APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Entity Content Report lists the following information for each component of an application.
You can produce a report for one type of component, or all types. If you include all types, the report provides a separate section for components by painter, with the painters arranged alphabetically.
This report helps you track the status of an evolving application. Use it to verify which components have been created and modified as planned.
CLSAPS.CLS2
SELECTION CRITERIA: ALL
CREATE DATE > 00/00/00
CREATE DATE < 99/99/99
SORTED BY: TYPE/NAME
********************************************************************************
CREATE UPDATE
TYPE NAME DATE DATE TITLE
---- ---- ------ ------ -----
APPL AEDEMO 10/20/89 02/16/90
APPL BCAPPL 11/07/90 11/07/90
APPL BFAPPL 11/07/90 11/07/90
.
.
CNIO PADEMO 08/13/90 08/15/90 CUSTOMER/ORDER MAIN MENU
CNIO PBDEMO 08/13/90 08/15/90 PARTS ORDER MAIN MENU
CNIO PCDEMO 08/13/90 08/15/90 CUSTOMER ORDER MAIN MENU
.
.
DATA APFIELDS 06/06/90 06/06/90 *** NOT AVAILABLE ***
DATA BATCH1 07/13/89 07/13/89 *** NOT AVAILABLE ***
DATA CONDATA 09/19/89 09/19/89 *** NOT AVAILABLE
.
REPORT CODE: MS02 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 4
CONTENT REPORT 06/17/92 15:26
CLSAPS.CLS2
SELECTION CRITERIA: ALL
CREATE DATE > 00/00/00
CREATE DATE < 99/99/99
SORTED BY: TYPE/NAME
********************************************************************************
CREATE UPDATE
TYPE NAME DATE DATE TITLE
---- -------- -------- -------- ----------------------------------------
PROG APP2 12/17/90 12/18/90
PROG EVOM 01/10/91 01/10/91
PROG EVPL 01/10/91 01/10/91
.
.
REPT COSTRPT 07/27/90 07/27/90 *** NOT AVAILABLE ***
REPT MERPT 08/24/90 08/24/90 *** NOT AVAILABLE ***
REPT T1RPT 07/27/90 07/27/90 *** NOT AVAILABLE ***
SCRN AAAAA 06/04/90 06/07/90 TEST SCREEN
SCRN DLMENU 03/29/90 03/29/90
.
.
APPLICATIONS: 45
SCENARIOS: 43
DATA-STRUCTURES: 27
PROGRAMS: 93
REPORTS: 3
SCREENS: 112APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Entity Cross Reference Report provides a list of application components and the painters where you create the components. Use this report for impact analysis, when you need to find the components affected by a proposed change. For example, when a data structure changes, that can affect components in a variety of applications and programs. This report can show at a glance all of the affected components that reference a particular data structure.
The report has a section for each cross-referenced component. The report arranges the associated components in alphabetical order, along with the type of each component and a description of it. The report ends with the total number of cross-referenced components.
Produce the Entity Cross Reference report from the Documentation Facility.
REPORT CODE: MD01 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 1
ENTITY CROSS REFERENCE 01/17/92 08:48
MKTAPS.MKT2
SELECTION CRITERIA: PROGRAM
ENTITY NAME = ADEMO
*********************************************************************************************
ENTITY: ADEMO CREATED: 09/17/90
TITLE: UPDATED: 09/18/90
*********************************************************************************************
ASSOCIATED ENTITY TYPE TITLE
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*** NO ASSOCIATED ENTITIES FOUND FOR THIS SELECTION ***
REPORT CODE: MD01 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 99
ENTITY CROSS REFERENCE 01/17/92 08:48
MKTAPS.MKT2
SELECTION CRITERIA: PROGRAM
ENTITY NAME = ALL
*********************************************************************************************
ENTITY: TDCM CREATED: 03/19/90
TITLE: UPDATED: 09/17/90
*********************************************************************************************
ASSOCIATED ENTITY TYPE TITLE
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MVS21 APSAPPL
TDDEMO APSAPPL
TDCM APSEXPS
REPORT CODE: MD01 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 100
ENTITY CROSS REFERENCE 01/17/92 08:48
MKTAPS.MKT2
SELECTION CRITERIA: PROGRAM
ENTITY NAME = ALL
*********************************************************************************************
ENTITY: TDCS CREATED: 04/26/90
TITLE: UPDATED: 08/24/90
*********************************************************************************************
ASSOCIATED ENTITY TYPE TITLE
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MVS21 APSAPPL
TDDEMO APSAPPL
TDCS APSEXPS
TOTAL NUMBER OF DEFINED PROGRAMS - 60
TOTAL NUMBER OF UNDEFINED PROGRAMS - 48APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Entity Parts List Report catalogs the components of one or more selected applications, data structures, programs, report mock-ups, screens, subschemas, user macros, APS macros, or COPYLIBs, down to the level of detail that you specify. The report categorizes information based on how it is used in the APS generation process. You can report on:
Together these items provide a record of the complete progression of your application from APS entity definitions to code.
REPORT CODE: EN01 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 1
ENTITY PARTS LIST 92/07/23 12:18
CTSAPS.TEST
ENTITY TYPE: APSAPPL
ENTITY NAME: *
APPLICATION:
EXPLOSION LIMIT:
USE TYPES: SOURCE
APSAPPL (DEMOAPPL) 92/07/23 12:17
APSPROG (DEMOPG1 ) 92/07/23 11:55
APSDATA (DEMODS1 ) 92/07/23 12:08
APSSCRN (DEMOSC1 ) 92/07/23 11:57
DDISYMB (DEMOPSB ) 92/05/15 15:20
COPYLIB (D2MASTER)
COPYLIB (D2STOCK )
USERMACS(DEMOUS1 ) 92/07/23 12:11
USERMACS(DEMOUS5 ) 92/07/23 12:14
APSPROG (DEMOPG2 ) 92/07/23 11:56
APSDATA (DEMODS2 ) 92/07/23 12:08
APSSCRN (DEMOSC2 ) 92/07/23 12:05
DDISYMB (DEMOPSB ) 92/05/15 15:20
COPYLIB (D2MASTER)
COPYLIB (D2STOCK )
USERMACS(DEMOUS2 ) 92/07/23 12:13
USERMACS(DEMOUS6 ) 92/07/23 12:15
APSPROG (DEMOPG3 ) 92/07/23 11:56
APSDATA (DEMODS3 ) 92/07/23 12:08
APSSCRN (DEMOSC3 ) 92/07/23 12:06
DDISYMB (DEMOPSB ) 92/05/15 15:20
COPYLIB (D2MASTER)
COPYLIB (D2STOCK )
USERMACS(DEMOUS3 ) 92/07/23 12:14
USERMACS(DEMOUS7 ) 92/07/23 12:15
APSPROG (DEMOPG4 ) 92/07/23 11:57
APSDATA (DEMODS4 ) 92/07/23 12:09
APSSCRN (DEMOSC4 ) 92/07/23 12:07
DDISYMB (DEMOPSB ) 92/05/15 15:20
COPYLIB (D2MASTER)
COPYLIB (D2STOCK )
USERMACS(DEMOUS4 ) 92/07/23 12:13
USERMACS(DEMOUS8 ) 92/07/23 12:16
1 TARGET WAS LISTED.APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Entity Search Utility Report lets you use search expressions to report on subsets of application data that meet the requirements that you specify. A search expression can be either a literal text string or a regular expression that lets you search for a certain criteria, such as all occurrences of certain data name strings in a group of data structures.
When you generate this report, you specify the level of detail that you want to report on. The available levels depend in part on the type of data that you select for the report.
| Metacharacter |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
. |
Match any value you seek. For example, DATA... matches such values as DATA-TY or DATASTR. |
||
|
" " |
Delimit spaces in an expression. For example, "% DEFINE." or '% DEFINE.' match % DEFINE and % DEFINED. |
||
|
( ) |
In a pair, specify a group that can be a range (such as A-Z) or a list (such as ABCD). Within a group, use only the following metacharacters. |
||
|
|
() |
Specify the first character in a group. |
|
|
|
Specify a range within a group. |
||
|
|
\ |
Represent a metacharacter as itself. |
|
|
* |
Match zero or
more occurrences of the single character or character group immediately
preceding the *. For example, PROG*1 matches PRO1, PROG1, and PROGGG1 but not
PR1, because the characters PRO must be part of the match. The quoted * simply
represents itself.
|
||
|
+ |
Match one or more occurrences of the single character or character group immediately preceding the +. The example is the same as the prior case, but there must be at least one match. The quoted + simply represents itself.
|
||
|
? |
Match zero or one occurrences of the single character or character group immediately preceding this metacharacter. The example is the same as the prior case, but there can be at most one match. The quoted ? simply represents itself.
|
||
|
^ |
In the first position, represent a logical not, and select data that does not specify the specified criteria. In the first position of an expression, it matches the rest of any expression. In any other position, it represents itself.
|
||
|
$ |
Specify the preceding character or group of characters if the metacharacter appears in the last position of the expression and the match appears at the end of the line. For example, WS-CNT$ matches ADD WS-CNT TO WS-TOT.
|
||
|
\ |
Indicate that the single metacharacter immediately following the \ is an ordinary text character rather than a metacharacter. For example, [A-Z\^] matches the character range A through Z and the ^ character.
|
||
REPORT CODE: GS01 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 1
ENTITY SEARCH UTILITY 92/07/10 02:06
APS.TEST
APPLICATION:
ENTITY: USERMACS
MEMBER: A1UTTREE
EXPLOSION LIMIT:
USE TYPES:
SEARCH EXPRESSIONS:
r:"% *DEFINE "
r:"% *END "
R:"% *IF"
R:"% *ELSE"
APPL ENTITY TYPE ENTITY NAME LINE
....+....1....+....2....+....3....+....4....+....5....+....6....+....7....+..
