Subscripting
Subscripts can be used only when reference is made to an individual element within a list or table of like elements that have not been assigned individual data-names (see the topic The OCCURS Clause).
The subscript can be represented either by a numeric literal that is an integer, by a data-name, or by a data-name followed by the operator "+" or "-" , followed by an unsigned integer numeric literal. The data-name must be a numeric elementary item that represents an integer, and the whole subscript must be delimited by the balanced pair of separators, left-parenthesis and right-parenthesis.
The subscript data-name can be signed and, if signed, must be positive. The lowest possible subscript value is 1. This value points to the first element of the table. The next sequential elements of the table are pointed to by subscripts whose values are 2, 3, ... . The highest permissible subscript value, in any particular case, is the maximum number of occurrences of the item as specified in the OCCURS clause.
The subscript, or set of subscripts, that identifies the table element is delimited by the balanced pair of separators, left parenthesis and right parenthesis following the table element data-name. The table element data-name appended with a subscript is called a subscripted data-name or an identifier. When more than one subscript is required, they are written in the order of successively less inclusive dimensions of the data organization. Up to 3 subscripts are permitted.
![]() Up to 7 subscripts are permitted.
Up to 7 subscripts are permitted.
![]() Up to 16 subscripts are permitted.
Up to 16 subscripts are permitted.
General Format
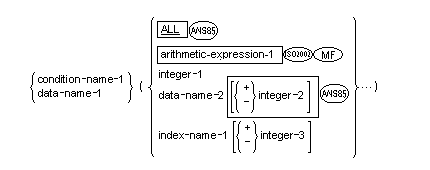
Syntax Rules
- The data description entry containing data-name-1 or the data-name associated with condition-name-1 must contain an OCCURS clause or must be subordinate to a data description entry which contains an OCCURS clause.
- Except as defined in Syntax Rule 7, when a reference is made to a table element, the number of subscripts must equal the number of OCCURS clauses in the description of the table element being referenced. When more than one subscript is required, the subscripts are written in the order of successively less inclusive dimensions of the table.
 The subscript ALL can be used only when the subscripted identifier is used as a function argument and cannot be used when
condition-name-1 is specified. (See the topic
Arguments.)
The subscript ALL can be used only when the subscripted identifier is used as a function argument and cannot be used when
condition-name-1 is specified. (See the topic
Arguments.)
- Integer-1 can be signed, and if signed, must be positive.
- Data-name-2 can be qualified and must be a numeric elementary item representing an integer.
- Index-name-1 must correspond to a data description entry in the hierarchy of the table being referenced which contains an
INDEXED BY phrase specifying that index-name.

 An index described for some other table can be used instead, provided the two tables have elements of the same size.
An index described for some other table can be used instead, provided the two tables have elements of the same size.
- Each table element reference must be subscripted except when such reference appears:
- In a USE FOR DEBUGGING statement
- As the subject of a SEARCH or SORT statement
- In a REDEFINES clause
- In the KEY IS phrase of an OCCURS clause.
-
 The mixing of subscripts and indices in the same identifier is illegal.
The mixing of subscripts and indices in the same identifier is illegal.
 The mixing of subscripts and indices in the same identifier is legal.
The mixing of subscripts and indices in the same identifier is legal.
General Rules
- The value of the subscript must be a positive integer. The lowest possible occurrence number represented by a subscript is
1. The first element of any given dimension of a table is referenced by an occurrence number of 1. Each successive element
within that dimension of the table is referenced by occurrence numbers of 2, 3, ... . The highest permissible occurrence number
for any given dimension of the table is the maximum number of occurrences of the item specified in the associated OCCURS clause.
 If the subscript is a floating-point data item, the value is rounded to the nearest integer, otherwise any fractional part
is truncated.
If the subscript is a floating-point data item, the value is rounded to the nearest integer, otherwise any fractional part
is truncated.
If arithmetic-expression-1 is specified, and the final result of the arithmetic expression is not an integer, the final result is truncated. Intermediate results are not truncated.
If arithmetic-expression-1 is specified, and if the final result or any intermediate result of the arithmetic expression is negative, the effect is unpredictable.
- The value of the index referenced by index-name-1 corresponds to the occurrence number of an element in the associated table.
- The value of the index referenced by index-name-1 must be initialized before it is used as a subscript. An index can be given an initial value by either a PERFORM statement with the VARYING phrase, a SEARCH statement with the ALL phrase, or a SET statement. An index can be modified only by the PERFORM, SEARCH, and SET statements.
- If
 integer-2 or
integer-2 or
integer-3 is specified, the value of the subscript is determined by incrementing by the value of
 integer-2 or
integer-2 or
integer-3 (when the operator "+" is used) or by decrementing by the value of
 integer-2 or
integer-2 or
integer-3 (when the operator "-" is used),
 either
either
the occurrence number represented by the value of the index referenced by index-name-1
 or the value of the data item referenced by data-name-2
or the value of the data item referenced by data-name-2
.
Comments: