encountered is matched with the nearest
preceding IF that has not been implicitly or explicitly terminated.

The INITIALIZE statement provides the ability to set selected types of
data fields to predetermined values; for example, numeric data to zeros or
alphanumeric data to spaces.
General Format
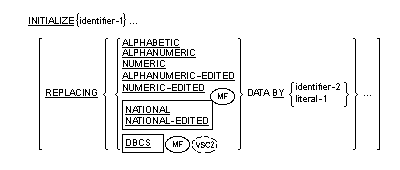
Syntax Rules
- Literal-1 and the data item referenced by identifier-2 represent the
sending area; the data item referenced by identifier-1 represents the
receiving area.
- Each category stated in the
REPLACING phrase must be a permissible category as a receiving
operand in a MOVE statement where the corresponding data item referenced
by identifier-2 or literal-1 is used as the sending operand. (See the
section The MOVE Statement later in this chapter.)
- The same category cannot be repeated in a REPLACING phrase.
- The description of the data item referenced by identifier-1 or any
items subordinate to identifier-1 can not contain the DEPENDING phrase
of the OCCURS clause.
 The data item referenced
by identifier-1 cannot be variably located, that is, it cannot follow
in the same record description an item containing the DEPENDING phrase
of the OCCURS clause unless identifier-1 is subordinate to that item
with the OCCURS clause.
The data item referenced
by identifier-1 cannot be variably located, that is, it cannot follow
in the same record description an item containing the DEPENDING phrase
of the OCCURS clause unless identifier-1 is subordinate to that item
with the OCCURS clause.
 The data item referenced
by identifier-1 can be variably located.
The data item referenced
by identifier-1 can be variably located.
- An index data item can not appear as an operand of an INITIALIZE
statement.
- The data description entry for the data item referenced by
identifier-1 must not contain a RENAMES clause.
-
 A floating-point data item
or literal can be used anywhere a numeric identifier or literal can be
specified.
A floating-point data item
or literal can be used anywhere a numeric identifier or literal can be
specified.
-
 NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can only be initialized with national character
values.
NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can only be initialized with national character
values.
General Rules
- The key word following the word REPLACING corresponds to a category
of data as defined elsewhere in this document. (See the section Concepts
Of Classes Of Data in the chapter Concepts of the COBOL Language.)
- Whether identifier-1 references an elementary item or a group item,
all operations are performed as if a series of MOVE statements had been
written, each of which has an elementary item as its receiving field,
subject to the following rules:
If the
REPLACING phrase is specified:
- If identifier-1 references a group item, any elementary item in
the data item referenced by identifier-1 is initialized only if it
belongs to the category specified in the REPLACING phrase.
- If identifier-1 references an elementary item, that item is
initialized only if it belongs to the category specified in the
REPLACING phrase.
This initialization takes place as follows: the data item referenced
by identifier-2 or literal-1 acts as the sending operand in an
implicit MOVE statement to the identified item.
All such elementary receiving fields, including all occurrences of
table items in the group, are affected; the only exceptions are those
fields specified in General Rules 3 and 4.
- Index
 and pointer
and pointer
data items and elementary FILLER data items are not affected by the
execution of an INITIALIZE statement.
- Any item that is subordinate to a receiving area identifier and which
contains the REDEFINES clause or any item that is subordinate to such an
item is excluded from this operation. However, a receiving area
identifier can itself have a REDEFINES clause or be subordinate to a
data item with a REDEFINES clause.
- When the statement is written without the REPLACING phrase, data
items of the categories alphabetic, alphanumeric, and alphanumeric
edited are set to spaces; data items of the categories numeric
 , external
floating-point
, external
floating-point
and numeric edited are set to zeros
 ; data items of the
categories national and national-edited are set to national-edited
spaces.
; data items of the
categories national and national-edited are set to national-edited
spaces.
In this case, the operation is as if each affected data item is the
receiving area an elementary MOVE statement with the indicated source
literal (that is, spaces or zeros).
- In all cases, the content of the data item referenced by identifier-1
is set to the indicated value in the order (left to right) of the
appearance of identifier-1 in the INITIALIZE statement. Within this
sequence, where identifier-1 references a group item, affected
elementary items are initialized in the sequence of their definition in
the group.
- If identifier-1 occupies the same storage area as identifier-2, the
result of the execution of this statement is undefined, even if they are
defined by the same data description entry. (See the section Overlapping
Operands earlier in this chapter.)
-
 NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can be initialized with national character
values.
NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can be initialized with national character
values.
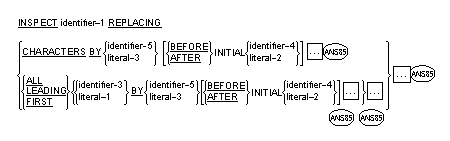
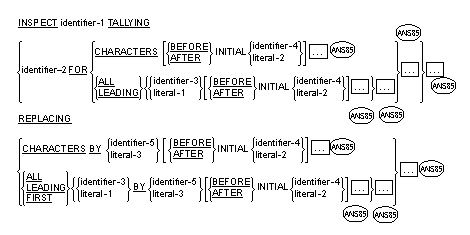
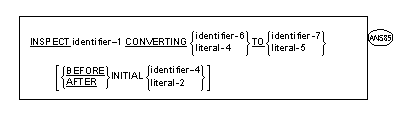
The INSPECT statement provides the ability to tally (Format 1), replace
(Format 2), tally and replace (Format 3)
 or convert (Format 4)
or convert (Format 4)
occurrences of single characters or group of characters in a data item.
Examples
- Examples of using INSPECT TALLYING, REPLACING, and CONVERTING are
provided in the Examples chapter in your Language
Reference - Additional Topics.
General Formats
Format 1
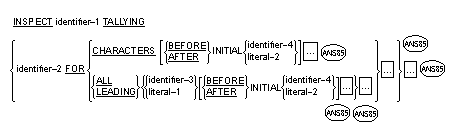
Format 2
Format 3
 F ormat 4
F ormat 4
Syntax Rules
All Formats
- Identifier-1 must reference either a group item or any category of
elementary item, described (either implicitly or explicitly) as USAGE IS
DISPLAY.
- Identifier-3 ... identifier-n must reference
 either a group item or
either a group item or
an elementary alphabetic, alphanumeric,
 alphanumeric edited,
numeric edited
alphanumeric edited,
numeric edited
or numeric item described (either implicitly or explicitly) as USAGE
IS DISPLAY.
- Each literal must be nonnumeric and can be any figurative constant,
except ALL. If literal-1, literal-2 or literal-4 is a figurative
constant, it refers to an implicit one character data item.
- No more than one
BEFORE phrase
 and /;
and /;
or one
AFTER phrase can
be specified for any one ALL, LEADING,
CHARACTERS, FIRST
 or CONVERTING
or CONVERTING
phrase.