USERMACS A1UTTREE 1 0019 %DEFINE $TREE-DEFINE(
3 0030 %IF &TREE = ""
3 0032 %IF &LENGTH(&TREE) > 6
3 0036 %IF &DEFINED(&A1UTTREE-<&TREE>-DEFINED)
3 0041 %IF &POINTER-SIZE = "HALF"
4 0044 %ELSE-IF &POINTER-SIZE = "FULL"
4 0047 %ELSE
3 0050 %IF &ALLOC-PARA NOT = ""
3 0053 %IF &DEBUG = 0
4 0055 %ELSE
3 0061 %IF NOT &DEFINED(&A1UTTREE-WORK-AREA)
3 0068 %IF &WS = "LINKAGE"
2 0115 %END
1 0122 %DEFINE $TREE-CLEAR(
3 0126 %IF &TREE = ""
2 0137 %END
1 0147 %DEFINE $TREE-ADD(
3 0158 %IF &TREE = ""
3 0163 %IF &NODEX = ""
4 0165 %ELSE-IF &INDEX( &NODEX, "(" )
3 0168 %IF &PREVX = ""
4 0170 %ELSE-IF &INDEX( &PREVX, "(" ) APS-generated report (see Application Reports
The Entity Use Report lists components that use the target component, as in a COPY or INCLUDE statement. For example, you can get a list of components that use a certain subschema.
When you generate this report, you specify the level of detail that you want to report on. The available levels depend in part on the type of data that you select for the report.
REPORT CODE: EN02 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 1
ENTITY USE REPORT 02/06/21 14:02
APS.MVS21DEV
TARGET: USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APPLICATION:
EXPLOSION LIMIT:
USE TYPE SELECTIONS:
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2CNFIG8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2NDMGD8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2NDMGU8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2RECGU8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2RECV8)
APSPROG (A2RECGU8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2RECV8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2SEND8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSLINK8)
APSPROG (A2SENGD8)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)
APSAPPL (APSPC)
APSPROG (APSNA)
USERMACS(ISPFMACS)
USERMACS(ISPFCOMM)
USERMACS(ISPFUSER)S-COBOL structure (see S-COBOL Structures)
Establish an entry point in a COBOL subprogram.
ENTRY literal . . . [USING identifier1, ..., identifierN]
Test for any Exceptional condition in the CICS environment.
APS generates a CICS IGNORE CONDITION command that ignores all CICS Exceptional conditions, and generates an 88-level EIBRCODE structure.
The APS/CICS default for inline error checking is to generate a global CICS IGNORE condition. You can generate a NOHANDLE on a call-by-call basis. Flags for both are in the APS CNTL file APCICSIN.
Test for the MAPFAIL condition and perform a user-defined paragraph to handle it.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
NTRY
IF MAPFAIL
PERFORM MAPFAIL-PARAThe variable that controls generation of the EIBRCODE structure is &CIC-APS-EIBRCODE, which resides in APCICSIN. The following is the APS-generated EIBRCODE structure, which resides in APCICSTP.
01 APS-EIBFN-EIBRCODE.
05 APS-EIBFN PIC X(01).
05 APS-EIBRCODE PIC X(06).
01 FILLER REDEFINES
APS-EIBFN-EIBRCODE.
05 APS-EIBFN-EIBRCODE-X PIC S9(04) COMP.
88 CBIDERR VALUE +1259.
88 DISABLED VALUE +1549.
88 DSIDERR VALUE +1537.
88 DSSTAT VALUE +7684.
88 DUPKEY VALUE +1668.
88 DUPREC VALUE +1666.
88 ENDDATA VALUE +4097.
88 ENDFILE VALUE +1551.
88 ENDINPT VALUE +1218.
88 ENQBUSY VALUE +4658.
88 ENVDEFERR VALUE +4329.
88 EODS VALUE +1040.
88 EOF VALUE +1028
+1217.
88 EXPIRED VALUE +4128.
88 FUNCERR VALUE +7688.
88 IGREQCD VALUE +1258.
88 ILLOGIC VALUE +1538.
88 INVERRTERM VALUE +6176.
88 INVMPSZ VALUE +6152.
88 INVREQ VALUE +736
+1248
+1544
+2592
+3808
+4351
+4832
+5122
+6145
+6880.
88 INVTSREQ VALUE +4116.
88 IOERR VALUE +1664
+2052
+2564
+4100
+5127.
88 ISCINVREQ VALUE +1745
+2257
+2769
+4305.
88 ITEMERR VALUE +2561.
88 JIDERR VALUE +5121.
88 LENGERR VALUE +1249
+1761
+2273
+2785
+3297
+4321
+5126
+6369
+7905.
88 MAPFAIL VALUE +6148.
88 NOJBUFSP VALUE +5129.
88 NOPASSBKRD VALUE +1255.
88 NOPASSBKWR VALUE +1256.
88 NOSPACE VALUE +1667
+2064
+2568.
88 NOSTG VALUE +3298.
88 NOTALLOC VALUE +1237.
88 NOTFND VALUE +1665
+4225.
88 NOTOPEN VALUE +1548
+2056
+5125.
88 PGMIDERR VALUE +3585.
88 QBUSY VALUE +2240.
88 QIDERR VALUE +2050
+2562.
88 QZERO VALUE +2049.
88 RDATT VALUE +1252
+6372.
88 RETPAGE VALUE +6146.
88 RTEFAIL VALUE +6272.
88 RTESOME VALUE +6208.
88 SEGIDERR VALUE +1540.
88 SELNERR VALUE +7692.
88 SESSBUSY VALUE +1236.
88 SESSIONERR VALUE +1234.
88 SIGNAL VALUE +1253.
88 SYSBUSY VALUE +1235.
88 SYSIDERR VALUE +1232
+1744
+2256
+2768
+4304.
88 TERMIDERR VALUE +1254
+4114.
88 TRANSIDERR VALUE +4113.
88 UNEXPIN VALUE +7696.
88 WRBRK VALUE +1251
+6371.
88 ERROR-FOUND VALUE +1259
+1537 +7684 +1668 +1666 +4097 +1551
+1218 +4658 +4329 +1040 +1028 +1217
+4128 +7688 +1258 +1538 +6176 +6152
+736 +1248 +1544 +2592 +3808 +4351
+4832 +5122 +6145 +6880 +4116 +1664
+2052 +2564 +4100 +5127 +1745 +2257
+2769 +4305 +2561 +5121 +1249 +1761
+2273 +2785 +3297 +4321 +5126 +6369
+7905 +6148 +5129 +1255 +1256 +1667
+2064 +2568 +3298 +1237 +1665 +4225
+1548 +2056 +5125 +3585 +2240 +2050
+2562 +2049 +1252 +6372 +6146 +6272
+6208 +1540 +7692 +1236 +1234 +1253
+1235 +1232 +1744 +2256 +2768 +4304
+1254 +4114 +4113 +7696 +1251 +6371.
05 FILLER PIC X(05). Test for any error condition in the IDMS DB environment. Check the call status in your program with flags provided by the APS/IDMS DB Generator. All flags are COBOL 88-level condition names.
|
Flag |
Status Code |
Error Condition |
|---|---|---|
|
AB-ON-REC |
0001 thru 0306 |
Any error other than those listed |
|
DUP-ON-REC |
0705 0805 1205 |
Duplicate key |
|
END-ON-REC |
0307 |
End of set, area, or index |
|
NTF-ON-REC |
0326 0626 |
Record not found |
|
OK-ON-REC |
0000 |
Successful operation |
|
POS-ON-REC |
All values of AB-ON-REC whose last 2 bytes are 06, 13 |
Positioning error |
|
VIO-ON-REC |
All values of AB-ON-REC whose last 2 bytes are 01, 02, 08, 09, 10, 14, 15, 23, 31 |
Update violates IDMS DB rules |
After any APS/IDMS call, the value of ERROR-STATUS moves to DBIO-STATUS. The program checks the associated 88-level flags for status checking. If a DB call contains a record name, such as DB-STORE REC CUSTOMER, you can move the value of ERROR-STATUS to record-STATUS, as well as DBIO-STATUS, and the program checks both fields.
Generated record-STATUS flags have the following format.
ORDER-STATUS PIC X(04) VALUE '0000'.
88 STABLE-ON-ORDER VALUE '0000'.
88 AT-END-ON-ORDER VALUE '0307'.
88 INVALID-KEY-ON-ORDER VALUE '0326' '0626'.
88 INVALID-DUP-ON-ORDER VALUE '1205' '0805 '0705'.
88 ABNORMAL-ON-OR VALUE '0001' THRU '0306'
'0308' THRU '0325'
'0327' THRU '0625'
'0627' THRU '0704'
'0706' THRU '0804'
'0806' THRU '1204'
'1206' THRU '9999'.
DB-OBTAIN REC IDMSREC AREA CUSTOMER-REGION FIRST
IF OK-ON-REC
DB-OBTAIN REF CUSTOMER REC ORDER FIRST
IF OK-ON-ORDER
PERFORM ORDER-PROCESSING-PARA
ELSE-IF AT-END-ON-ORDER
... OR INVALID-KEY-ON-ORDER
PERFORM NO-ORDERS-PARA
ELSE
PERFORM ABNORMAL-ON-ORDER-PARA
DB-OBTAIN and DB-GET generate record-STATUS flag values (when the record name is given). All other calls generate DBIO-STATUS values.
01 DBIO-STATUS PIC X(04) VALUE '0000'.
88 OK-ON-REC VALUE '0000'.
88 END-ON-REC VALUE '0307'.
88 NTF-ON-REC VALUE '0326' '0626'.
88 DUP-ON-REC VALUE '1205' '0805'
'0705'.
88 AB-ON-REC VALUE '0001' THRU '0306'
'0308' THRU '0325'
'0327' THRU '0625'
'0627' THRU '0704'
'0706' THRU '0804'
'0806' THRU '1204'
'1206' THRU '9999'.
01 APS17-STATUS REDEFINES DBIO-STATUS.
02 APS17-MAJOR-CODE PIC X(02).
02 APS17-MINOR-CODE PIC X(02).
88 POS-ON-REC VALUE '06' '13'.
88 VIO-ON-REC VALUE '01' '02'
'08' '09'
'10' '14'
'15' '23'
'31'.Test for any error condition in the IMS DB environment. Check the call status in your program with flags provided by the APS/IMS DB Generator. All flags are COBOL 88-level condition names.
|
Flag |
Status Code |
Error Condition |
|---|---|---|
|
AB-ON-REC |
Any not listed below |
For any error code not listed below |
|
DUP-ON-REC |
I, NI LB |
Call failed because the new segment would create a duplicate for a key or sequence field defined as unique |
|
END-ON-REC |
GB |
End of database reached |
|
NTF-ON-REC |
GE GB |
Requested record not found |
|
OK-ON-REC |
2 spaces, GA GD GK |
Everything is OK |
|
POS-ON-REC |
DJ LC LD LE |
Positioning error; requested positioning not established |
|
RTY-ON-REC |
GG |
Record not available; retry |
|
VIO-ON-REC |
AM DA DX RX IX |
Update violates IMS DB rules |
By default, the APS-supplied IMS database error macros--$IM-ERR-CONDITION and $IM-ERR-ACTION--use APS-supplied status flags.
The macros also call DFS0AER, the IMS-supplied error display routine. To enable the call to DFS0AER, go to the APS CNTL file APSDBDC and set the variable % &IM-USE-DFS0AER to 1. If you don't have DFS0AER at your installation, or you want to disable it, just leave the variable set to 0.
APS supplies two error macros in the APSMACS file IMSPHYS.
To modify $IM-ERR-CONDITION, write an overriding macro of the same name in the USERMACS macro library. Use the override macro for
% DEFINE $DB-SUBSCHEMA-EXIT-2
% INCLUDE USERMACS(MY-OVERRIDE-MAC)
% END
Notes:
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
&ERR-PCB |
Name of PCB used for call. |
|
&ERR-MACNAME |
Name of call resulting in error. |
|
&ERR-FUNC |
IMS function code used in call. |
|
&ERR-SEGNAME |
Name of segment requested in call. |
|
&ERR-PAR-SEGNAME |
Segment name of parent requested in call. |
|
&ERR-IOAREA |
COBOL name of record I/O area. |
|
&ERR-PAR-IOAREA |
COBOL name of parent record I/O area. |
|
&ERR-USER-MSG |
COBOL name of 72 byte error message field. |
|
&ERR-SSA1 thru 15 |
SSA(s) used in call. |
|
&IM-LVL-MAX |
Maximum level of the call. |
DB-OBTAIN RECORD EMPLOYEE-MASTER ... WHERE EMP-NO = NEEDED-EMP-NO
DB-OBTAIN RECORD EMPLOYEE-MASTER ... WHERE EMP-NO = NEEDED-EMP-NO REC WEEKLY-TIME-SEG ... WHERE WEEK-END-DATA = PERIOD-DATE REC PROJECT-TIME-REC ... WHERE PROJ-CODE = CURRENT-PROJ
IMS provides error fields that show how far your call was processed prior to failure.
|
IM-DB-PCB-SEGLEV |
Lowest level of the segment found in the database, for example, 15, if a 15th-level segment is found. Default 00. |
|
IM-DB-PCB-SEGNAME |
8-character IMS name for the lowest-level segment located. |
|
IM-DB-PCB-KEY-FEED-BACK |
Concatenated key information for the path from the root-level to the lowest-level segment found. |
|
IM-DB-PCB-KEY-KFBLEN |
Length of data in the IM-DB-PCB-KEY-FEED-BACK field. |
Test for any error condition in the IMS DC environment. Check the call status in your program with flags provided by the APS/IMS DC Generator. All flags are COBOL 88-level condition names.
|
Flag |
Status Code |
Error Condition |
|---|---|---|
|
AB-ON-DC-CALL |
CH X1 X8 |
Category 5 status code return; call not complete. |
|
FP-ERR |
FF FH FS FV |
Category 3 status code return. Fast Path error; call complete. |
|
NO-MORE-MSGS |
QC |
Category 3 status code return on the TP call; no more input messages exist. |
|
NO-MORE-SEGS |
QD |
Category 3 status code return; no more segments exist for this message. |
|
SEG-NOT-FOUND |
GE |
Category 1 status code return; segment not found. |
|
OK-ON-DC-CALL |
2 spaces, CC CE CF CG CI CJ CK CL FD FW FF FH FS FV GE QC QD |
Categories 1 and 2 status code return; processing proceeds. |
|
SEC-VIO |
A4 FI |
Category 4 status code returned; security violation occurred; call not complete. |
|
SPA-IO-ERR |
XA XB XE XF XG X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 |
Categories 4 and 5 status code return; SPA error; call not complete. |
|
TP-PGM-ERR |
AA AB AD AL AP AT AY AZ A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 CA CB CD QE QH |
Category 4 status code return; programming error; call not complete. |
By default, the APS-supplied IMS data communication error macros--$TP-ERR-CONDITION and $TP-ERR-ACTION--use APS-supplied status flags.
The macros also call DFS0AER, the IMS-supplied error display routine. To enable the call to DFS0AER, to to the APS CNTL file APSDBDC and set the variable % &IM-USE-DFS0AER to 1. If you don't have DFS0AER at your installation, or you want to disable it, just leave the variable set to 0.
APS supplies these two error macros in the APSMACS file IMSPHYS.
To modify $TP-ERR-CONDITION, write an overriding macro of the same name in the USERMACS macro library. You can use the override macro for a specific application or an entire Project and Group.
The override the macro for $TP-ERR-CONDITION, generate a simple or compound S-COBOL conditional statement that tests APS data communication status flags (found in the generated Working-Storage field TP-FLGS), the IMS status code (in the field TP-STATUS), or both.
To modify $TP-ERR-ACTION, write an overriding macro of the same name. You can use the override macro for a specific application or an entire Project and Group. The override macro must generate S-COBOL procedural code for the action specified when a condition(s) tested by $TP-ERR-CONDITION is True. You can use the following parameters that are passed to $TP-ERR-ACTION after a bad data communication call.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
&TP-ERR-PCB |
Name of the I/O PCB used for the call |
|
&TP-ERR-FUNC |
Generated Working Storage field, IM-CALL-FUNC, to which the DC call function is moved prior to the call |
|
&TP-ERR-MSG |
Generated 72-byte Working Storage field, IM-ERR-MSG, containing an error message |
|
&TP-ERR-SEG-IOAREA |
Generated Working Storage field, either TP-SEGMENT or user record area |
|
&TP-ERR-SPA |
Generated Working Storage field, TP-SPA, present only in IMS conversational programs |
Test for any error condition in the SQL environment. Check the call status in your program with flags provided by the APS/SQL Generator; test SQLCODE. All flags are COBOL 88-level condition names.
|
Flag |
Error
Condition |
|---|---|
|
AB-ON-REC |
Any error not listed in this table. |
|
DB2-DEADLOCK |
DB-PROCESS calls check this status to ensure the cursor is not already closed before closing it; SQL closes the cursor if database is locked. |
|
DUP-ON-REC |
DB-STORE failed because the row already exists; duplicates not allowed. |
|
END-ON-REC |
End of table or cursor set reached. |
|
NTF-ON-REC |
Requested row not found. |
|
OK-ON-REC |
Operation successful. |
|
RI-ON-REC |
Referential Integrity check successful (corresponds to SQLCODE -532 to -530). |
APS/SQL provides flags for you to code in your program to check the status of SQL calls. When the AB-ON-REC flag is returned, it invokes an abnormal condition processing macro ($D2-ERROR-PARA) that displays a message and, for IMS and CICS programs, terminates the program.
If your DC target is IMS, and you are not running IMS under BTS, set &D2-EXEC-UNDER-BTS=NO in the APS CNTL file APDB2IN. This eliminates "Display" statements in the APS-generated error handling routine.
To disable &D2-ERROR-PARA, go to the APS CNTL file APDB2IN and set &D2-AUTO-ERROR-HANDLING to OFF.
You can modify error processing in two ways.
Use the S-COBOL trace flag for debugging. This facility displays where APS performs each paragraph.
The Trace facility differs from the IBM READY-TRACE because it displays the paragraph name only when a PERFORM executes a paragraph, and not each time a loop executes.
Note: To activate the Trace facility, specify SCBTRACE on the Precompiler Options screen.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
.
.
.
02 SAGE-TRACE-FLAG PIC X VALUE "T".
.
.
.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
.
.
.
paragraphname
IF SAGE-TRACE-FLAG = TRUE
DISPLAY "EXEC:--paragraphname--".
.
.
.
MOVE FALSE TO SAGE-TRACE-FLAG
Test for any error condition in the VSAM batch environment. Check the call status in your program with flags provided by the APS/VSAM Batch Generator. All flags are COBOL 88-level condition names.
|
Flag |
Status Code |
Error Condition |
|---|---|---|
|
OK-ON-REC |
00 |
Successful operation |
|
DUP-ON-REC |
02 |
Duplicate key; duplicates allowed |
|
END-ON-REC |
10 |
End of file |
|
INV-ON-REC |
20 21 22 23 24 |
Invalid key condition |
|
IVD-ON-REC |
22 |
Duplicate key; duplicates not allowed |
|
NTF-ON-REC |
23 |
Record not found |
|
AB-ON-REC |
30 34 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 |
Abnormal condition |
DB-STORE REC CUST-RECORD
IF OK-ON-REC
SCREEN-MSG = 'CUSTOMER ADDED TO FILE'
ELSE-IF IVD-ON-REC
SCREEN-MSG = 'DUPLICATE CUSTOMER - NOT ADDED' When the AB-ON-REC flag is returned, it invokes an abnormal condition processing macro ($DB-ERR-CALL) to identify and process run-time I/O errors, terminate the program, and display a message giving the following information.
Note: APS identifies the status code values listed in the previous table; the developer should test for all other conditions, such as, 00, 02, 10, 20, 21, 22, 23, and 24.
Program generation options
There are three ways to modify AB-ON-REC processing.
To override $DB-ERR-CALL, define (or % INCLUDE in your program, using the SYM1 keyword) your own $DB-ERR-CALL macro.
% DEFINE $DB-ERR-CALL
PERFORM LOG-VSAM-ERROR
% END
% SET EPILOGUE $LOG-VSAM-ERROR
% DEFINE $LOG-VSAM-ERROR
% SET WORKING-STORAGE
COPY LOGDATA.
% SET PROCEDURE
LOG-VSAM-ERROR.
/* CAPTURE EIB DATA
MOVE EIBFN TO CA-EIBFN
MOVE EIBRCODE TO CA-EIBRCODE
MOVE EIBDS TO CA-EIBDS
MOVE EIBDATE TO CA-EIBDATE
MOVE EIBTIME TO CA-EIBTIME
MOVE EIBTASKN TO CA-EIBTASKN
MOVE EIBTRMID TO CA-EIBTRMID
MOVE EIBTRNID TO CA-EIBTRNID
/* TRANSFER CONTROL TO LOG PROGRAM
CICS XCTL
... PROGRAM('LOGERROR')
... COMMAREA(CA-EIB-AREA)
... LENGTH(CA-EIB-AREA-LENGTH)
% END Test for any error condition in the VSAM online environment. Check the call status in your program with flags provided by the APS/VSAM Generator. All flags are COBOL 88-level condition names. Two equivalent sets of flags, APS/CICS VSAM and APS/CICS EIBRCODE, are provided.
|
VSAM Flag |
EIBRCODE Flag |
ISI-Errors/ Exceptional Condition |
Error Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AB-ON-REC |
DSIDERR ILLOGIC IOERR LENGERR NOSPACE NOTOPEN SYSIDERR |
DSIDERR ILLOGIC IOERR LENGERR NOSPACE NOTOPEN SYSIDERR |
Abnormal condition |
|
DUP-ON-REC |
DUPKEY |
DUPKEY |
Duplicate key; duplicates allowed |
|
END-ON-REC |
ENDFILE |
ENDFILE |
End of file |
|
INV-ON-REC |
NOTFND DUPREC |
NOTFND DUPREC |
Invalid key condition |
|
IRQ-ON-REC |
INVREQ |
INVREQ |
Invalid request |
|
IVD-ON-REC |
DUPREC |
DUPREC |
Duplicate key; duplicates not allowed |
|
NTF-ON-REC |
NOTFND |
NOTFND |
Record not found |
|
OK-ON-REC |
N/A |
N/A |
Successful operation |
With APS/CICS VSAM flags:
DB-STORE REC CUST-RECORD
IF OK-ON-REC
SCREEN-MSG = 'CUSTOMER ADDED TO FILE'
ELSE-IF IVD-ON-REC
SCREEN-MSG = 'DUPLICATE CUSTOMER - NOT ADDED'
With APS/CICS EIBRCODE flags:
DB-STORE REC CUST-RECORD
IF EIBRCODE = LOW-VALUES
SCREEN-MSG = 'CUSTOMER ADDED'
ELSE-IF DUPREC
SCREEN-MSG = 'DUPLICATE CUSTOMER - NOT ADDED'When the AB-ON-REC flag is returned, it invokes an abnormal condition processing macro ($D2-ERR-CALL) to identify and process run-time I/O errors, terminate the program, and display a message giving the following information.
Note: APS identifies the status code values listed in the previous table; all other conditions, such as, DUPKEY, DUPREC, ENDFILE, INVREQ, and NOTFND, are processed by the programmer.
Program generation options:
There are three ways to modify AB-ON-REC processing.
To override $DB-ERR-CALL, define (or % INCLUDE in your program, using the SYM1 keyword) your own $DB-ERR-CALL macro.
% DEFINE $DB-ERR-CALL
PERFORM LOG-VSAM-ERROR
% END
% SET EPILOGUE $LOG-VSAM-ERROR
% DEFINE $LOG-VSAM-ERROR
% SET WORKING-STORAGE
COPY LOGDATA.
% SET PROCEDURE
LOG-VSAM-ERROR.
/* CAPTURE EIB DATA
MOVE EIBFN TO CA-EIBFN
MOVE EIBRCODE TO CA-EIBRCODE
MOVE EIBDS TO CA-EIBDS
MOVE EIBDATE TO CA-EIBDATE
MOVE EIBTIME TO CA-EIBTIME
MOVE EIBTASKN TO CA-EIBTASKN
MOVE EIBTRMID TO CA-EIBTRMID
MOVE EIBTRNID TO CA-EIBTRNID
/* TRANSFER CONTROL TO LOG PROGRAM
CICS XCTL
... PROGRAM('LOGERROR')
... COMMAREA(CA-EIB-AREA)
... LENGTH(CA-EIB-AREA-LENGTH)
% ENDScreen Painter feature (see Field Edits)
Code default error messages to display when the end user enters invalid data or neglects to enter data that is required. You can code these messages for each screen field, or globally for all screen fields.
Note: A field-specific message overrides a global message.
To assign an error message for a specific field, follow these steps.
attribute+attribute+...
The default attributes are bright intensity and cursor positioning on the field.
To assign an error message that applies to all screen fields, or to bypass input edits for the screen, follow these steps.
attribute+attribute+...
The default attributes are bright intensity and cursor positioning on the field.
| Field |
Description and Values |
|---|---|
|
Field Name |
Specify any field on the screen, including a field in a repeated block, to bypass. |
|
Value(s) |
Specify the value or values that let end users bypass input edits. Valid COBOL reserved words are spaces, low-values, and high-values. |
|
Additional Value(s) |
Enter as many additional bypass values that can fit on the line; separate each value with a comma. |
|
Program Function Keys |
Select the PF keys the end user can press to bypass the input edits. |
S-COBOL structure (see S-COBOL Structures)
Exit from the current paragraph.
ESCAPE
Processing resumes with the first statement after the statement performing the paragraph, except if ESCAPE occurs in the first or main logic paragraph of
If the condition in line 2220 is true, pass control back to line 2050.
. . . 002030 CHECK-DATA 002040 PERFORM STEP-1 002050 ADD 1 TO COUNTER . . . 002210 STEP-1 002220 IF X = 1 002230 ESCAPE 002240 ADD 1 TO FIELD-A
S-COBOL structure (see S-COBOL Structures)
Perform logic by cases, such as a decision table.
Format 1, standard evaluation procedure:
EVALUATE identifier
WHEN valuexpression1
statementblock
[ .
.
.
WHEN valuexpressionN
statementblockN ]
[WHEN OTHER
statementblock ]
Format 2, decision table:
EVALUATE identifier1[, ..., identifierN]
WHEN valuexpression1[, ..., valuexpressionN]
statementblock
[ .
.
.
WHEN valuexpressionN+1[, ..., valuexpressionN+N]
statementblock ]
[WHEN OTHER
statementblock ]
|
identifier |
Any COBOL identifier |
|
valuexpression |
In Format 1, a data name or a group of COBOL literals, identifiers, and arithmetic expressions forming expression1, expression2, . . .. |
|
|
In Format 2, one of the following ANY, or expression1 [THRU expression2] Symbols such as =, <, and > are not valid. |
If the above criteria are met and the evaluated field is not defined as numeric, a COBOL error occurs.
Create a mailing list that includes new subscribers (less than 1 year) and preferred subscribers (more than 5 years) broken down by region.
EVALUATE MONTHS, REGION
WHEN 1 THRU 11, 'EAST'
WRITE NEW-EAST-REC
WHEN 1 THRU 11, 'WEST'
WRITE NEW-WEST-REC
WHEN 61 THRU 9999, 'EAST'
WRITE PREFERRED-EAST-REC
WHEN 61 THRU 9999, 'WEST'
WRITE PREFERRED-WEST-RECDatabase calls (see Database Calls)
SQL, VSAM Batch, and VSAM Online targets
At various program locations, you can write your own rules to customize methods. In your program, you write a rule using one of the APS-supplied predefined rule names, and APS invokes it at its proper location. You can write rules that are automatically invoked at the beginning and end of the processing using either of these predefined rule name formats.
For DB-ERASE:
$D2-DB-ERASE-BEGIN-EXIT $D2-DB-ERASE-END-EXIT
For DB-MODIFY:
$D2-DB-MODIFY-BEGIN-EXIT $D2-DB-MODIFY-END-EXIT
For DB-OBTAIN:
$D2-DB-OBTAIN-BEGIN-EXIT $D2-DB-OBTAIN-END-EXIT
For DB-PROCESS:
$D2-DB-PROCESS-BEGIN-EXIT $D2-DB-PROCESS-END-EXIT
For DB-STORE:
$D2-DB-STORE-BEGIN-EXIT $D2-DB-STORE-END-EXIT
For DB-ERASE:
$VS-DB-ERASE-BEGIN-EXIT $VS-DB-ERASE-END-EXIT
For DB-MODIFY:
$VS-DB-MODIFY-BEGIN-EXIT $VS-DB-Modify-END-EXIT
For DB-OBTAIN:
$VS-DB-OBTAIN-BEGIN-EXIT $VS-DB-OBTAIN-END-EXIT
For DB-PROCESS:
$VS-DB-PROCESS-BEGIN-EXIT $VS-DB-PROCESS-END-EXIT
For DB-STORE:
$VS-DB-STORE-BEGIN-EXIT $VS-DB-STORE-END-EXIT
S-COBOL structure (see S-COBOL Structures)
End the execution sequence of a program or subprogram and return control to the invoking source.
EXIT PROGRAM
SQL target
APS/SQL supports expressions for the DB-DECLARE, DB-OBTAIN, and DB-PROCESS calls.
|
Sample Expressions |
Return INTO
Host |
Null
Indicator |
|---|---|---|
|
INTEGER (DOB) - INTEGER(PERF - 1) (WS-RET-INT) |
WS-RET-INT |
IND-DOB |
|
CURRENT DATE - 1 DAY (WS-CURRDATE) |
WS-CURRDATE |
-------- |
|
RATE + (DED / 2.0) |
RATE |
IND-RATE |
|
YTD + RATE + DED / 2 |
YTD |
IND-YTD |
|
PERF / 2 |
PERF |
IND-PERF |
|
INTEGER(YTD - DED) * INTEGER(RATE) (WS-INT-FLD) |
WS-INT-FLD |
INT-YTD |
|
HIREDTE + YEAR(CURRENT DATE) YEARS |
HIREDTE |
IND-HIREDTE |
|
SUM(YTD) / 2 |
YTD |
IND-YTD |
|
AVG(DED - 1) / 5 (WS-AVG-DED) |
WS-AVG-DED |
IND-DED |
|
SUM(RATE) + SUM(DED) (WS-RATE-DED) |
WS-RATE-DED |
IND-RATE |
If an INTO variable is not specified, the result returns to the host variable for the first column.
DB-OBTAIN REC TABLE1 ... RATE + (DED / 2.0) ... PERF / 2 ... INTEGER(DOB) - INTEGER(PERF - 1) (WS-RET-INT) ... WHERE PERF > 100
DB-OBTAIN REC RECORD1-RED ... RATE + YEAR_TO_DATE (WS-CALC-RATE) ... MONTH(HIREDATE) - DAY(HIREDATE) (WS-DATE-RETURN ... AVG(RATE - 1) / 4 (WS-AVG-RATE) ... YEAR((CURRENT DATE - HIREDTE),WS-CALC-DATE,Y) ... CHAR((HIREDTE - 28 DAYS,USA),WS-DATE-AREA,Y) ... WHERE RATE > 7
Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Define the file descriptions for input and output files, including report files.
Format 1:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
FD inputfilename|outputfilename
[Applicable COBOL FD clauses]
Format 2:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
FD filename
[Applicable COBOL FD clauses]
.
.
.
REPORT IS|REPORTS ARE reportname1 [... reportname15]
Record Size = Report mock-up size (maximum 247 characters)
+ 1 byte for carriage control
+ 2 bytes for the CODE clause, if used.
Input REALLY-LONG-REPORT-NAME
Output RLR-NAME-RECORD
Report example:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
FD INPUT-FILE
LABEL RECORDS ARE STANDARD
BLOCK CONTAINS 0 RECORDS.
01 PART-STOCK-REC PIC X(80).
FD REPORT-OUTPUT-FILE
LABEL RECORDS ARE STANDARD
REPORT IS STOCK-REPORT.Screen Painter feature
Screen fields can be one of the following types:
Depending on the type of field you create, you assign field edits that define the data representations for the field. APS supports the following field edits.
When users fail to enter data correctly, you can display an error message that explains the problem. You can define two error messages, one for when the end user enters invalid data, and one for when the end user neglects to enter data that is required.
These can be global messages that display for all screen fields, or specific messages that display for individual fields. Messages defined for a specific field override the global messages. You can also define conditions for bypassing input edits under certain conditions.
|
See... |
For other information about Field Edits... |
|---|---|
|
Assigning the internal picture, input format and data requirements, and output display format for:
|
|
|
Specifying editing and testing routines for input or output data |
|
|
Displaying error messages for invalid field data |
|
|
Ensuring that fields accept only certain data values |
Screen Painter feature (see Field Edits)
Specify the data storage requirements, the format and data requirements that the end user must adhere to when entering data into the field, and specify the format requirements for displaying the data.
Follow these steps.
|
Values or Conversions |
Enter s to transfer to the Values or Conversions screen to specify valid values, ranges of values, or conversion values. See Values, Conversion Values, and Value Ranges. |
|
Application Edits |
Enter s to transfer to the Application Editing screen to specify your own edits in a paragraph, subprogram, or APS macro. See Application Field Edit Routines. |
|
Error Processing |
Enter s to transfer to the Error Processing screen to specify error messages and attributes that display if the field fails input edits. See Error Processing Messages. |
|
Option |
Description |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Data Type |
|
||||||||
|
Internal Length |
Enter the number of characters. The default is the screen field length. For numeric fields, enter the number of digits that precede the decimal point. |
||||||||
|
Justified Right |
Type s to generate right justification on the COBOL picture. |
||||||||
|
Decimal Places |
Enter the number of digits that follow the decimal point. |
||||||||
|
COMP (Binary) |
Type s to store input data in binary format. Not valid with signed data. |
||||||||
|
COMP-3 (Packed) |
Type s to store input data in packed format. Not valid with signed data. |
||||||||
|
Signed |
Type s to store the input data with either a positive or negative value. Not valid with a binary or packed format. |
||||||||
|
Sign Leading |
Type s to store the sign at the left of the number. Not valid with a binary or packed format. |
||||||||
|
Sign Separate |
Type s to store the sign in a separate byte from the number. Not valid with a binary or packed format. |
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Internal Picture |
Enter s to transfer to the Internal Picture screen to change the storage format. |
|
Required |
Enter s to indicate that the end user must enter a value in the field. |
|
Input Mask |
Enter the pattern or mask to accept input data and separators. Or, enter s to transfer to the Masking screen and specify the mask in the Input Mask field. Note the following.
|
|
|
Note the following for character fields.
|
|
|
Note the following for numeric fields.
|
|
Minimum Input |
Enter the length of the shortest valid entry. Default is zero. You cannot specify an input mask with this option. This option does not imply that data is required. |
|
Maximum Input |
Enter the length of the longest valid entry. Default is field length. You cannot specify an input mask with this option. This option does not imply that data is required. |
|
No Embedded Spaces |
Enter s to reject characters separated by spaces. Leading and trailing blank spaces are unaffected by this option. |
|
Numeric Test |
Enter s to allow only numeric data. |
|
Numeric De-Edit |
Enter s to validate that the data is numeric and to remove special characters. Select this option if you specify an output COBOL picture; doing so removes the special characters for data computations. This option does not imply that data is required. Not valid with an input mask. |
|
Zero When Blank |
Move zero to the internal picture if no data is entered. Not valid with required fields or fields with input masks. To prevent zeroes from appearing in the field when data is not entered, zero suppress the output picture on the Output Picture screen. |
|
Minimum Digits |
Enter the smallest number of digits required before the decimal point. Default is zero. You cannot specify an input mask with this option. This option does not imply that data is required. |
|
Minimum Decimals |
Enter the smallest number of digits required to follow the decimal point. Default is zero. This option does not imply that data is required. |
|
Maximum Digits |
Enter the largest number of digits allowed before the decimal point. Default is the maximum number that fits in the internal picture. Not valid with an input mask. This option does not imply that data is required. |
|
Maximum Decimals |
Enter the largest number of digits allowed to follow the decimal point. Default is the maximum number that fits in the internal picture. This option does not imply that data is required. |
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Internal Picture |
Enter s to transfer to the Internal Picture screen to change the storage format. |
|
Output Mask |
Enter the pattern or mask to position data and separators. Or, enter s to transfer to the Masking screen and specify the mask in the Output Mask field. Note the following.
|
|
Output Picture |
Enter the output COBOL picture. Or, enter s to transfer to the Output Picture screen and specify the mask in the Picture field. You cannot assign an output picture if you use an output mask. |
|
Right Justify |
Enter s to generate right justification for the output format. |
|
Insert Comma(s) |
Enter s to format data with commas in appropriate positions. |
|
Zero Suppression |
Enter s to generate the zero suppression symbol. |
|
Floating Symbol |
Enter a $, +, or - symbol to generate a floating dollar, plus sign, or minus sign to the left of the first digit. |
|
Fixed Leading Symbol |
Enter a $, +, or - symbol to generate a fixed dollar, plus sign, or minus sign in the leftmost position. |
|
Fixed Trailing Symbol |
Enter a $, +, or - symbol to generate a fixed dollar, plus sign, or minus sign in the rightmost position. |
| Optional Mask Characters |
Verification |
|---|---|
|
No |
Left to right scan |
|
Yes, on the left |
Left to right scan |
|
Yes, on the right |
Right to left scan |
% &FE-DECIMAL-POINT-IS-COMMA = "YES" % &FE-TP-SPECIAL-NAMES-MACMBR = "TPSPEC"|"membername"
Then, copy TPSPEC from &SSMAPS..CNTL to &SSMDSN..USERMACS. Modify the $TP-SPECIAL-NAMES macro as desired to generate statements in the SPECIAL-NAMES paragraph.
% &FE-DECIMAL-POINT-IS-COMMA = "YES"
To determine how to invoke a CICS program, APS/CICS provides the following 88-level flags to indicate the mode of program invocation.
TP-INVOCATION-MODE PIC X(01). 88 TP-TRANSID-INVOKED VALUE 'T'. 88 TP-PROGRAM-INVOKED VALUE 'P'. 88 TP-SCREEN-INVOKED VALUE 'S'. 88 TP-LINK-INVOKED VALUE 'L'.
|
TP-TRANSID-INVOKED |
A transaction code entered on a blank screen invokes the program. |
|
TP-PROGRAM-INVOKED |
An XCTL call from another program invokes the program. |
|
TP-SCREEN-INVOKED |
The SEND call sends the screen and a PF key or ENTER key invokes the program. |
|
TP-LINK-INVOKED |
A LINK call from another program invokes the program. |
To determine how to invoke an IMS DC program, APS provides the following 88-level program support variable flags.
TP-INVOCATION-MODE PIC X.
88 TP-TRANSID-INVOKED VALUE 'T'.
88 TP-PROGRAM-INVOKED VALUE 'P'.
88 TP-SCREEN-INVOKED VALUE 'S'.
|
TP-TRANSID-INVOKED |
A transaction code invokes the program; the input message contains no additional data. |
|
TP-SCREEN-INVOKED |
Program reads an input message consisting of more than just the transaction code; often this is screen data. |
|
TP-PROGRAM-INVOKED |
A program, rather than a terminal, sends the input message. Program-invoked mode applies only to conversational programs. |
APS tests for a TRUE value to determine which invocation paragraph to perform.
To determine how to invoke an ISPF Dialog program, APS provides the following 88-level flags.
TP-INVOCATION-MODE PIC X(01). 88 TP-TRANSID-INVOKED VALUE 'T'. 88 TP-PROGRAM-INVOKED VALUE 'P'. 88 TP-SCREEN-INVOKED VALUE 'S'. 88 TP-LINK-INVOKED VALUE 'L'.
|
TP-TRANSID-INVOKED |
Provided for upward compatibility; has no function. |
|
TP-PROGRAM-INVOKED |
A LINK call from another program invokes the program. |
|
TP-SCREEN-INVOKED |
The SEND call sends the screen and a PF key or ENTER key invokes the program. |
|
TP-LINK-INVOKED |
Provided for upward compatibility; has no function. |
Use APS-defined data fields and S-COBOL flags in your program.
| Name |
Associated Calls |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
APS-END-PROCESS |
DB-PROCESS |
Flag that terminates a DB-PROCESS loop. Example: TRUE RESET-OBTAIN |
|
ddname-RRN |
DB-OBTAIN |
Field that controls relative record number (RRN) of a retrieved or stored RRDS file record; generates value for the RELATIVE KEY clause of the SELECT statement. Ddname is the external file name specified in the subschema. Generated field definition ddname-RRN PIC 9(09). |
|
RESET-OBTAIN |
DB-OBTAIN |
Flag that resets browse to beginning of file. Example: TRUE RESET-OBTAIN |
In RRDS processing, APS/VSAM generates ddname-RRN, deriving the RRN (relative record number) of the current retrieved record. This allows access to a specific RRN. The field value is the RRN of each retrieved or stored record, and is updated after every successful READNEXT operation.
Assign a RRN value to ddname-RRN prior to a DB-STORE, if the SELECT statement ACCESS clause is either RANDOM or DYNAMIC.
An ESDS file is opened in I/O mode.
Use APS-defined data fields and S-COBOL flags in your program.
|
Name |
Associated Calls |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
APS-shortrecname-VAR |
DB-OBTAIN |
Field that contains actual record length after a successful record retrieval (direct or sequential for DB-OBTAIN and DB-PROCESS). Supplies value to dataarea in CICS LENGTH option. Shortrecname comes from the subschema definition; it is the REC card SHORT keyword. See also "Skip Sequence Processing" below. |
|
APS-END-PROCESS |
DB-PROCESS |
Flag that terminates DB-PROCESS loop. Example: TRUE RESET-OBTAIN |
|
APS-VSAM-NUMREC |
DB-ERASE |
Field that contains number of records deleted after key-qualified ERASE with partial key length specified. |
|
ddname-APS-KEYnumber |
DB-OBTAIN DB-PROCESS |
Field that contains APS-generated key name for use in skip-sequential processing. Ddname is the subschema file. See also "Skip Sequence Processing" below. Example: ORDER-APS-KEY1 |
|
ddname-RBA |
DB-OBTAIN DB-PROCESS DB-STORE |
Field that contains relative byte address (RBA) of a retrieved, stored ESDS file record; supplies value to CICS RIDFLD option. See also "ESDS Support" and "Skip Sequence Processing" below. Ddname is the subschema file. Generated field definition ddname-RBA PIC S9(08) COMP |
|
ddname-RRN |
DB-OBTAIN |
Field that contains relative record number (RRN) of a retrieved or stored RRDS file record; supplies value to CICS RIDFLD option. See also "RRDS Support" and "Skip Sequence Processing" below. Generated field definition ddname-RRN PIC S9(08) COMP |
|
RESET-OBTAIN |
DB-OBTAIN |
Flag that resets browse to beginning of file. When used with PREV, resets to end of file. Example: TRUE RESET-OBTAIN |
Ddname-RBA provides access to a specific relative byte address (RBA). The current retrieved or written (stored) record determines the RBA; every successful READNEXT, READPREV, and WRITE operation updates the RBA. Note the following.
