APS enforces the following size and programming limitations.
|
Item |
Max |
|---|---|
|
24 |
|
Item |
Max |
|---|---|
|
50 |
|
|
Nested macros |
139 |
|
Macro call arguments |
1000 |
|
Nested INCLUDEs |
10 |
|
|
|
|
Subscripts |
300 |
|
12 |
|
System limits |
|
|
8 |
|
Item |
Max |
|---|---|
|
50 |
|
|
Record name occurrences |
20 |
|
Field qualification occurrences |
70 |
|
Scrolling for repeated blocks |
1 |
|
Field mapping for repeated blocks |
2 |
|
Subschema limits |
|
|
130 |
|
Item |
Max |
|---|---|
|
Application Painter |
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
500 |
|
400 |
|
Item |
Max |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
Number of reports for FD |
15 |
|
Number SOURCE/SUM/ VALUE statements per program |
300 |
|
Item |
Max |
|---|---|
|
600 |
|
|
Characters in paragraph name |
24 |
|
Indentation levels per nested IF structure |
14 |
|
Paragraph arguments per program |
400 |
|
|
|
|
255 |
|
Symbol table entries (such as, paragraph names, file names, record names, verbs,section names, keywords, arguments, indexes, flags) |
1801 |
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
Transfer control and optionally send Commarea data from a CICS program at one logical level to a CICS APS or non-APS application subprogram; or, transfer control to an IMS or ISPF Dialog subprogram.
Format 1, link to an APS program:
[TP-]LINK programname [errorpara] ... [DLIUIB pcbname [pcbname] ...] ... [userparm [userparm]...] ... [COMMAREA(dataarea) LENGTH(value)]|[NOCA]
Format 2, linking to a non-APS program:
[TP-]LINK programname(NONAPS)[errorpara] ... [COMMAREA(dataarea) LENGTH(value)]|[NOCA]
Format 1, CALL format:
[TP-]LINK programname [errorpara] ... [userparm [userparm]...] ... [COMMAREA]
[TP-]LINK subprogram [errorpara] [argument1 ... argument36]
Format 1, CALL format:
[TP-]LINK programname [errorpara] ... [userparm [userparm]...] ... [COMMAREA]
Format 2, SELECT format:
[TP-]LINK programname ... [errorpara] ... [options]
[TP-]LINK programname [errorpara] ... [COMMAREA(dataarea) LENGTH(value)]|[NOCA]
Additionally, code the following before your NTRY statement:
%
&TP-PROGRAM-INVOCATION = "NONAPS"
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
% &DLG-COMMAREA-IN-LINKAGE = 'YES'
Link to PGM001. No PSB is active and no arguments pass.
LINK PGM001
Link to the program stored in WS-PROGNAME. No PSB is active and no arguments pass.
LINK /WS-PROGNAME
Move the value PGM003 to WS-PROGNAME and link to that program.
LINK PGM003/WS-PROGNAME
Link to PGM004; execute an error routine for an abnormal condition. There is no active PSB and no arguments pass.
LINK PGM004 ERROR-PARA
Link to PGM005. Schedule a PSB and use a PCB named ABC-PCB for the linked-to program. Omit the positional parameter errorpara .
LINK PGM005 * DLIUIB ABC-PCB
Link to PGM006 and pass a Linkage data area SCR6-RECORD so that PGM006 can move data directly to screen fields.
LINK PGM006 * SCR6-RECORD
Link to PROG001, a non-APS program, passing TP-USERAREA only.
LINK PROG001(NONAPS)
Link to PROG002, a non-APS program, passing the data area WS-COMMAREA.
LINK PROG002(NONAPS) * COMMAREA(WS-COMMAREA) LENGTH(100)
Link to PROG003, a non-APS program, without passing a COMMAREA.
LINK PROG003(NONAPS) * NOCA
The following examples show the CALL statements generated in the program after linking to subprograms.
Coding LINK SUBPGM * ARG1 ARG2 ARG3 Yields CALL 'SUBPGM' USING TP-COMMAREA ARG1 ARG2 ARG3 Coding LINK SUBPGM * *NOSPA ARG1 ARG2 ARG3 Yields CALL 'SUBPGM' USING ARG1 ARG2 ARG3 Coding LINK SUBPGM * ARG1 TP-USERAREA ARG2 ARG3 Yields CALL 'SUBPGM' USING ARG1 TP-USERAREA ARG2 ARG3
Invoke PGM001 as a new program function. The SELECT service option NEWPOOL creates a new shared variable pool. The SELECT option is in effect.
LINK PGM001 * NEWPOOL
Invoke PGM001 as a new program function. The SELECT service option PARM passes data to PGM001 via LINKAGE SECTION. To pass variable data, VDEFINE a dialog variable. The SELECT option is in effect.