- Literal-1, literal-2, literal-3, literal-4, and literal-5, and the
data items referenced by identifier-3, identifier-4, identifier-5,
identifier-6, and identifier-7 can be any number of characters in length
up to the limit allowed for literals or data items.
-
 6..All identifiers, except
identifier-2 (the TALLYING field), can be external floating-point items.
External floating-point items are treated as if redefined as
alphanumeric with the INSPECT statement referring to the alphanumeric
item.
6..All identifiers, except
identifier-2 (the TALLYING field), can be external floating-point items.
External floating-point items are treated as if redefined as
alphanumeric with the INSPECT statement referring to the alphanumeric
item.
Formats 1 and 3
- Identifier-2 must reference an elementary numeric data item.
Formats 2 and 3
- The size of the data referenced by literal-3 or identifier-5 must be
equal to the size of the data referenced by literal-1 or identifier-3.
When a figurative constant is used as literal-3, the size of the
figurative constant is equal to the size of literal-1 or the size of the
data item referenced by identifier-3.
- When the CHARACTERS phrase is used, literal-3 or the size of the data
item referenced by identifier-5 must be one character in length.
 This restriction does not
apply to literal-2 or identifier-4.
This restriction does not
apply to literal-2 or identifier-4.
Format 4
-
 The size of literal-5 or
the data item referenced by identifier-7 must be equal to the size of
literal-4 or the data item referenced by identifier-6. When a figurative
constant is used as literal-5, the size of the figurative constant is
equal to the size of literal-4 or the size of the data item referenced
by identifier-6.
The size of literal-5 or
the data item referenced by identifier-7 must be equal to the size of
literal-4 or the data item referenced by identifier-6. When a figurative
constant is used as literal-5, the size of the figurative constant is
equal to the size of literal-4 or the size of the data item referenced
by identifier-6.
-
 The same character must not
appear more than once either in literal-4 or in the data item referenced
by identifier-6.
The same character must not
appear more than once either in literal-4 or in the data item referenced
by identifier-6.
General Rules
All Formats
-
 For the purpose of
determining its length, identifier-1 is treated as if it were a sending
data item. (See the section The OCCURS clause in this chapter.)
For the purpose of
determining its length, identifier-1 is treated as if it were a sending
data item. (See the section The OCCURS clause in this chapter.)
- Inspection (which includes the comparison cycle, the establishment of
boundaries for the BEFORE or AFTER phrase, and the mechanism for
tallying and/or replacing) begins at the leftmost character position of
the data item referenced by identifier-1, regardless of its class, and
proceeds from left to right to the rightmost character position as
described in General Rules 11, 12 and 13.
- For use in the INSPECT statement, the contents of the data item
referenced by identifier-1, identifier-3, identifier-4, identifier-5,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 will be treated as follows:
- If any of identifier-1, identifier-3, identifier-4, identifier-5,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 is described as alphanumeric, the
INSPECT statement treats the contents of each such identifier as a
character-string.
- If any of identifier-1, identifier-3, identifier-4, identifier-5,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 is described as alphanumeric edited,
numeric edited or unsigned numeric, the data item is inspected as
though it had been redefined as alphanumeric (see General Rule 3a.)
and the INSPECT statement had been written to reference the
redefined data item.
- If any of identifier-1, identifier-3, identifier-4, identifier-5,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 is described as signed numeric, the
data item is inspected as though it had been moved to an unsigned
numeric data item with length equal to the length of the signed item
excluding any separate sign position and then the rules in General
Rule 3b had been applied. (See the section The MOVE Statement
later in this chapter.)
- In General Rules 6 through 19, all references to literal-1,
literal-2, literal-3, literal-4, and literal-5 apply equally to the
contents of the data item referenced by identifier-3, identifier-4,
identifier-5, identifier-6, and identifier-7, respectively.
- If any identifier is subscripted
 or is a
function-identifier
or is a
function-identifier
, the subscript
 or function-identifie
or function-identifie
is evaluated only once as the first operation in the execution of
the INSPECT statement.
Format 1
-
 Identifier-1 is a sending
data item.
Identifier-1 is a sending
data item.
- The required words ALL and LEADING are adjectives that apply to each
succeeding literal-1 until the next adjective appears.
- The contents of the data item referenced by identifier-2 are not
initialized by the execution of the INSPECT statement.
- The rules for tallying are as follows:
- If the ALL phrase is specified, the contents of the data item
referenced by identifier-2 are incremented by one for each
occurrence of literal-1 matched in the contents of the data item
referenced by identifier-1.
- If the LEADING phrase is specified, the contents of the data item
referenced by identifier-2 are incremented by one for the first and
each subsequent contiguous occurrence of literal-1 matched in the
contents of the data item referenced by identifier-1, provided that
the leftmost such occurrence is at the point where comparison began
in the first comparison cycle in which literal-1 was eligible to
participate.
- If the CHARACTERS phrase is specified, the contents of the data
item referenced by identifier-2 are incremented by one for each
character matched, in the sense of Format 1 and 2, General Rule 12e,
in the contents of the data item referenced by identifier-1.
- If identifier-1, identifier-3 or identifier-4 occupies the same
storage area as identifier-2, the result of the execution of this
statement is undefined, even if they are defined by the same data
description entry. (See the section Overlapping Operands earlier
in this chapter.)
Formats 1 and 2
- During inspection of the contents of the data item referenced by
identifier-1, each properly matched occurrence of literal-1 is tallied
(Format 1) or replaced by literal-3 (Format 2).
- The comparison operation to determine the occurrences of literal-1 to
be tallied or to be replaced, occurs as follows:
- The operands of the TALLYING or
REPLACING phrases are considered in the order they are
specified in the INSPECT statement from left to right. The first
literal-1 is compared to an equal number of contiguous characters,
starting with the leftmost character position in the data item
referenced by identifier-1. Literal-1 matches that portion of the
contents of the data item referenced by identifier-1 if, and only
if, they are equal, character for character, and:
- If neither LEADING nor FIRST is specified, or:
- If the LEADING adjective applies to literal-1 and literal-1
is a leading occurrence as defined in General Rules 9 and 15,
or:
- If the FIRST adjective applies to literal-1 and literal-1 is
the first occurrence as defined in General Rule 9.
- If no match occurs in the comparison of the first literal-1, the
comparison is repeated with each successive literal-1, if any, until
either a match is found or there is no next successive literal-1.
When there is no next successive literal-1, the character position
in the data item referenced by identifier-1 immediately to the right
of the leftmost character position considered in the last comparison
cycle is considered as the leftmost character position, and the
comparison cycle begins again with the first literal-1.
