 How to
How toThis chapter describes the basic operations you need to perform when developing IMS applications.
To generate DBDs you must first have added them to your project.
Note: When you build a project, the non-COBOL files are built in the order in which they were added to the project. To ensure that a project's DBD files are genned before its PSB files you must add the DBD files to the project before the PSB files.
These files contain DBD source information that has been extracted and formatted into a smaller structure optimized for faster access during execution. The .dat files files are indexed files and can contain one or more generated DBD members.
When you generate the first DBD you will see message DBDUT0U35U informing you that dbdgen2.dat does not exist. Enter C to specify that you want to create dbdgen2.dat (and dbdgen2f.dat) and message DBDUT0U35U will not be displayed on subsequent DBD generations.
The dbdgen*.* and dbdname.acb files are created in the current directory. You need to ensure that you specify the location of these files to the enterprise server that you will be using. See the section Specifying the Location of Genned Files in the chapter Configuring IMS-enabled Enterprise Servers for more information.
Once you have generated the DBDs you need to generate the PSBs. To generate PSBs you must first have added them to your project.
Note: When you build a project, the non-COBOL files are built in the order in which they were added to the project. To ensure that a project's DBD files are genned before its PSB files you must add the DBD files to the project before the PSB files.
Generating a PSB updates the following files:
These files contain PSB source information that has been extracted and formatted into a smaller structure optimized for faster access during execution. psbgen3.dat is an indexed file and can contain one or more generated PSB members.
When you generate the first PSB you will see message DBDUT0U35U informing you that psbgen3.dat does not exist. Enter C to specify that you want to create psbgen3.dat and message DBDUT0U35U will not be displayed on subsequent PSB generations.
The psbgen3.dat and psbname.acb files are created in the current directory. You need to ensure that you specify the location of these files to the enterprise server that you will be using. See the section Specifying the Location of Genned Files in the chapter Configuring IMS-enabled Enterprise Servers for more information.
To generate MFSs you must first have added them to your project.
In addition to the .mid and .mod files, generating an MFS updates the following files:
These files contain MFS source information that has been extracted and formatted into a smaller structure optimized for faster access during execution. The .dat files are indexed files and can contain one or more generated MFS members.
The .mid and .mod files are created in the current directory. You need to ensure that you specify the location of these files to the enterprise server that you will be using. See the section Specifying the Location of Genned Files in the chapter Configuring IMS-enabled Enterprise Servers for more information.
When you generate the first MFS you will see message DBDUT0U35U informing you that mfspef.dat does not exist. Enter C to specify that you want to create mfspef.dat (and the other files from the above list) and message DBDUT0U35U will not be displayed on subsequent MFS generations.
The database management utility (IMSDBU) enables you to perform a number of database management operations, such as loading, unloading and zeroloading.
To start the database management utility you use the following command from a Net Express command prompt:
mfims imsdbu
Figure shows the database management utility's opening screen.
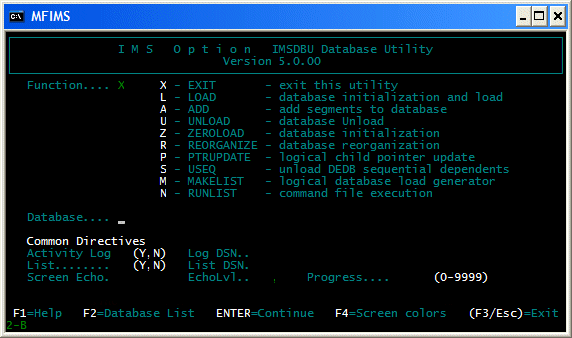
Figure 7-1: IMS Database Management Utility
To use the database management utility specify a function in the Function field (L for load, for example), the name of the database you want to work with in the Database field, then press Enter. Some operations require you to specify additional information on extra pages.
Note: The IMS Database Utility is inoperable if no IMS databases have been compiled in the project. Attempts to access this utility will result in an error message displayed to the screen.
For full information on IMSDBU see the IMSDBU Reference.
To load a database you can either use the database management utility (as described in the section Using the Database Management Utility) or perform the following steps:
mfims imsdbu load datfilenameNote:
for %i in (*.dat) do mfims imsdbu load %i
By default, this loads the database from a file with the same basename as datfilename but with the extension .DBU. You can change this behavior using the DSN and LAYOUT options.
The product includes a segment exit routine called IMSDBUEA that you can use to convert segments from EBCDIC to ANSI. You can use it in three ways:
IMSDBUEA uses a segment layout (.slf) file to determine which fields of each segment need to be converted, so you must create an .slf file using Mainframe Express's IMS database editor before you can use IMSDBUEA. The .slf file must be in the directory specified by the ES_IMSDAT environment variable, or if the ES_IMSDAT environment variable is not set the .slf file must be in the current directory.
How you use IMSDBUEA depends on whether you are using the database management utility or the command line:
segexit=imsdbuea
Notes:
Before you run your IMS transaction in an enterprise server you must first run the /IMS transaction to set up the enterprise server to run in IMS mode. Once you have done this, you run an IMS transaction in the same way as you would run it on the mainframe. If you run it from a 3270 terminal or emulator, you enter transaction IDs at the terminal. Note that on a PC the keys assigned to act as the CICS keys depend on your TN3270 emulator. For example, in many cases the Escape key is used as the 3270 Clear key, and the right-hand Ctrl key is used as the 3270 Enter key.
To run an IMS transaction from a 3270 session:
Notes:
If your message processing regions for an enterprise server become unresponsive for some reason you need to perform a cold start. Performing a cold start involves deleting the IMS message queue for an enterprise server, so any outstanding messages are lost and need to be resubmitted after the cold start.
To perform a cold start you delete the file %USERPROFILE%\My Documents\Micro Focus\Net Express ver\WORKAREA\ES_name\imsmesgq.dat, where USERPROFILE is a Windows environment variable and ES_name is the name of the enterprise server whose message processing regions are unresponsive.
Copyright © 2008 Micro Focus (IP) Ltd. All rights reserved.