Scan settings: General
To access this feature, click the Edit menu and select Default Scan Settings or Current Scan Settings. Then, in the Scan Settings category, select General.
Scan details
The Scan Details options are described in the following table.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Path Truncation |
Path truncation attacks are requests for known directories without file names. This may cause directory listings to be displayed. OpenText DAST truncates paths, looking for directory listings or unusual errors within each truncation. Example: If a link consists of http://www.site.com/folder1/folder2/file.asp, then truncating the path to look for http://www.site.com/folder1/folder2/ and http://www.site.com/folder1/ may cause the server to reveal directory contents or may cause unhandled exceptions. |
|
Case-sensitive request and response handling |
Select this option if the server at the target site is case-sensitive to URLs. |
| Recalculate correlation data | This option is used only for comparing scans. The setting should be changed only upon the advice of Customer Support personnel. |
|
Compress response data |
If you select this option, OpenText DAST saves disk space by storing each HTTP response in a compressed format in the database. |
| Enable Traffic Monitor Logging | During a Basic Scan, OpenText DAST displays in the navigation pane only those sessions that reveal the hierarchical structure of the website plus those sessions in which a vulnerability was discovered. However, if you select the Traffic Monitor option, OpenText DAST adds the Traffic Monitor button to the Scan Info panel, allowing you to display and review every single HTTP request sent by OpenText DAST and the associated HTTP response received from the server. |
|
Encrypt Traffic Monitor File |
All sessions are normally recorded in the traffic monitor file as clear text. If you are concerned about storing sensitive information such as passwords on your computer, you can elect to encrypt the file. Encrypted files cannot be compressed. Selecting this option will significantly increase the size of exported scans containing log files. Note: The Traffic Viewer tool does not support the encryption of traffic files. The Encrypt Traffic Monitor File option is reserved for use under special circumstances with legacy traffic files only. |
|
Maximum crawl-audit recursion depth |
When an attack reveals a vulnerability, OpenText DAST crawls that session and follows any link that may be revealed. If that crawl and audit reveals a link to yet another resource, the depth level is incremented and the discovered resource is crawled and audited. This process can be repeated until no other links are found. However, to avoid the possibility of entering an endless loop, you may limit the number of recursions. The default value is 2. The maximum recursion level is 1,000. |
Crawl details
By default, OpenText DASTt uses breadth-first crawling, which begins at the root node and explores all the neighboring nodes (one level down). Then for each of those nearest nodes, it explores their unexplored neighbor nodes, and so on, until all resources are identified. The following illustration depicts the order in which linked pages are accessed using a breadth-first crawl. Node 1 has links to nodes 2, 3, and 4. Node 2 has links to nodes 5 and 6.
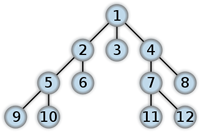
You cannot change this crawling method in the user interface. However, the configurable Crawl Details options are described in the following table.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable keyword search audit |
A keyword search, as its name implies, uses an attack engine that examines server responses and searches for certain text strings that typically indicate a vulnerability. Normally, this engine is not used during a crawl-only scan, but you can enable it by selecting this option. |
| Perform redundant page detection |
Highly dynamic sites could create an infinite number of resources (pages) that are virtually identical. If allowed to pursue each resource, OpenText DAST would never be able to finish the scan. This option compares page structure to determine the level of similarity, allowing OpenText DAST to identify and exclude processing of redundant resources. Important! Redundant page detection works in the crawl portion of the scan. If the audit introduces a session that would be redundant, the session will not be excluded from the scan. You can configure the following settings for redundant page detection:
|
| Limit maximum single URL hits to |
Sometimes, the configuration of a site will cause a crawl to loop endlessly through the same URL. Use this field to limit the number of times a single URL will be crawled. The default value is 5. |
| Include parameters in hit count |
If you select Limit maximum single URL hits to (above), a counter is incremented each time the same URL is encountered. However, if you also select Include parameters in hit count, then when parameters are appended to the URL specified in the HTTP request, the crawler will crawl that resource up to the single URL limit. Any differing set of parameters is treated as unique and has a separate count. For example, if this option is selected, then "page.aspx?a=1" and "page.apsx?b=1" will both be counted as unique resources (meaning that the crawler has found two pages). If this option is not selected, then "page1.aspx?a=1" and "page.aspx?b=1" will be treated as the same resource (meaning that the crawler has found the same page twice). Note: This setting applies to both GET and POST parameters. |
| Limit maximum directory hit count to | This setting defines the maximum number of sub-directories and pages to be traversed within each directory during the crawl. This setting reduces the scope of the crawl and might be useful in reducing scan times for some sites, such as those consisting of a content management system (CMS). The default setting is 200. |
| Minimum folder depth | If you select Limit maximum directory hit count to (above), this setting defines the folder depth at which the maximum directory hit count will begin to apply. The default setting is 1. |
| Limit maximum link traversal sequence to |
This option restricts the number of hyperlinks that can be sequentially accessed as OpenText DAST crawls the site. For example, if five resources are linked as follows
and if this option is set to "3," then Page E will not be crawled. The default value is 15. |
|
Limit maximum crawl folder depth to |
This option limits the number of directories that may be included in a single request. The default value is 15. For example, if the URL is http://www.mysite.com/Dir1/Dir2/Dir3/Dir4/Dir5/Dir6/Dir7 and this option is set to "4," then the contents of directories 5, 6, and 7 will not be crawled. |
|
Limit maximum crawl count to |
This feature restricts the number of HTTP requests sent by the crawler and should be used only if you experience problems completing a scan of a large site. Note: The limit set here does not directly correlate to the |
|
Normally, when OpenText DAST encounters a form that contains controls having multiple options (such as a list box), it extracts the first option value from the list and submits the form; it then extracts the second option value and resubmits the form, repeating this process until all option values in the list have been submitted. This ensures that all possible links will be followed. There are occasions, however, when submitting the complete list of values would be counterproductive. For example, if a list box named "State" contains one value for each of the 50 states in the United States, there is probably no need to submit 50 instances of the form. Use this setting to limit the total number of submissions that OpenText DAST will perform. The default value is 3. |
|
| Suppress Repeated Path Segments |
Many sites have text that resembles relative paths that become unusable URLs after OpenText DAST parses them and appends them to the URL being crawled. These occurrences can result in a runaway scan if paths are continuously appended, such as With the setting enabled, the options are: 1 – Detect a single sub-folder repeated anywhere in the URL and reject the URL if there is a match. For example, 2 – Detect two (or more) pairs of adjacent sub-folders and reject the URL if there is a match. For example, 3 – Detect two (or more) sets of three adjacent sub-folders and reject the URL if there is a match. 4 – Detect two (or more) sets of four adjacent sub-folders and reject the URL if there is a match. 5 – Detect two (or more) sets of five adjacent sub-folders and reject the URL if there is a match. If the setting is disabled, repeating sub-folders are not detected and no URLs are rejected due to matches. |
See also
Scan settings: Cookies/Headers
Scan settings: Custom Parameters