- Whenever a match occurs, tallying and/or replacing takes place as
described in General Rules 9 and 15. The character position in the
data item referenced by identifier-1 immediately to the right of the
rightmost character position that participated in the match is now
considered to be the leftmost character position of the data item
referenced by identifier-1, and the comparison cycle starts again
with the first literal-1.
- The comparison operation continues until the rightmost character
position of the data item referenced by identifier-1 has
participated in a match or has been considered as the leftmost
character position. When this occurs, inspection is terminated.
- If the CHARACTERS phrase is specified, an implied one character
operand participates in the cycle described in paragraphs 12a
through 12d above, except that no comparison to the contents of the
data item referenced by identifier-1 takes place. This implied
character is considered always to match the leftmost character of
the contents of the data item referenced by identifier-1
participating in the current comparison cycle.
- The comparison operation defined in General Rule 12 is affected by
the BEFORE and AFTER phrases as follows:
- If neither the BEFORE nor the AFTER phrase is specified,
literal-1 or the implied operand of the CHARACTERS phrase is first
eligible to participate in matching at the leftmost character
position of identifier-1.
- If the BEFORE phrase is specified, the associated literal-1, or
the implied operand of the CHARACTERS phrase participates only in
those comparison cycles which involve that portion of the contents
of the data item referenced by identifier-1 from its leftmost
character position up to, but not including, the first occurrence of
literal-2, in the contents of the data item referenced by
identifier-1.
The position of this first occurrence is determined before the
first cycle of the comparison operation described in General Rule
12 is begun. If, on any comparison cycle, literal-1, or the
implied operand of the CHARACTERS phrase is not eligible to
participate, it is considered not to match the contents of the
data item referenced by identifier-1. If there is no occurrence of
literal-2, in the contents of the data item referenced by
identifier-1, its associated literal-1, or the implied operand of
the CHARACTERS phrase participates in the comparison operation as
though the BEFORE phrase had not been specified.
- If the AFTER phrase is specified, the associated literal-1, or
the implied operand of the CHARACTERS phrase can participate only in
those comparison cycles which involve that portion of the contents
of the data item referenced by identifier-1 from the character
position immediately to the right of the rightmost character
position of the first occurrence of literal-2, in the contents of
the data item referenced by identifier-1 to the rightmost character
position of the data item referenced by identifier-1.
The position of this first occurrence is determined before the
first cycle of the comparison operation described in General Rule
12 is begun. If, on any comparison cycle, literal-1, or the
implied operand of the CHARACTERS phrase is not eligible to
participate, it is considered not to match the contents of the
data item referenced by identifier-1. If there is no occurrence of
literal-2, in the contents of the data item referenced by
identifier-1, its associated literal-1, or the implied operand of
the CHARACTERS phrase is never eligible to participate in the
comparison operation.
Format 2
- The required words ALL, LEADING and FIRST are adjectives that apply
to each succeeding BY phrase until the next adjective appears.
- The rules for replacement are as follows:
- When the CHARACTERS phrase is specified, each character matched
in the sense of Format 1 and 2, General Rule 12e in the contents of
the data item referenced by identifier-1, is replaced by literal-3.
- When the adjective ALL is specified, each occurrence of literal-1
matched in the contents of the data item referenced by identifier-1
is replaced by literal-3.
- When the adjective LEADING is specified, the first and each
subsequent contiguous occurrence of literal-1 matched in the
contents of the data item referenced by identifier-1 is replaced by
literal-3, provided that the leftmost occurrence is at the point
where comparison began in the first comparison cycle in which
literal-1 was eligible to participate.
- When the adjective FIRST is specified, the leftmost occurrence of
literal-1 matched in the contents of the data item referenced by
identifier-1 is replaced by literal-3.
- If identifier-3, identifier-4 or identifier-5 occupies the same
storage area as identifier-1, the result of the execution of this
statement is undefined, even if they are defined by the same data
description entry. (See the section Overlapping Operands earlier
in this chapter.)
Format 3
- A Format 3 INSPECT statement is interpreted and executed as though
two successive INSPECT statements specifying the same identifier-1 had
been written with one statement being a Format 1 statement with TALLYING
phrases identical to those specified in the Format 3 statement, and the
other statement being a Format 2 statement with REPLACING phrases
identical to those specified in the Format 3 statement. The General
Rules given for matching and counting apply to the Format 1 statement
and the General Rules given for matching and replacing apply to the
Format 2 statement.
Format 4
-
 A Format 4 INSPECT
statement is interpreted and executed as though a Format 2 INSPECT
statement specifying the same identifier-1 had been written with a
series of ALL phrases, one for each character of literal-4. The effect
is as if each of these ALL phrases referenced, as literal-1, a single
character of literal-4 and referenced, as literal-3, the corresponding
single character of literal-5. Correspondence between the characters of
literal-4 and the characters of literal-5 is by ordinal position within
the data item.
A Format 4 INSPECT
statement is interpreted and executed as though a Format 2 INSPECT
statement specifying the same identifier-1 had been written with a
series of ALL phrases, one for each character of literal-4. The effect
is as if each of these ALL phrases referenced, as literal-1, a single
character of literal-4 and referenced, as literal-3, the corresponding
single character of literal-5. Correspondence between the characters of
literal-4 and the characters of literal-5 is by ordinal position within
the data item.
-
 If identifier-4,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 occupies the same storage area as
identifier-1, the result of the execution of this statement is
undefined, even if they are defined by the same data description entry.
If identifier-4,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 occupies the same storage area as
identifier-1, the result of the execution of this statement is
undefined, even if they are defined by the same data description entry.
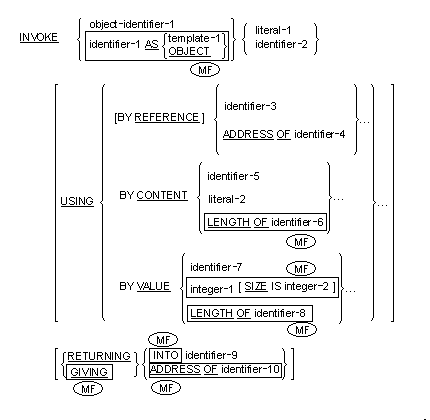
The INVOKE statement causes a method to be invoked.
General Format
Syntax Rules
- Object-identifier-1 must be an object reference or a class-name.
-
 Identifier-1 must be a
four-byte data item.
Identifier-1 must be a
four-byte data item.
- Literal-1 must be an alphanumeric literal.
- Neither literal-1 nor literal-2 may be a figurative constant.
-
 If object-identifier-1
references a universal object reference, neither the BY CONTENT nor BY
VALUE phrase can be specified and the BY REFERENCE phrase, if not
specified explicitly, is assumed implicitly.
