Overview of Debugging in Visual Studio Code
Debugging in Visual Studio Code requires that you create a launch configuration with the settings which the debugger requires to enable it to debug your COBOL code. This is how you debug your code with the default launch configuration:
- Open the folder that contains your sources in Visual Studio Code.
- Click (Run > Start Debugging).
This shows the Task Picker with the available debugging tasks:
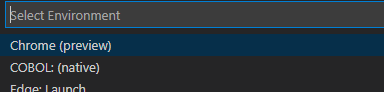
- Select
COBOL (native): (native) from the drop-down list. This is the default task provided with the
Micro Focus COBOL extension for debugging native COBOL applications.
This creates a launch.json file in a .vscode subfolder in the folder that holds your sources. By default, the launch.json contains two configurations - one for debugging a standalone application, and one for attaching the debugger to a running process:
"configurations": [ { "type": "cobol", "request": "launch", "name": "COBOL (native): Launch", "program": "${workspaceFolder}/<insert-program-name-here>", "cwd": "${workspaceFolder}", "stopOnEntry": true }, { "type": "cobol", "request": "attach", "name": "COBOL (native): Attach to process", "processId": "${command:pickProcess}" } ] }You can add more configurations to this file as required.
- In the Activity bar, click
 to open the Run panel.
to open the Run panel.
The two default launch configurations are listed in the Configuration drop-down within the Run panel:
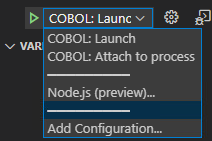
- Select the launch configuration,
COBOL (native): Launch, and click
 (Start Debugging).
(Start Debugging).
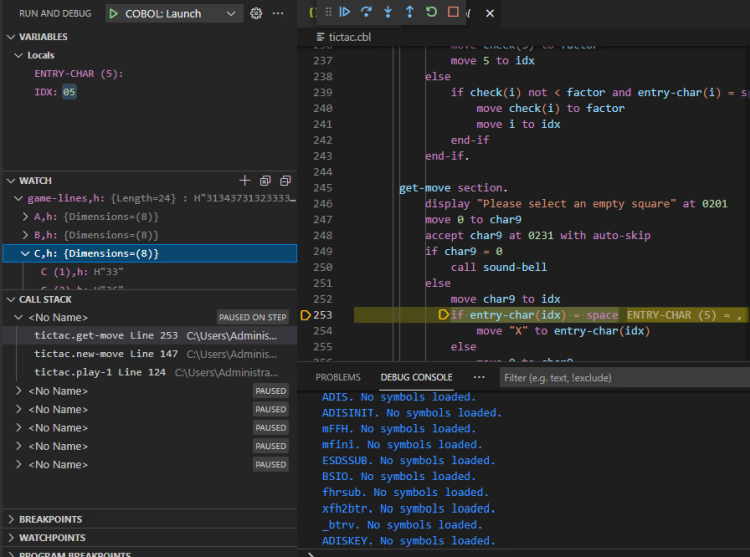
- Use the commands in the Debug widget to step through the code.

- Use the available views to watch how variables change.
- As you step through the code, the values of variables on the current line are shown inline in the editor, at the end of the
line:
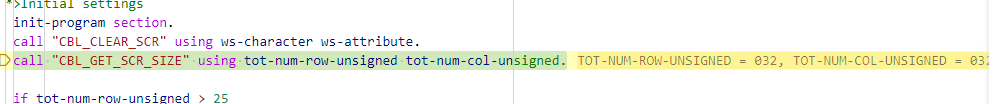
You can control whether to display the inline values with the Microsoft Debug: Inline Values setting of Visual Studio Code.
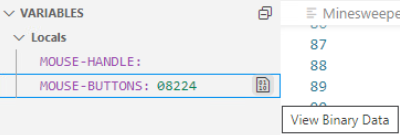
- In the VARIABLES panel, click the
View Binary Data icon on a row for a variable.
This opens a Memory window that enables you to view and edit data in the memory associated with the selected item.