Ddname-RRN provides access to a specific relative record number (RRN). The current retrieved determines the RRN; every successful READNEXT and READPREV operation updates the RBA.
Assign ddname-RRN a RRN value prior to a DB-STORE or direct (key-specified) call.
Skip-sequential processing moves new key search criteria to an APS-generated key while an active sequential DB-OBTAIN or DB-PROCESS browse is in progress. The following indicates the APS-generated keys by target.
|
File Type |
Record
Key |
|---|---|
|
ESDS |
ddname-RBA PIC S9(08) COMP. |
|
RRDS |
ddname-RRN PIC S9(08) COMP. |
|
KSDS |
ddname-APS-KEYnumber Number indicates the key number, as follows: |
APS/VSAM provides the APS-shortrecname-VAR field, which contains length information for variable length files, for each record definition in the subschema.
APS-shortrecname-VAR must be updated with the calculated record length prior to all DB-STORE and DB-MODIFY calls.
For example, the following updates APS-CUST-VAR with the actual length of CUST-RECORD prior to the DB-STORE.
APS-CUST-VAR = WS-FIXED-PORTION + ... (CUST-NBR-ORDERS * WS-OCCURS-LENGTH) DB-STORE REC CUST-RECORD
APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Field/Screen Cross Reference Report lists all the screens containing I/O fields, along with the attribute values for the field in each screen. The fields appear alphabetically on the report. For each field, the report lists the field attributes assigned in the Screen Painter, and the number of field occurrences within a repeated block. The reports denotes default values with periods (..). The end of the report shows the total number of fields cross-referenced, the associated screens reported, and the actual number of stored screens. The report documents this aspect of your application to support future maintenance and enhancement efforts.
REPORT CODE: SC02 APS SCREEN PAINTER PAGE 1
FIELD/SCREEN CROSS REFERENCE 01/17/9211:57
CLSAPS.CLS2
SELECTION CRITERIA:
*********************************************************************************************
EDIT
FIELD SCREEN CC ROW COL LEN TYPE INTEN MDT NUMDET MASK MOD
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A-ROW005-FLD001 AAAAA 5 2 7 UNPR ...... . .. .. .
.. .
A-ROW008-FLD001 RXK001 8 26 25 UNPR ...... . .. .. .
.. .
.
BASE-PRICE DLORDRM 5 17 44 10 UNPR ...... . .. ..
.. .
D2ORDRM 5 17 44 10 UNPR ...... . .. ..
.. .
LHORDRM 5 17 44 10 UNPR ...... . .. ..
.. .
OXPARTL 8 11 49 10 UNPR ...... . .. ..
.. .
CUST-ENTRY-DATE EVOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
KSOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
LBOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
LJOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
PSOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
TDOJ 8 14 18 8 PROT ...... . .. ..
.. .
TDOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
TIOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
TLOM 11 24 8 UNPR BRIGHT . .. ..
.. .
TPOM 12 22 5 UNPR BRIGHT . .. .
.. .
WPORDI 8 14 18 8 PROT ...... . .. ..
.. .
.
.
TOTAL FIELDS REPORTED: 113
TOTAL SCREENS REPORTED: 112
TOTAL SCREENS IN FILE: 112Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Pass COBOL or S-COBOL statements to the APS Generator without translation, in a freeform manner, and insert the statements in the program section where they are coded.
Format 1, for Working-Storage and Linkage Sections only:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 FRFM COBOLstatements|S-COBOLstatements
Format 2, for Procedure Division only:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
ENTER COBOL|ENTER S-COBOL|++INCLUDE membername
COBOLstatements|S-COBOLstatements
Code 77-level data structures and put the data elements in column 8:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
FRFM 77 FIELD-A PIC S99 COMP-3.
77 FIELD-B PIC S99 COMP-3.
77 FIELD-C PIC S99 COMP-3.
Code 77-levels with Customizer symbols:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
SYWS &08+77 FIELD-A PIC S99 COMP-3.
&08+77 FIELD-B PIC S99 COMP-3.
&08+77 FIELD-C PIC S99 COMP-3.Database call keywords (see Database Calls)
SQL target
Code SQL built-in and scalar functions as keywords for the database access calls DB-DECLARE, DB-OBTAIN, AND DB-PROCESS.
For DB-DECLARE:
DB-DECLARE cursorname [correlname1.]copylibname-REC
... function1[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
... function2[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
.
.
.
... functionN[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
... WHERE ...
For DB-OBTAIN:
DB-OBTAIN REC [correlname1.]copylibname-REC
... function1[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
... function2[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
.
.
.
... functionN[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
... WHERE ...
For DB-PROCESS:
DB-PROCESS REC [correlname1.]copylibname-REC
... [DB-PROCESS-ID name]
... function1[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
... function2[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
.
.
.
... functionN[(](expression)[,resultfield[,Y][)]]
... WHERE ...
Select the minimum unit base price and count the number of colors it finds for a given part number; create the result fields and appropriate indicator variables in Working-Storage.
DB-DECLARE D2MAST-CURSOR D2TAB-REC ... MIN((PM_UNIT_BASE_PRICE),WS-PM-UNIT-BASE-PRICE,Y) ... COUNT((DISTINCT PM_COLOR),WS-PM-COLOR,Y) ... WHERE PM_PART_NO = :WS-PART-NO
SQL code with MIN and MAX functions:
DB-OBTAIN REC D2TAB-REC ... MAX((PM_UNIT_BASE_PRICE),WS-MAX-PRICE,Y) ... MIN((PM_UNIT_BASE_PRICE * PM_UNITS),WS-MIN-RESULT,Y) ... WHERE PM_PART_SHORT_DESC = 'WIDGET'
Generated code:
EXEC SQL SELECT
MAX(PM_UNIT_BASE_PRICE)
MIN(PM_UNIT_BASE_PRICE * PM_UNITS)
INTO :WS-MAX-PRICE, :WS-MAX-PRICE-IND
:WS-MIN-RESULT :WS-MIN-RESULT-IND
FROM AUTHID.D2MASTER
WHERE PM_PART_SHORT_DESC = 'WIDGET'
END-EXEC.
SQL code with SUM and AVG functions:
DB-OBTAIN REC D2TAB-REC ... SUM(PM_UNITS) ... AVG((PM_UNITS),WS-AVG-UNITS,Y) ... WHERE PM_PART_NO = '23432'
Generated code:
EXEC SQL select
SUM(PM_UNITS)
AVG(PM_UNITS)
INTO :D2TAB-REC.PM-UNITS :IND-D2TAB-REC.IND-PM-UNITS,
:WS-AVG-UNITS :WS-AVG-UNITS-IND
FROM AUTHID.D2MASTER
WHERE PM_PART_NO = '23432'
END-EXEC.
SQL code with COUNT function:
DB-OBTAIN REC D2MASTER-REC ... MAX((PM-UNITS),WS-MAX-PM-UNITS) ... COUNT((*),WS-PM-COUNT-FLD) ... AVG((PM-UNIT-BASE-PRICE),WS-AVG-PRICE) ... WHERE PM-PART-SHORT-DESC='WIDGET' ... AND PM-COLOR='RED'
Generated code:
EXEC SQL select
MAX(PM-UNITS)
MIN(PM-UNIT-BASE-PRICE)
COUNT(*)
AVG(PM-UNIT-BASE-PRICE)
INTO WS-MAX-PM-UNITS WS-MAX-PM-UNITS-IND,
WS-PM-COUNT-FLD,
WS-AVG-PRICE WS-AVG-PRICE-IND
FROM AUTHID.D2MASTER
WHERE PM-PART-SHORT-DESC='WIDGET'
AND PM-COLOR='RED'
END-EXEC.
SQL code with DATE, TIME, and AVG scalar functions:
DB-OBTAIN REC D2INVEN-REC ... IN_PART_NO ... DATE(IN_DATE_LAST_UPDTE) ... TIME((IN_TIME_LAST_UPDTE),WS-TIME-RETURN,Y) ... CHAR((IN_DATE_LAST_ORDER,ISO),WS-CHAR-RETURN) ... IN_QTY_ONHAND ... WHERE IN_PART_NO = '23432'
Generated code:
EXEC SQL SELECT
IN_PART_NO
DATE(IN_DATE_LAST_UPDTE)
TIME(IN_TIME_LAST_UPDTE)
CHAR(IN_DATE_LAST_ORDER,ISO)
IN_QTY_ONHAND
INTO :D2INVEN-REC.IN-PART-NO,
:D2INVEN-REC.IN-DATE-LAST-UPDTE
:IND-D2INVEN-REC.IN-DATE-LAST-UPDTE,
:WS-TIME-RETURN :WS-TIME-RETURN-IND,
:WS-CHAR-RETURN :WS-CHAR-RETURN-IND,
:D2INVEN-REC.IN-QTY-ONHAND
:IND-D2INVEN-REC.IN-QTY-ONHAND
FROM AUTHID.D2INVTRY
WHERE IN_PART_NO = '23432'
END-EXEC.