If object-identifier-1
references a universal object reference, neither the BY CONTENT nor BY
VALUE phrase can be specified and the BY REFERENCE phrase, if not
specified explicitly, is assumed implicitly.
 The BY CONTENT and BY
VALUE phrases can be specified.
The BY CONTENT and BY
VALUE phrases can be specified.
- Identifier-2 must be defined as an alphanumeric data item.
-
 If identifier-2 is
specified, object-identifier-1 must be a universal object reference.
If identifier-2 is
specified, object-identifier-1 must be a universal object reference.
 Object-identifier-1 is
not required to be a universal object reference.
Object-identifier-1 is
not required to be a universal object reference.
- If the data item referenced by identifier-1 is not a universal object
reference, the rules for conformance as specified in Conformance for
parameters and returning items apply.
- If the data item referenced by identifier-1 is not a universal object
reference and a BY CONTENT or BY REFERENCE phrase is specified for an
argument, a BY REFERENCE phrase must be specified for the corresponding
formal parameter in the procedure division header.
- Identifier-3 must reference a data item defined in the file,
working-storage,
 object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
- Neither
 identifier-4, identifier-5,
identifier-4, identifier-5,
 identifier-6, identifier-7,
nor
identifier-6, identifier-7,
nor
 identifier-8 can be a
function-identifier.
identifier-8 can be a
function-identifier.
- If a BY VALUE phrase is specified for an argument, a BY VALUE phrase
must be specified for the corresponding formal parameter in the
procedure division header.
-
 Integer-1 may be signed or
zero.
Integer-1 may be signed or
zero.
-
 GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
-
 Identifier-9 must be a data
item no more than 8 bytes in size that is defined in the file,
working-storage,
Identifier-9 must be a data
item no more than 8 bytes in size that is defined in the file,
working-storage,
 object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
-
 Identifier-10 must be
defined as a data item in the Linkage Section with a level number of 01
or 77.
Identifier-10 must be
defined as a data item in the Linkage Section with a level number of 01
or 77.
- If the data item referenced by identifier-1 is not a universal object
reference, the rules for conformance as specified in Conformance for
parameters and returning items shall apply.
- Identifier-3 is both a sending and receiving operand.
- Identifier-1, identifier-2, identifier-4, identifier-5, identifier-6,
identifier-7 and identifier-8 are a sending operands.
- Identifier-9 and identifier-10 are receiving operands.
General Rules
- The instance of the program or method that executes the INVOKE
statement is the activating runtime element.
- Object-identifier-1 or
 identifier-1 identifies an
object instance. If object-identifier-1 is specified as a class-name,
object-identifier-1 identifies the factory object of that class-name.
Literal-1 or the content of the data item referenced by identifier-2
identifies a method of that object that will act upon that object
instance:
identifier-1 identifies an
object instance. If object-identifier-1 is specified as a class-name,
object-identifier-1 identifies the factory object of that class-name.
Literal-1 or the content of the data item referenced by identifier-2
identifies a method of that object that will act upon that object
instance:
- If the method to be invoked is a COBOL method, literal-1 or the
content of the data item referenced by identifier-2 is the name of
the method to be invoked as specified in its METHOD-ID paragraph..
- If the method to be invoked is not a COBOL method, the rules for
the formation of the method-name are dependent upon the domain
involved.
-
 The AS phrase enables you
to invoke methods on a COBOL data item. If template-1 is specified, it
is used as a class template. Creation of templates is a function
provided by objects in the supplied Class Library. (See the book OO Programming
with Object COBOL for details.)
The AS phrase enables you
to invoke methods on a COBOL data item. If template-1 is specified, it
is used as a class template. Creation of templates is a function
provided by objects in the supplied Class Library. (See the book OO Programming
with Object COBOL for details.)
- When an INVOKE statement is executed, the method specified is made
available for execution and control is transferred to the invoked
method. If the invoked method is a COBOL method, its execution is
described in the general rules of The PROCEDURE DIVISION Header;
otherwise, the execution is defined by the implementor of the language
in which the method is written. After control is returned from the
method, control is transferred to the end of the INVOKE statement.
- The run unit is not aware of whether an invoked method is a COBOL
method or a non-COBOL method until the invoked method has been located,
prior to being made available for execution. The form of the method-name
cannot be used to determine whether the method is a COBOL method or not.
- The process of invoking a method or exiting from an invoked method
does not alter the status or positioning of a file associated with any
external file connector.
- This implementation does not maintain any synchronization between the
argumenrts and the linkage section data items. That is the
responsibility of the user.
Note: The COBOL language places no restrictions on the
alignment of the addresses of data items, whereas non-COBOL languages
typically do make assumptions about addresses and will fail in some
way if a misaligned data item is referenced. Alignment can be achieved
by one or more of the following actions:
- modifying group items to include additional filler items
- ensuring operands in the USING phrase are level 01 or level 77
data items in conjunction with the ALIGN Compiler directive or
- use of the SYNCHRONIZED clause in conjunction with the IBMCOMP
Compiler directive
If a RETURNING phrase is specified on the INVOKE statement, a
non-COBOL method must return a result in the appropriate format.
- The sequence of arguments in the USING phrase of the INVOKE statement
and the corresponding formal parameters in the USING phrase of the
invoked method's Procedure Division header determines the correspondence
between arguments and formal parameters. This correspondence is
positional and not by name equivalence; the first argument corresponds
to the first formal parameter, the second to the second, etc.
If a parameter is an index-name, no such correspondence is
established. Index-names in the invoked method and the invoking
runtime element always refer to separate indices.
The effect of the USING phrase on the activated runtime element is
described in the general rules of The PROCEDURE DIVISION Header.
- The values of the parameters referenced in the USING phrase of the
INVOKE statement are made available to the invoked method at the time
the INVOKE statement is executed.
- The BY CONTENT, BY REFERENCE and BY VALUE phrases are transitive
across the parameters that follow them until another BY CONTENT, BY
REFERENCE or BY VALUE phrase is encountered.
If no BY CONTENT, BY REFERENCE or BY VALUE phrase is specified prior
to the first parameter, the BY REFERENCE phrase is assumed.
- If the BY REFERENCE ADDRESS OF phrase is specified or implied then
the method operates as if a data item had been declared with USAGE
POINTER and that data item passed BY REFERENCE with a value acquired by
a SET data item TO ADDRESS OF identifier-4 statement.
-
 If identifier-4 is in the
Linkage Section and has a level number other than 01 or 77 or is in the
Working-Storage Section, it is equivalent to passing the item BY CONTENT
and the address of identifier-4 cannot be modified by the invoked
method. If the BY REFERENCE literal-2 phrase is specified or implied
then the method processes literal-2 as described for literal-3.
