 | Data General Interactive COBOL V1.3 Syntax Support |
When the DIALECT Compiler directive is set to BS2000 or BS2000-OFFLOAD, the syntax listed in this chapter is accepted by your COBOL system for compatibility with Siemens BS2000 COBOL. Many features found in Siemens BS2000 COBOL exist already in this COBOL implementation. These are documented in your Language Reference and include the features marked in that document as ANS85. Some of the compatibility syntax listed in this chapter is identical to standard COBOL syntax, but behaves differently if you set the DIALECT Compiler directive to BS2000 or BS2000-OFFLOAD when you submit your source code to your COBOL system. See the COBOL85 (BS2000) COBOL Compiler Reference Manual for a full description of the Siemens BS2000 COBOL syntax.
This chapter is organized in the same order as the Language Reference, which differs from the order of presentation in the Siemens documentation.
A comment line may appear anywhere in the compilation group.
The level number 01 may begin in either area A or area B.
The special registers SORT-CORE-SIZE, SORT-FILE-SIZE, SORT-MODE-SIZE, SORT-RETURN and TALLY are supported as described in the Language Reference. The special register RETURN-CODE is also supported, but it has the description PIC S9(8) COMP-5 SYNC.
Nonnumeric literals may be from 1 to 180 characters in length.
Floating-point literals are supported as described in the Language Reference.
A function-identifier that references an integer or numeric function can be used as the source of a MOVE statement, as well as in an arithmetic expression.
| Decimal digits in the PICTURE clause |
Bytes required in computer storage |
Alignment |
| 1-4 5-9 10-18 |
2 4 8 |
halfword fullword fullword |
The line sequential file organization is supported as described in the Language Reference. This support is consistent with the X/Open Portability Guide.
A subscript may be an arithmetic expression that has the value of a positive integer.
As specified in the standard, the value of an index should correspond to a valid occurrence number of the associated table. This compiler also permits corresponding occurrence numbers for 0, negative numbers, and values beyond the maximum permissible occurrence number, but the binary value of the index must remain within the range that is representable in 4 bytes, i.e. -2 ** 31 to 2 ** 31 -1. In these cases, the index must be set to a valid occurrence number before it is used (e.g. with SET UP or SET DOWN), or relative indexing must be used to ensure that only valid table elements are addressed.
The following additional format of the Identification Division header is supported:
ID DIVISION.
The paragraphs of the Identification Division can be written in any order.
ARGUMENT-NAME, ARGUMENT-VALUE, ENVIRONMENT-NAME and ENVIRONMENT-VALUE may be specified in the Special-Names paragraph for use in ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements. Their use is consistent with the X/Open Portability Guide and the MERANT Micro Focus implementation.
An implementor-name is a system-name and must be a name from the left column of the following table. The implementor-names and their meanings are:
| Implementor-name | Meaning |
| COMPILER-INFO | used in ACCEPT statement |
| CONSOLE | System or main console or subconsole; used in ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements |
| CPU-TIME | used in ACCEPT statement |
| DATE-ISO4 | used in ACCEPT statement |
| JV_jobvariable-name | used in ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements |
| PRINTER | System logical printer; used in DISPLAY statement |
| PRINTER01 ... PRINTER99 |
treated as PRINTER-1 |
| PROCESS-INFO | used in ACCEPT statement |
| SYSIPT SYSOPT |
treated as comment |
| TERMINAL | used in ACCEPT and DISPLAY statements; same as CONSOLE |
| TERMINAL-INFO | used in ACCEPT statement |
| TSW-0 ... TSW-31 | task switches, used in SET statement and in compares |
| USW-0 ... USW-31 | user switches, used in SET statement and in compares |
The mnemonic-name can be the same as the implementor-name. For example:
TERMINAL IS TERMINAL
JV_jobvariable-name, TSW-n, and USW-n only work when the BS/2000 add-on is present to provide the necessary run-time support.
For all file organizations, the data-name-1 phrase in the ASSIGN clause is supported as described in the Language Reference.
For all file organizations, a second data-name may be specified in the FILE STATUS clause, but it is treated as commentary only.
The LINE SEQUENTIAL phrase is supported in the ORGANIZATION clause as described in the Language Reference.
The RECORDING MODE clause may be specified as documented in the Language Reference. The S phrase is not permitted.
Data-name-1 may be specified in the LABEL RECORDS clause as documented in the Language Reference.
The RECORDING MODE clause is permitted, however, there is no need for it since the compiler can determine the information from the associated record descriptions.
