 | Database Integrity | Advanced Operation |  |
Fileshare provides security features which enable you to restrict access to a Fileshare Server. You can also restrict access to specific data files under the control of a Fileshare Server. These restrictions are implemented via:
Note: In Mainframe Express, Fileshare is only supported for use by the components of Mainframe Express. Therefore some of the following information about writing applications that use Fileshare is not relevant to Mainframe Express users.
If you invoke the Fileshare Server with the Password System enabled, all Fileshare Clients must supply a valid user-ID and password before they can connect to the Fileshare Server. By default, the Fileshare Password System is not enabled when you invoke the Fileshare Server.
If you want to use the Fileshare Password System you must code your program to pass a user-ID and password to the File Handling Redirector module and you must create a password file on the Fileshare Server machine which contains the user-ID and password that your program will use.
Then, to enable the Fileshare Password System, you must use the
/pf option to specify the name
of the password file to the Fileshare Server.
With the Fileshare Password System enabled, the sequence of steps that your program and Fileshare follow is: (see Figure 5-1)
Each of these steps is explained in more detail in the sections that follow.
When Fileshare security is active, your program must supply a user-ID and a password before the first I/O operation is performed.
Even if you have not activated security, your program can still supply the Fileshare Client with a user-ID and password. This enables your program to run unchanged on Fileshare whether or not security is activated.
To register a user-ID and password, your program must call the module FHRdrPwd as follows:
call "fhrdrpwd" using function-code,
user-ID,
user-password
end-call
where the parameters are:
01 function-code pic x comp-x. 01 user-ID pic x(20). 01 user-password pic x(20).
The function code to register a user-ID and password is 1.
The following example shows how to register a user-ID and password:
working-storage section.
01 function-code pic x comp-x.
01 user-name pic x(20).
01 user-password pic x(20).
...
procedure division.
...
move 1 to function-code
move "UserID" to user-name
move "Password" to user-password
call "fhrdrpwd" using function-code,
user-name,
user-password
end-call
...
open output testfile
...
You can substitute the FHRdrPwd module supplied with the Fileshare System with your own. This enables you to retrieve the user-ID and password from somewhere other than the application program. See the section Writing Your Own FHRdrPwd Module for further details.
By default, the Fileshare Password System is not active when you invoke
the Fileshare Server. If you want password security activated, use the
/pf (Password File) option in
the Fileshare Server configuration file, for example:
Windows:
/pf password.fil
/s server1
UNIX:
-pf password.fil
-s server1
specifies that for the Fileshare Server, server1,
Fileshare Password Security is enabled and the password file is password.fil.
The Fileshare Server uses this file to determine whether a Fileshare
Client is allowed to connect to this Fileshare Server.
The Password File Maintenance Utility is used to create the password file and add user-ID and password entries. See the section Password File Maintenance for further information on this utility.
To register a user-ID and password, your program must call the File Handling Redirector password module supplying a user-ID and password. If you do not want to hard-code this call into your program, you can replace the supplied File Handling Redirector password module with one that obtains the user-ID and password using a different method (for example, via a screen prompt). Your new module must still conform to the File Handling Redirector password module interface, that is:
| Function Code
|
Action |
|---|---|
| = 1: | Register the supplied user-ID and password |
| = 0: | Return the user-ID and password. The File Handling Redirector module uses this call to obtain the user-ID and password when it is about to connect to the Fileshare Server. |
Compile your new File Handling Redirector password module to a .gnt file, then:
Create an object module and link it into any application executable as required.
If you have not activated the Fileshare Password System, the Fileshare Server validates requests to log on by calling the Fileshare Security Logon validation module (FSSecLog).
The FSSecLog module supplied with Fileshare allows any Fileshare Client to log on to a Fileshare Server. If you need to restrict the Fileshare Clients that can log on to a Fileshare Server, you must provide your own, alternative, FSSecLog module for the Fileshare Server to call.
For example, your own module can enable integration with the native operating system security, if this is needed.
The sequence of steps that your program and Fileshare follow is (see Figure 5-2):
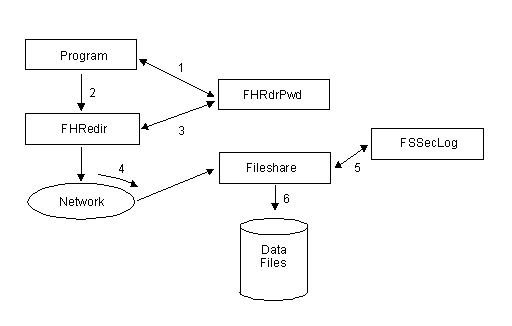
Figure 5-2: Logon Validation Module
To validate a request to log on from a Fileshare Client, the Fileshare Server calls the module FSSecLog (the Fileshare Security at Logon Validation module) to validate the user-ID and password. You can replace FSSecLog with your own module in order to use your own criteria for validating the log on request. Your new module must comply with the FSSecLog interface described below.
call "fsseclog" using user-ID
password
return-status
user-ID
password
return-status |
pic x(20).
pic x(20). pic x comp-x. |
user-ID |
The Fileshare Client's user-ID |
password |
The Fileshare Client's password |
user-ID |
Unchanged |
password |
Unchanged |
return-status |
Set to 0 if the Fileshare Client is allowed to log onto the Fileshare Server. Any other status indicates the Fileshare Client is not allowed to log on and an error is returned to the Fileshare Client. |
Windows:
You can create your own fsseclog module
and link it into the Fileshare Server. See the
section Linking
the Fileshare Server on Windows in the chapter Advanced
Operation for further details.