If identifier-4 is in the
Linkage Section and has a level number other than 01 or 77 or is in the
Working-Storage Section, it is equivalent to passing the item BY CONTENT
and the address of identifier-4 cannot be modified by the invoked
method. If the BY REFERENCE literal-2 phrase is specified or implied
then the method processes literal-2 as described for literal-3.
-
 If LENGTH OF identifier-6
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-6.
If LENGTH OF identifier-6
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-6.
-
 If integer-1 is specified
then the implied data description of the argument is a signed numeric
item USAGE COMP-5 that occupies the number of bytes of storage specified
by the value of integer-2, if specified, or 4 bytes otherwise.
If integer-1 is specified
then the implied data description of the argument is a signed numeric
item USAGE COMP-5 that occupies the number of bytes of storage specified
by the value of integer-2, if specified, or 4 bytes otherwise.
-
 If LENGTH OF identifier-8
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-8.
If LENGTH OF identifier-8
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-8.
-
 If identifier-10 is
specified, the invoked method must return a value with explicit or
implicit USAGE POINTER. The result of the method is assigned to
identifier-10 using the rules for the SET statement.
If identifier-10 is
specified, the invoked method must return a value with explicit or
implicit USAGE POINTER. The result of the method is assigned to
identifier-10 using the rules for the SET statement.
- Invoked methods may contain INVOKE statements. An invoked method may
execute an INVOKE statement that directly or indirectly invokes the
invoking method.
Copyright © 1998 Micro Focus Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.
 | Procedure Division - ACCEPT - DIVIDE |
| Procedure Division - MERGE - OPEN |  |




 The ENTER statement is
classed as an obsolete element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to
be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI Standard.
The ENTER statement is
classed as an obsolete element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to
be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI Standard.  All dialects in this COBOL
implementation support this syntax for documentation purposes only. The
FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect all occurrences of this
syntax.
All dialects in this COBOL
implementation support this syntax for documentation purposes only. The
FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect all occurrences of this
syntax.  Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, this feature is explicitly excluded from the
X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in an X/Open
COBOL conforming source program.
Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, this feature is explicitly excluded from the
X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not be used in an X/Open
COBOL conforming source program. 


 File Section or
File Section or
 Working-Storage Section.
Working-Storage Section.
 Data-name-2 must be defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the Linkage Section, File Section
or Working-Storage Section. Data-name-2 can be of any class, but the
length must be no greater than 8 bytes.
Data-name-2 must be defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the Linkage Section, File Section
or Working-Storage Section. Data-name-2 can be of any class, but the
length must be no greater than 8 bytes. Format 2 can only be used
in a program in which the EXTERNAL clause is specified in the PROGRAM-ID
paragraph, that is a call prototype.
Format 2 can only be used
in a program in which the EXTERNAL clause is specified in the PROGRAM-ID
paragraph, that is a call prototype.
 Data-name-1 and
data-name-2 must be defined as 01 level records in the LINKAGE SECTION.
Data-name-1 and
data-name-2 must be defined as 01 level records in the LINKAGE SECTION.
 Typedef-name-1,
typedef-name-2, and typedef-name-3 must be previously defined in the
same source file as a programmer-defined usage by means of a TYPEDEF
clause.
Typedef-name-1,
typedef-name-2, and typedef-name-3 must be previously defined in the
same source file as a programmer-defined usage by means of a TYPEDEF
clause.  If data-name-1 is defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the File Section or Working-Storage
Section then the object program operates as if a data item had been
declared in the Linkage Section with the same data declaration as
data-name-1 and the contents of that data item were moved to data-name-1
prior to executing the first statement in the called program. In an
initial program, these values are overwritten by the initialization of
the program's Working-Storage data and are therefore not available to
the called program.
If data-name-1 is defined
as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the File Section or Working-Storage
Section then the object program operates as if a data item had been
declared in the Linkage Section with the same data declaration as
data-name-1 and the contents of that data item were moved to data-name-1
prior to executing the first statement in the called program. In an
initial program, these values are overwritten by the initialization of
the program's Working-Storage data and are therefore not available to
the called program.
 If the argument is passed
by value, the called program operates as if the record in the linkage
section were allocated by the calling runtime element during the process
of initiating the call and as if this record does not occupy the same
storage area as the argument in the calling runtime element. This
allocated record is exactly the same number of alphanumeric character
positions in length as the argument. That argument is moved to this
allocated record without conversion. This record is then treated by the
called program as if it were the argument and as if it were passed by
reference.
If the argument is passed
by value, the called program operates as if the record in the linkage
section were allocated by the calling runtime element during the process
of initiating the call and as if this record does not occupy the same
storage area as the argument in the calling runtime element. This
allocated record is exactly the same number of alphanumeric character
positions in length as the argument. That argument is moved to this
allocated record without conversion. This record is then treated by the
called program as if it were the argument and as if it were passed by
reference.
 data-name-2 and
data-name-2 and
 data-name-3 are resolved in
accordance with their description in the Linkage Section. If this
description defines a greater number of character positions than the
corresponding data item in the activating element, unpredictable results
can occur. Failure to comply with this rule or exceeding the maximum
allowed size of the system area for a particular run time environment
may result in the system becoming catastrophically corrupt.
data-name-3 are resolved in
accordance with their description in the Linkage Section. If this
description defines a greater number of character positions than the
corresponding data item in the activating element, unpredictable results
can occur. Failure to comply with this rule or exceeding the maximum
allowed size of the system area for a particular run time environment
may result in the system becoming catastrophically corrupt.
 When a program is called
and a BY REFERENCE operand in the USING phrase corresponds to a
parameter in the calling program, a referential connection is
established and endures until control is returned to the calling
program. If the program is called a second time, without any intervening
cancel of the program, and that same BY REFERENCE operand does not
correspond to a parameter in the calling program, then you must not
reference that operand unless the STICKY-LINKAGE Compiler directive is
specified.
When a program is called
and a BY REFERENCE operand in the USING phrase corresponds to a
parameter in the calling program, a referential connection is
established and endures until control is returned to the calling
program. If the program is called a second time, without any intervening
cancel of the program, and that same BY REFERENCE operand does not
correspond to a parameter in the calling program, then you must not
reference that operand unless the STICKY-LINKAGE Compiler directive is
specified.


 Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference floating-point data items.
Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference floating-point data items.
 Where numeric literals
are permitted, floating-point literals are permitted.
Where numeric literals
are permitted, floating-point literals are permitted.
 Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference pointer data items.
Where identifiers are
permitted, they can reference pointer data items.  If partial-expression-1 or
partial-expression-2 is specified as a selection object, it must
correspond to a selection subject that is an identifier, a literal or an
arithmetic expression. Partial-expression-1 and partial-expression-2
must be a sequence of COBOL words which, when following the
corresponding selection subject, make the resultant text a valid
conditional expression.