The LABEL RECORDS clause may be specified.
The following clause is accepted in level-01 entries in the Working-Storage Section:
IS DYNAMIC
In an OCCURS clause with the DEPENDING phrase, the lower bound (integer-1) may be omitted.
External floating-point data items are supported as described in the Language Reference
Data-name-2 may qualified, however, the qualification is ignored since the required placement of the REDEFINES clause determines the item that is redefined.
The SYNCHRONIZED clause may be specified on a group item. The clause applies to the items subordinate to that group.
The SYNCHRONIZED clause may be specified for a data item whose usage is index, in addition to the usages allowed by the standard.
The additional usages COMPUTATIONAL-1 (COMP-1), COMPUTATIONAL-2 (COMP-2) and COMPUTATIONAL-3 (COMP-3) are supported as described in the Language Reference.
The additional usage COMPUTATIONAL-5 (COMP-5) is described in Representation of Numeric Items in this document.
The WHEN SET TO FALSE phrase is supported, as described in the Language Reference.
The VALUE clause may be used to initialize the elements of a table.
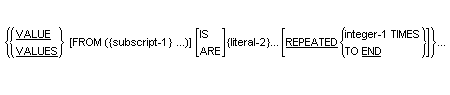
The number of table elements to be initialized must not exceed the maximum number of occurrences in the table from the point of reference to the end of the table.
If the TO END phrase is specified, this reuse occurs until the end of the table is reached.
If the integer-1 TIMES phrase is specified, the occurrences of literal-2 are reused, in the order specified, integer-1 times.
If the REPEATED phrase is not specified, the occurrences of literal-2 are used, in the order specified, only once.
If the category of the item is numeric, all literals in the VALUE clause must be numeric. The literal is aligned in the data item according to the standard alignment rules.
If the category of the item is alphabetic or alphanumeric, all literals in the VALUE clause must be nonnumeric literals. The literal is aligned in the data item as if the data item had been described as alphanumeric.
Initialization is not affected by any BLANK WHEN ZERO or JUSTIFIED clause that was specified.
The identifier in the class condition can be of usage COMPUTATIONAL-3, as well as the usages DISPLAY and PACKED-DECIMAL that are allowed by the standard.
In addition to the intrinsic functions specified in the standard, the following intrinsic functions are supported: ADDR, DATE-TO-YYYYMMDD, DAY-TO-YYYYDDD, and YEAR-TO-YYYY. The ADDR function is described below. The other intrinsic functions are described in the Language Reference.
The ADDR function returns an integer representing the address of argument-1. The type of this function is integer
FUNCTION ADDR (argument-1)
Mnemonic-names associated with the implementor-names ARGUMENT-NUMBER, ARGUMENT-VALUE, ENVIRONMENT-NAME and ENVIRONMENT-VALUE are supported as described in the Language Reference.
Mnemonic-name may be associated with one of the following implementor-names: COMPILER-INFO, CONSOLE, CPU-TIME, DATE-ISO4, job-variable-name (BS2000 job variable), PROCESS-INFO, SYSIPT, TERMINAL or TERMINAL-INFO.
Job-variable-names only work when the BS/2000 add-on is present to provide the necessary run-time support.
SYSIPT, TERMINAL, or CONSOLE specifies the system file from which data is to be read. SYSIPT refers to the system file of that name. TERMINAL refers to the system file SYSDTA (normally assigned to the data terminal). CONSOLE refers to the system console.
When a mnemonic-name is associated with a job-variable-name, it references the associated operating system job variable which is to be read in. If the job variable cannot be read in for some reason, the runtime system issues an error message, and the program is then either continued or aborted, as determined by a compiler directive. In the former case, /* is assumed as the value of identifier.
When mnemonic-name is associated with COMPILER-INFO, CPU-TIME, PROCESS-INFO, or TERMINAL-INFO, it specifies the information which is to be requested. COMPILER-INFO refers to information provided by the compiler. CPU-TIME, PROCESS-INFO, TERMINAL-INFO and DATE-ISO4 refer to information provided by the operating system.
CPU-TIME is moved in accordance with the rules of the MOVE statement from a field with the description PIC 9(6)V9(4).
Identifiers in the USING phrase may be groups or elementary items and may have any level number except 88.
BY VALUE identifier may be specified in the USING phrase. Additional details are specified in the Language Reference.
BY CONTENT literal may be specified in the USING phrase. Additional details are specified in the Language Reference.