In this example, the following occurs.
Report Writer statement (see Report Writer Structures in your APS User's Guide chapter Creating Reports with Report Writer.)
Batch environments
Produce either a detail report or a summary report; test controls; generate control breaks; print totals, detail lines, headings, and footings; clear counters and accumulators; and, paginate the report.
GENERATE dataname|reportname
|
dataname |
Produce a detail report. Specify dataname in the TYPE clause as DETAIL. |
|
reportname |
Produce a summary report that contains no detail lines. Use reportname only if the referenced report group description contains:
|
See the APS User's Guide chapter Creating Reports with Report Writer.
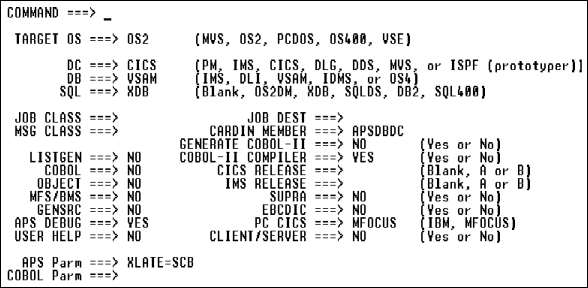
Application generation
Define the development environment for application, program, and screen generation.
To select generator options, follow these steps.
| Option |
Description and Values |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Target OS |
Operating system. |
||||||
|
DC |
Data communications target. For valid DB/DC combinations see DB/DC Target Combinations. |
||||||
|
DB |
Database target. For valid DB/DC combinations see DB/DC Target Combinations. |
||||||
|
SQL |
SQL target. |
||||||
|
Job Class |
Specify any job class valid at your site and known to the APS generators. |
||||||
|
Msg Class |
Site-specific. |
||||||
|
Listgen |
|
||||||
|
COBOL |
|
||||||
|
Object |
|
||||||
|
MFS/BMS |
|
||||||
|
GENSRC |
|
||||||
|
User Help |
|
||||||
|
Job Dest |
Site-specific. |
||||||
|
CARDIN Member |
Specify the CNTL library APSDBDC member. |
||||||
|
Generate COBOL II |
|
||||||
|
COBOL Compiler |
|
||||||
|
CICS Release |
Specify the CICS release at your site. |
||||||
|
IMS Release |
Specify the IMS release at your site. |
||||||
|
SUPRA |
|
||||||
|
APS Parm |
Override the APS Parm field on the Precompiler Options screen. Display all options whose default values you have overridden in the Precompiler Options screen. You can temporarily override these values simply by overtyping them in this field, but changes made here are not saved; they remain in effect only until you exit APS. |
||||||
|
COBOL Parm |
Specify parameters or directives for COBOL compiler. See the COBOL Language Operating Guide for valid values. |

Screen Painter feature
Change parameter values that affect the screen in any environment, as desired. Applicable parameters and valid values on the Screen Generation Parameters screen are:
|
Parameter |
Description
and Values |
|---|---|
|
Associated Trans |
Specify an associated transaction ID; default is the first four characters of the screen. If more than one screen begins with the same four characters, you need to define a unique transid. |
|
Mapset Name |
Override an APS-generated mapset name; maximum seven characters. To generate a multiple-map mapset that includes some or all screens, assign the same mapset name to the applicable screens in the application The default mapset name reflects the number of characters in the screen name, as follows. 4-character name: screennameSET |
|
Line |
Starting line of the map on the physical screen; default is 001; value cannot exceed the screen depth. |
|
Parameter |
Description
and Values |
|---|---|
|
Associated Pgm |
Name of the program receiving control from the screen; default program name is screenname. |
|
Parameter |
Description
and Values |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Device Type |
Standard device characters for different model terminals and printers. Defaults are IBM-recommended device characters. See your IBM MFS or IMS installation manual for further details. |
||||
|
Cursor Feedback |
Cursor feedback fields do not affect output cursor positioning. |
||||
|
DIF-DOF Name |
Override APS-generated name. Default reflects the number of characters in the screen name, as follows. 4-character name: screennameDF |
||||
|
Optional Fld Name |
Specify fieldname or MFS PFKEY to hold the trancode or operator logical paging command. Alternatively, enter *PF and assign the PF key value on the MFS Function Keys screen, or *TC and construct a trancode on the Trancode Construction screen. |
||||
|
MID Segment Exit: |
Generate the EXIT parameter on the MID segment statement with
Number as the exit routine number and Vector as the exit vector number. Valid
values are: |
||||
|
Opr Logical Paging |
|
||||
|
MID Name |
Override APS-generated name. Default reflects the number of characters in the screen name, as follows. 4-character name: screennameMI |
||||
|
MID Default Values |
|
||||
|
MOD Name |
Override APS-generated name. Default reflects the number of characters in the screen name, as follows. 4-character name: screennameMO |
||||
|
MOD Fill Char |
Generate fill characters in the MOD seqment statement. Valid characters are --, NULL, PT, C, or 'x', where x is any character value. |
||||
|
DSCA |
Override the Default System Control Area default value of X'00A0'. |
||||
|
"Labeled" Screen |
|
||||
|
Lines Per Page |
If device type is a printer, specify number of lines to print on a page. |
||||
|
Trancode: |
Specify any literal value as the trancode. Default is the screen name. |
Database call clause (see Database Calls)
SQL target
Apply column functions to data elements that are collected into groups and define a hierarchy for these groups.
This statement:
DB-PROCESS REC EMPLOYEE-REC ... DB-PROCESS-ID D2EMP ... EMP-DEPT ... MAX(EMP-SALARY) ... WHERE EMP-NAME NOT NULL ... GROUP BY EMP-DEPT ... ORDER BY EMP-DEPT
Results in:
EMP-DEPT EMP-SALARY -------- ---------- FIN001 66700.000 FIN201 45250.000 MKT001 72300.000 PAY001 68800.000 PAY002 43500.000 SYS001 75000.000
This statement, which first groups rows by EMP-DEPT number, then within department by EMP-SEX, and then calculates maximum rates and salaries for each group:
DB-PROCESS REC EMPLOYEE-REC ... DB-PROCESS-ID D2EMP ... EMP-DEPT ... EMP-SEX ... MAX(EMP-RATE) ... MAX(EMP-SALARY) ... WHERE EMP-NAME NOT NULL ... GROUP BY EMP-DEPT,EMP-SEX ... HAVING COUNT(*) > 2 ... AND MIN(EMP-RATE) > 3 ... ORDER BY EMP-DEPT,EMP-SEX
Results in:
EMP-DEPT EMP-SEX EMP-RATE EMP-SALARY --------- ------- --------- ---------- FIN001 F 32.067 66700.000 FIN001 M 31.105 64700.000 FIN201 F 19.711 41000.000 FIN201 M 21.754 45250.000 PAY001 F 33.076 68800.000 PAY001 M 31.884 66320.000 SYS001 F 32.692 68000.000 SYS001 M 36.058 75000.000
IMS database calls
IMS DB target
Access GSAM databases.
IM-CLSE view IM-OPEN view IM-OPEN-INP view IM-OPEN-OUT view IM-OPEN-OUTA view IM-OPEN-OUTM view IM-GN PCBname [ssa1 [...ssa15]] IM-GU PCBname ssa1 [...ssa15] IM-ISRT PCBname [ssa1 [...ssa15]]
|
pcbname |
Database view; can be up to 20 characters. Default is IO-PCB. |
|
ssa |
SSA (record search) arguments that trigger COBOL MOVEs to or from the generated I/O area IM-IO-AREA. Default is IM-IO-AREA with a length of 32,000 bytes; set IM-IO-AREA-LEN in your program or DDISYMB member to override the length. Specify only one SSA per hierarchical level along a path. These arguments generate 8-byte records in Working-Storage to hold the corresponding values. |
|
view |
Database view. Must correspond to a GSAM PCB. |
The following code:
$IM-OPEN ("PARDBINP")
$IM-OPEN-INP ("PARDBINP")
$IM-GN ("PARDBINP")
Generates in the Procedure Division:
CALL 'CBLTDLI' USING ... IM-OPEN PARDBINP-PCB MOVE PARDBINP-STATUS TO IM-STATUS MOVE 'INP' TO IM-IO-AREA CALL 'CBLTDLI' USING ... IM-OPEN PARDBINP-PCB ... IM-IO-AREA MOVE PARDBINP-STATUS TO IM-STATUS CALL 'CBLTDLI' USING ... IM-GN PARDBINP-PCB ... GSAM-IN-IO-AREA MOVE PARDBINP-STATUS TO IM-STATUS
Copyright © 2002 Micro Focus International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.