If partial-expression-1 or
partial-expression-2 is specified as a selection object, it must
correspond to a selection subject that is an identifier, a literal or an
arithmetic expression. Partial-expression-1 and partial-expression-2
must be a sequence of COBOL words which, when following the
corresponding selection subject, make the resultant text a valid
conditional expression.  If the selection object is
specified by partial-expression-1 or partial-expression-2, the
corresponding selection subject is considered to be the word TRUE. The
selection object is considered to be condition-1 or condition-2
respectively, where condition-1 or condition-2 is the conditional
expression resulting from partial expression-1 or partial-expression-2
following the original corresponding selection-subject-1 or
selection-subject-2 respectively.
If the selection object is
specified by partial-expression-1 or partial-expression-2, the
corresponding selection subject is considered to be the word TRUE. The
selection object is considered to be condition-1 or condition-2
respectively, where condition-1 or condition-2 is the conditional
expression resulting from partial expression-1 or partial-expression-2
following the original corresponding selection-subject-1 or
selection-subject-2 respectively. 




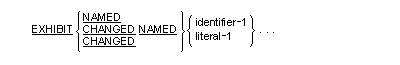
 The EXIT statement can also
exit an inline PERFORM, a paragraph or a section.
The EXIT statement can also
exit an inline PERFORM, a paragraph or a section.  You can also return values to
activating runtime
elements written in any language.
You can also return values to
activating runtime
elements written in any language.  The EXIT METHOD statement
marks the logical end of an invoked method.
The EXIT METHOD statement
marks the logical end of an invoked method.



 This rule is not enforced.
This rule is not enforced.  This rule is not enforced.
This rule is not enforced.  This rule is not
enforced.
This rule is not
enforced.  This rule is not
enforced.
This rule is not
enforced.  Integer-1 may be signed.
Integer-1 may be signed.
 GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
 If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, identifier-1 must be no larger than 8 bytes in size.
If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, identifier-1 must be no larger than 8 bytes in size.
 An EXIT METHOD statement
may be specified only in a method procedure division.
An EXIT METHOD statement
may be specified only in a method procedure division.
 The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement without a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to
an implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately following the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.
The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement without a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to
an implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately following the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.
 The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement with a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to an
implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately preceding the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.
The execution of an EXIT
PERFORM statement with a CYCLE phrase causes control to be passed to an
implicit CONTINUE statement, immediately preceding the END-PERFORM
associated with the nearest inline PERFORM statement.  The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the PARAGRAPH phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the paragraph.
The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the PARAGRAPH phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the paragraph.
 The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the SECTION phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the last paragraph in the section.
The execution of a Format 3
EXIT statement with the SECTION phrase causes control to pass to an
implicit CONTINUE statement immediately following
the last statement in the last paragraph in the section.
 If the EXIT PROGRAM
statement is executed in a program which is not under the control of a
calling runtime element, the EXIT PROGRAM statement causes execution of
the program to continue with the next executable statement.
If the EXIT PROGRAM
statement is executed in a program which is not under the control of a
calling runtime element, the EXIT PROGRAM statement causes execution of
the program to continue with the next executable statement.
 The
execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement in a called program which does
not possess the initial attribute causes execution to continue with the
next executable statement following the CALL statement in the calling
runtime element. The state of the calling runtime element is not altered
and is identical to that which existed at the time it executed the CALL
statement except that the contents of data items and the contents of
data files shared between the calling and called runtime elements may
have been changed. The program state of the called program is not
altered except that the ends of the ranges of all PERFORM statements
executed by that called program are considered to have been reached.
The
execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement in a called program which does
not possess the initial attribute causes execution to continue with the
next executable statement following the CALL statement in the calling
runtime element. The state of the calling runtime element is not altered
and is identical to that which existed at the time it executed the CALL
statement except that the contents of data items and the contents of
data files shared between the calling and called runtime elements may
have been changed. The program state of the called program is not
altered except that the ends of the ranges of all PERFORM statements
executed by that called program are considered to have been reached.
 Besides the actions
specified in General Rule 7, the execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement
in a called program which possesses the initial attribute is equivalent
to also executing a CANCEL statement referencing that program except
that the statement will not free any memory. See the section The
CANCEL Statement earlier in this chapter.
Besides the actions
specified in General Rule 7, the execution of an EXIT PROGRAM statement
in a called program which possesses the initial attribute is equivalent
to also executing a CANCEL statement referencing that program except
that the statement will not free any memory. See the section The
CANCEL Statement earlier in this chapter.
 An EXIT PROGRAM statement
must not be executed while executing a declarative procedure in which
the GLOBAL phrase is specified except in a program called while
executing that declarative procedure.
An EXIT PROGRAM statement
must not be executed while executing a declarative procedure in which
the GLOBAL phrase is specified except in a program called while
executing that declarative procedure.
 Execution of an EXIT
PROGRAM statement in a program that is under the control of a calling
runtime element,
causes a return value to be set in the system area generally available
for non-COBOL programs to return a value. This system area is never
smaller than 4 bytes in size but may be larger in some environments.
Execution of an EXIT
PROGRAM statement in a program that is under the control of a calling
runtime element,
causes a return value to be set in the system area generally available
for non-COBOL programs to return a value. This system area is never
smaller than 4 bytes in size but may be larger in some environments.
 If the GIVING phrase is
not specified and the calling convention specifies updating the
RETURN-CODE special-register (see the CALL CONVENTION clause in the
earlier section The Special-Names Paragraph) then the object
program operates as if the system area were declared as a COBOL
numeric data item with USAGE COMP-5 and with a size determined by the
operating environment external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE
statement had been executed with the RETURN-CODE as the sending item
and the system area as the receiving item. (See the section
Special Registers in the chapter Concepts of the COBOL
Language for details of RETURN-CODE.)
If the GIVING phrase is
not specified and the calling convention specifies updating the
RETURN-CODE special-register (see the CALL CONVENTION clause in the
earlier section The Special-Names Paragraph) then the object
program operates as if the system area were declared as a COBOL
numeric data item with USAGE COMP-5 and with a size determined by the
operating environment external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE
statement had been executed with the RETURN-CODE as the sending item
and the system area as the receiving item. (See the section
Special Registers in the chapter Concepts of the COBOL
Language for details of RETURN-CODE.)  If the GIVING ADDRESS OF
phrase is specified, the object program operates as if the system area
were declared as a COBOL data item with USAGE POINTER and as if a SET
statement had been executed with TO ADDRESS OF identifier-1 as the
first operand and the system area as the second operand. The ADDRESS
OF phrase may be used to indirectly pass a value that is larger than
the system area.