UNIX:
You can create your own fsseclog module
in generated code format and replace the one supplied in your COBOL system
directory.
Whenever a Fileshare Server receives an open request on a file from a Fileshare Client, the Fileshare Server calls the Fileshare Security at Open validation module (FSSecOpn).
The Fileshare Security at Open Validation module supplied with Fileshare allows any Fileshare Client to access a data file. If you need to restrict access to specific files, you must provide your own, alternative, Fileshare Security at Open Validation module for the Fileshare Server to call.
If the Fileshare Security at Open Validation module allows the file access, the operation is allowed to complete. If the module does not allow the file access, a file status of 9/037 "access denied" is returned to the Fileshare Client and the operation is not allowed to complete.
Note: This file access security check is entirely independent of the Fileshare Password System and the User Supplied Logon Validation Module.
The sequence of steps that your program and Fileshare follow are:
To validate an open request from a Fileshare Client, the Fileshare Server calls the Fileshare Security at Open Validation module (FSSecOpn).
You can replace the supplied Fileshare Security at Open Validation module with one of your own in order to use your own criteria for validating the open request. Your new module must comply with the Fileshare Security at Open Validation module's interface described below:
call "fssecopn" using filename
filename-length
operation-code
user-ID
return-status
filename |
pic x(n). |
filename-length |
pic x(2) comp-x. |
operation-code |
pic x(2) comp-x. |
user-ID |
pic x(20). |
return-status |
pic x comp-x. |
filename |
The name of the data file that the Fileshare Client wants to open |
filename-length
|
The length of filename |
operation-code |
The operation code specifying the I/O operation. These codes are those used by the Callable File Handler. See your Net Express online help for details on the Callable File Handler. |
user-ID |
The user-ID of the Fileshare Client making the open request |
return-status |
Set to 0 if the open request is allowed. Any other status indicates that the Fileshare Client is not allowed to open the data file and an error status is returned. |
Windows:
You can create your own fssecopn module
and link it into the Fileshare Server. See the
section Linking the Fileshare Server on Windows
in the chapter Advanced Operation for further details.
UNIX:
You can create your own fssecopn module
in generated code format and replace the one supplied in your COBOL system
directory.
The password file contains details of user-IDs and passwords that the Fileshare Server uses when Fileshare Password Security is enabled. Because the information in the password file is encrypted for security reasons, you can only add records to and remove records from the password file using the Password File Maintenance Utility.
Notes:
Use the /pf (password file)
option to add or remove entries in the password file, for example:
fs /pf pass.dat [options]
This invokes password file maintenance and appends the specified options to the password file pass.dat. If this file does not exist, it is created.
The following options are available:
/u user-ID /pw password
This adds the specified user-ID and password to the password file. Both user-ID and password are case-sensitive and can be up to 20 characters in length.
[/e]
This erases the record from the password file and is the only way to remove a record once the password file has been created.
Example
fs /pf pass.dat /u pkel /pw fishwife
This example invokes password file maintenance, creates or updates a password file called pass.dat and adds a user-ID of pkel and password of fishwife.
In order to use the password-restricted functions of Fileshare Manager, a supervisor password must be defined (see the section Fileshare Manager in the chapter Advanced Operation).
To define a supervisor password, an entry must be made in the password file using the reserved user-ID, FSVIEW. Note that the user-ID FSVIEW must be entered in upper case.
If you are already using Fileshare Password Security, simply add the FSVIEW entry to your existing file.
If you are not using Fileshare Password Security, you can create a password file that contains a single entry, the FSVIEW user-ID. This defines a supervisor password without enabling Fileshare Password Security.
Example
The following example defines a supervisor password of "abracadabra" in the password file password.fil. If the file does not exist, it is created.
fs /pf password.fil /u FSVIEW /pw abracadabra
Once you have defined a supervisor password, you must specify the password file, either in the Fileshare Server configuration file, or on the command line when the Fileshare Server is started.
Note: If FSVIEW is the only entry in the password file, the Fileshare Server displays a message indicating that Fileshare Password Security is disabled, even though a password file has been specified.
Copyright © 1999 MERANT International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.
 | Database Integrity | Advanced Operation |  |