The REEL and UNIT phrases are treated as commentary.
The only optional phrase permitted for a line sequential file is the WITH LOCK phrase.
Mnemonic-names associated with the implementor-names ARGUMENT-NUMBER, ENVIRONMENT-NAME and ENVIRONMENT-VALUE are supported as described in the Language Reference.
Mnemonic-name may be associated with one of the following implementor-names: CONSOLE, PRINTER, PRINTER01 - PRINTER99, SYSOPT, TERMINAL, job-variable-name (BS2000 job variable).
Job-variable-names only work when the BS/2000 add-on is present to provide the necessary run-time support.
A mnemonic-name associated with CONSOLE, SYSOPT or TERMINAL specifies that the data is to be written to the system operator console.
A mnemonic-name associated with PRINTER or PRINTER01 - PRINTER99 specifies that the data is to be written to the printer.
A mnemonic-name associated with a job-variable-name references a job variable which has a maximum record length of 256 characters. If the total number of characters in the sending operands exceeds the maximum record length, the record will be truncated to the maximum length.
The ENTRY statement is supported as documented in the Language Reference.
Partial expressions are supported in the WHEN and ALSO phrases of the EVALUATE statement as described in the Language Reference.
The EXIT PERFORM statement makes it possible to branch to the end of the PERFORM statement or to a repetition of the loop from an in-line PERFORM statement.
EXIT [TO TEST OF] PERFORM
The GOBACK statement is supported as documented in the Language Reference.
Identifier-3 ... identifier-n may reference a group item, as well as the elementary items allowed by the standard.
The optional word KEY in the ASCENDING or DESCENDING phrase may be replaced by the word KEY-YY. When KEY-YY is specified, the behavior of the MERGE statement is not changed.
Multiple receiving identifiers may be specified in a MOVE statement with the CORRESPONDING phrase.
For line sequential files, the only permissible open modes are INPUT and OUTPUT; and the REVERSED and NO REWIND phrases must not be specified.
The NO LOCK phrase may be specified in both formats of the READ statement. The effect of the NO LOCK phrase is described in the Language Reference. The placement of the phrase differs from the placement in the MF dialect, here the NO LOCK phrase immediately follows the file-name.
In a format 1 READ statement in which the AT END phrase or the NOT AT END phrase is specified, the NEXT phrase is implied and may be omitted.
The REWRITE statement is not permitted for line sequential files.
The key (data-name-1 or data-name-2) in a format 2 SEARCH statement (SEARCH ALL) may be specified on either the right hand side or the left hand side of the equality operator in the WHEN phrase. This is shown in the general format of the Language Reference as an OSVS extension.
The FALSE phrase is supported in a format 2 SET statement, as specified in the Language Reference.
The value of an index-name after the execution of a format 5 or format 6 SET statement need not be a valid occurrence number in the corresponding table, but must be within the range of permissible values for the index as specified in Subscripts earlier in this chapter.
Format 2 of the SORT statement (table sort) is supported. Most of the details are given in the Language Reference. Additional details are contained in this section.
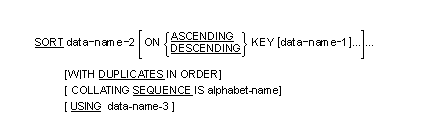
In both formats 1 and 2 of the SORT statement, the optional word KEY in the ASCENDING or DESCENDING phrase may be replaced by the word KEY-YY. When KEY-YY is specified, the behavior of the SORT statement is not changed.
The NO LOCK phrase may be specified immediatly after START file-name, but is treated as a comment.
The relational operators LESS, LESS OR EQUAL, NOT GREATER and their equivalents are supported as specified in the Language Reference.
As in the Micro Focus dialect, the following extension is supported:
The DELIMITED phrase may be omitted only immediately preceding the INTO phrase. If it is omitted, DELIMITED BY SIZE is implied.
A PERFORM statement within a declarative procedure may reference a nondeclarative procedure, as well as a declarative procedure.
Formats 2 and 3 are supported as specified in the Language Reference.
The identifier in the ADVANCING phrase of the WRITE statement may be an elementary one-character nonnumeric item, as well as an elementary integer data item. If a nonnumeric item is specified, the ADVANCING phrase is treated as a comment.
The SUPPRESS phrase of the COPY statement is supported as described in the Language Reference.
COPY statements may be nested as described in the Language Reference.
Copyright © 2000 MERANT International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.
 | Data General Interactive COBOL V1.3 Syntax Support |