If the GIVING ADDRESS OF
phrase is specified, the object program operates as if the system area
were declared as a COBOL data item with USAGE POINTER and as if a SET
statement had been executed with TO ADDRESS OF identifier-1 as the
first operand and the system area as the second operand. The ADDRESS
OF phrase may be used to indirectly pass a value that is larger than
the system area.  If the GIVING
identifier-1 phrase is specified, identifier-1 must describe the same
number of character positions as is required to hold the return value
in the system area and must be of the type and usage that is expected
by the calling runtime
element. The object program operates as if a MOVE statement had
been executed with identifier-1 as the sending item and the system
area as the receiving item.
If the GIVING
identifier-1 phrase is specified, identifier-1 must describe the same
number of character positions as is required to hold the return value
in the system area and must be of the type and usage that is expected
by the calling runtime
element. The object program operates as if a MOVE statement had
been executed with identifier-1 as the sending item and the system
area as the receiving item.  If the GIVING integer-1
phrase is specified, integer-1 must not be larger than the value that
can be held in the system area. The object program operates as if the
system area were declared as a COBOL numeric data item with USAGE
COMP-5 and with a size determined by the operating environment
external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE statement had been
executed with integer-1 as the sending item and the system area as the
receiving item.
If the GIVING integer-1
phrase is specified, integer-1 must not be larger than the value that
can be held in the system area. The object program operates as if the
system area were declared as a COBOL numeric data item with USAGE
COMP-5 and with a size determined by the operating environment
external to the COBOL system and as if a MOVE statement had been
executed with integer-1 as the sending item and the system area as the
receiving item.  The execution of an EXIT
METHOD statement causes the executing method to terminate, and control
to return to the invoking statement. If a RETURNING phrase is present in
the containing method definition, the value in the data item referenced
by the RETURNING phrase becomes the result of the method invocation.
The execution of an EXIT
METHOD statement causes the executing method to terminate, and control
to return to the invoking statement. If a RETURNING phrase is present in
the containing method definition, the value in the data item referenced
by the RETURNING phrase becomes the result of the method invocation.
 You can also return values to
calling runtime elements
written in any language or to the operating system environment.
You can also return values to
calling runtime elements
written in any language or to the operating system environment. 
 GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
 If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, the data item referenced by identifier-1 must be no
larger than 8 bytes in size.
If the ADDRESS OF clause is
not specified, the data item referenced by identifier-1 must be no
larger than 8 bytes in size.
 The option of omitting
procedure-name-1 in a Format 1 GO TO statement is classed as an obsolete
element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to be deleted from the
next full revision of the ANSI Standard.
The option of omitting
procedure-name-1 in a Format 1 GO TO statement is classed as an obsolete
element in the ANSI'85 standard and is scheduled to be deleted from the
next full revision of the ANSI Standard.  All dialects in this COBOL
implementation fully support this syntax. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive
can be used to detect all occurrences of this syntax.
All dialects in this COBOL
implementation fully support this syntax. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive
can be used to detect all occurrences of this syntax.  Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, omitting the procedure-name in Format 1 is
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should
not be used in an X/Open COBOL conforming source program.
Although it is a part of the
standard COBOL definition, omitting the procedure-name in Format 1 is
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should
not be used in an X/Open COBOL conforming source program. 

 This restriction is not
enforced.
This restriction is not
enforced.  A Format 2 statement can
be written with only one procedure name.
A Format 2 statement can
be written with only one procedure name.  If an ALTER statement
referring to the paragraph containing this GO TO statement has not
been executed before this GO TO statement is executed, this GO TO
statement is treated like a CONTINUE statement.
If an ALTER statement
referring to the paragraph containing this GO TO statement has not
been executed before this GO TO statement is executed, this GO TO
statement is treated like a CONTINUE statement. 
 If the END-IF phrase is
specified, the
NEXT SENTENCE phrase must not be specified.
If the END-IF phrase is
specified, the
NEXT SENTENCE phrase must not be specified.
 NEXT SENTENCE can be
specified with END-IF.
NEXT SENTENCE can be
specified with END-IF.  An END-IF phrase at the
same level of nesting.
An END-IF phrase at the
same level of nesting.
 IF statements within IF
statements are considered matched IF, ELSE, and END-IF ordered
combinations, proceeding from left to right. Thus, any ELSE
encountered is matched with the nearest preceding IF that has not been
already matched with an ELSE or has not been implicitly or explicitly
terminated. Any END-IF encountered is matched with the nearest
preceding IF that has not been implicitly or explicitly terminated.
IF statements within IF
statements are considered matched IF, ELSE, and END-IF ordered
combinations, proceeding from left to right. Thus, any ELSE
encountered is matched with the nearest preceding IF that has not been
already matched with an ELSE or has not been implicitly or explicitly
terminated. Any END-IF encountered is matched with the nearest
preceding IF that has not been implicitly or explicitly terminated.


 The data item referenced
by identifier-1 cannot be variably located, that is, it cannot follow
in the same record description an item containing the DEPENDING phrase
of the OCCURS clause unless identifier-1 is subordinate to that item
with the OCCURS clause.
The data item referenced
by identifier-1 cannot be variably located, that is, it cannot follow
in the same record description an item containing the DEPENDING phrase
of the OCCURS clause unless identifier-1 is subordinate to that item
with the OCCURS clause.  The data item referenced
by identifier-1 can be variably located.
The data item referenced
by identifier-1 can be variably located.  A floating-point data item
or literal can be used anywhere a numeric identifier or literal can be
specified.
A floating-point data item
or literal can be used anywhere a numeric identifier or literal can be
specified.
 NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can only be initialized with national character
values.
NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can only be initialized with national character
values.  and pointer
and pointer  , external
floating-point
, external
floating-point  ; data items of the
categories national and national-edited are set to national-edited
spaces.
; data items of the
categories national and national-edited are set to national-edited
spaces.  NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can be initialized with national character
values.
NATIONAL and
NATIONAL-EDITED fields can be initialized with national character
values.  or convert (Format 4)
or convert (Format 4) 



 either a group item or
either a group item or
 alphanumeric edited,
numeric edited
alphanumeric edited,
numeric edited  and /;
and /;  or CONVERTING
or CONVERTING  6..All identifiers, except
identifier-2 (the TALLYING field), can be external floating-point items.
External floating-point items are treated as if redefined as
alphanumeric with the INSPECT statement referring to the alphanumeric
item.
6..All identifiers, except
identifier-2 (the TALLYING field), can be external floating-point items.
External floating-point items are treated as if redefined as
alphanumeric with the INSPECT statement referring to the alphanumeric
item.  This restriction does not
apply to literal-2 or identifier-4.
This restriction does not
apply to literal-2 or identifier-4.  The size of literal-5 or
the data item referenced by identifier-7 must be equal to the size of
literal-4 or the data item referenced by identifier-6. When a figurative
constant is used as literal-5, the size of the figurative constant is
equal to the size of literal-4 or the size of the data item referenced
by identifier-6.
The size of literal-5 or
the data item referenced by identifier-7 must be equal to the size of
literal-4 or the data item referenced by identifier-6. When a figurative
constant is used as literal-5, the size of the figurative constant is
equal to the size of literal-4 or the size of the data item referenced
by identifier-6.
 The same character must not
appear more than once either in literal-4 or in the data item referenced
by identifier-6.
The same character must not
appear more than once either in literal-4 or in the data item referenced
by identifier-6.  For the purpose of
determining its length, identifier-1 is treated as if it were a sending
data item. (See the section The OCCURS clause in this chapter.)
For the purpose of
determining its length, identifier-1 is treated as if it were a sending
data item. (See the section The OCCURS clause in this chapter.)
 or is a
function-identifier
or is a
function-identifier  or function-identifie
or function-identifie
 Identifier-1 is a sending
data item.
Identifier-1 is a sending
data item.
 A Format 4 INSPECT
statement is interpreted and executed as though a Format 2 INSPECT
statement specifying the same identifier-1 had been written with a
series of ALL phrases, one for each character of literal-4. The effect
is as if each of these ALL phrases referenced, as literal-1, a single
character of literal-4 and referenced, as literal-3, the corresponding
single character of literal-5. Correspondence between the characters of
literal-4 and the characters of literal-5 is by ordinal position within
the data item.
A Format 4 INSPECT
statement is interpreted and executed as though a Format 2 INSPECT
statement specifying the same identifier-1 had been written with a
series of ALL phrases, one for each character of literal-4. The effect
is as if each of these ALL phrases referenced, as literal-1, a single
character of literal-4 and referenced, as literal-3, the corresponding
single character of literal-5. Correspondence between the characters of
literal-4 and the characters of literal-5 is by ordinal position within
the data item.
 If identifier-4,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 occupies the same storage area as
identifier-1, the result of the execution of this statement is
undefined, even if they are defined by the same data description entry.
If identifier-4,
identifier-6 or identifier-7 occupies the same storage area as
identifier-1, the result of the execution of this statement is
undefined, even if they are defined by the same data description entry.

 Identifier-1 must be a
four-byte data item.
Identifier-1 must be a
four-byte data item.
 If object-identifier-1
references a universal object reference, neither the BY CONTENT nor BY
VALUE phrase can be specified and the BY REFERENCE phrase, if not
specified explicitly, is assumed implicitly.
If object-identifier-1
references a universal object reference, neither the BY CONTENT nor BY
VALUE phrase can be specified and the BY REFERENCE phrase, if not
specified explicitly, is assumed implicitly.
 The BY CONTENT and BY
VALUE phrases can be specified.
The BY CONTENT and BY
VALUE phrases can be specified.  If identifier-2 is
specified, object-identifier-1 must be a universal object reference.
If identifier-2 is
specified, object-identifier-1 must be a universal object reference.
 Object-identifier-1 is
not required to be a universal object reference.
Object-identifier-1 is
not required to be a universal object reference. object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
 identifier-4, identifier-5,
identifier-4, identifier-5,
 identifier-6, identifier-7,
nor
identifier-6, identifier-7,
nor
 identifier-8 can be a
function-identifier.
identifier-8 can be a
function-identifier.
 Integer-1 may be signed or
zero.
Integer-1 may be signed or
zero.
 GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
GIVING and RETURNING are
equivalent.
 Identifier-9 must be a data
item no more than 8 bytes in size that is defined in the file,
working-storage,
Identifier-9 must be a data
item no more than 8 bytes in size that is defined in the file,
working-storage,
 object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
object-storage,
local-storage, linkage, or communication section.
 Identifier-10 must be
defined as a data item in the Linkage Section with a level number of 01
or 77.
Identifier-10 must be
defined as a data item in the Linkage Section with a level number of 01
or 77.
 identifier-1 identifies an
object instance. If object-identifier-1 is specified as a class-name,
object-identifier-1 identifies the factory object of that class-name.
Literal-1 or the content of the data item referenced by identifier-2
identifies a method of that object that will act upon that object
instance:
identifier-1 identifies an
object instance. If object-identifier-1 is specified as a class-name,
object-identifier-1 identifies the factory object of that class-name.
Literal-1 or the content of the data item referenced by identifier-2
identifies a method of that object that will act upon that object
instance:
 The AS phrase enables you
to invoke methods on a COBOL data item. If template-1 is specified, it
is used as a class template. Creation of templates is a function
provided by objects in the supplied Class Library. (See the book OO Programming
with Object COBOL for details.)
The AS phrase enables you
to invoke methods on a COBOL data item. If template-1 is specified, it
is used as a class template. Creation of templates is a function
provided by objects in the supplied Class Library. (See the book OO Programming
with Object COBOL for details.)
 If identifier-4 is in the
Linkage Section and has a level number other than 01 or 77 or is in the
Working-Storage Section, it is equivalent to passing the item BY CONTENT
and the address of identifier-4 cannot be modified by the invoked
method. If the BY REFERENCE literal-2 phrase is specified or implied
then the method processes literal-2 as described for literal-3.
If identifier-4 is in the
Linkage Section and has a level number other than 01 or 77 or is in the
Working-Storage Section, it is equivalent to passing the item BY CONTENT
and the address of identifier-4 cannot be modified by the invoked
method. If the BY REFERENCE literal-2 phrase is specified or implied
then the method processes literal-2 as described for literal-3.
 If LENGTH OF identifier-6
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-6.
If LENGTH OF identifier-6
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-6.
 If integer-1 is specified
then the implied data description of the argument is a signed numeric
item USAGE COMP-5 that occupies the number of bytes of storage specified
by the value of integer-2, if specified, or 4 bytes otherwise.
If integer-1 is specified
then the implied data description of the argument is a signed numeric
item USAGE COMP-5 that occupies the number of bytes of storage specified
by the value of integer-2, if specified, or 4 bytes otherwise.
 If LENGTH OF identifier-8
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-8.
If LENGTH OF identifier-8
is specified then the data description of the argument is PIC S9(9)
USAGE BINARY and its content is set to the number of bytes of storage
allocated to identifier-8.
 If identifier-10 is
specified, the invoked method must return a value with explicit or
implicit USAGE POINTER. The result of the method is assigned to
identifier-10 using the rules for the SET statement.
If identifier-10 is
specified, the invoked method must return a value with explicit or
implicit USAGE POINTER. The result of the method is assigned to
identifier-10 using the rules for the SET statement.