DLG-VDEFINE 01 WS-EMPL-NBR PIC X(05) AS EMPNBR
MOVE EMPL-NBR TO WS-EMPL-NBR
LINK PGM001 * PARM('&EMPNBR')
DLG-VDELETE EMPNBR
Link to the program in WS-PROGNAME. The CALL option is in effect.
MOVE 'PGM001' TO WS-PROGRAM LINK /WS-PROGNAME
Link to PGM006 and pass Linkage data area SCR6-RECORD so that PGM006 can move data directly to screen fields. The CALL option is in effect.
LINK PGM006 * SCR6-RECORD
Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Create or include data structures in the Linkage Section.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 LK kywd associated data structure
|
kywd |
Associated data structure keywords are: 01, DS, REC, See SQL, ++, or 01. |
Code Working-Storage and Linkage data structures using section keywords.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
IO INPUT-FILE ASSIGN TO UT-S-INPUT
FD INPUT-FILE
LABEL RECORDS ARE STANDARD
BLOCK CONTAINS 0 RECORDS
01 INPUT-REC PIC X(80).
WS
REC WS-INPUT-REC.
WS-IN-PART-NO N8
WS-IN-DESC X50
WS-IN-BASE-PRICE N6V2
++ PANWSREC
LK
REC LK-INPUT-REC
LK-IN-PART-NO N8
LK-IN-DESC X50
LK-IN-BASE-PRICE N6V2
01 LK-OUT-REC.
DS05 LK-OUT-REC APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Macro/Program Cross Reference Report lists the macros used in one or more applications, along with all of the programs that invoke the macros, and the macro libraries that the programs reside in. Use the report to find all the programs and applications that use a given macro.
The cross-referenced macros appear alphabetically within an application on the report. If you report on all applications, the applications display alphabetically in the report. Specific macro libraries are listed as follows.
After each application, summary statistics provide the:
Produce the Macro/Program Cross Reference Report from the Documentation Facility.
REPORT CODE: MC01 APS APPLICATION PAINTER PAGE 1
MACRO/PROGRAM CROSS REFERENCE 01/17/92 08:26
MKTAPS.MKT2
SELECTION CRITERIA: TDDEMO
APPLICATION: TDDEMO
*********************************************************************************
MACROLIB. PROGRAM / STUB TYPE NO.OF TIMES
NAME OF MACRO / MACROLIB: IND. USING MACRO IND MACRO CALLED
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CLEAR TDCM 1
TDOM 1
TDPM 1
DB-ERASE TDCM 1
TDOM 1
TDPM 1
.
.
.
PX-CA-COMPUTE-LEN TDOM 1
.
.
.
TP-ATTR TDOM 13
TDOT 1
TP-PERFORM TDCM 36
TDCS 27
TDME 3
TDOJ 27
TDOM 80
TDOT 16
TDOU 9
TDPF 7
TDPL 27
TDPM 36
.
.
.
XCTL TDCM 1
TDCS 1
TDME 7
TDOJ 1
TDOM 1
TDOT 1
TDOU 1
TDPF 1
TDPL 1
TDPM 1
TOTAL MACROS & LIBRARIES REPORTED 14
NO. OF PGMS. WITH MACRO CALL IN CODE 10
NO. OF COMMON MACROLIBS IN APPLN. 0
TOTAL NO. OF PROGRAMS IN APPLN. 10 IMS DC target
Screen Painter feature
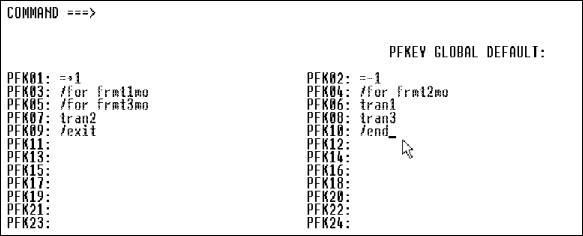
Assign trancodes, operator logical paging, other IMS commands, and nulls or spaces to the MFS PF key fields.
To define MFS function key values, follow these steps.

IMS DC target
Screen Painter feature
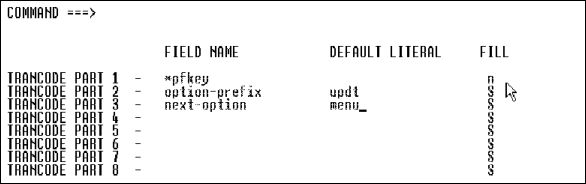
Construct trancodes of up to eight parts by concatenating screen fields, literals, and PF keys.
To create a trancode, follow these steps.
| Field |
Description and Values |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Field Name |
Enter name of field or *pf. If you enter *pf, specify PF key values on the MFS Function Keys screen. If you specify a field, APS ignores all field attributes, including an initial value entered in the Value field. You must enter the initial value in the Default Literal field. |
||||
|
Default Literal |
Enter any literal. If you supply a literal on the same line as a field name or *PFKEY, APS transmits the literal in the MID when no value is entered for the field or when the PF key is not invoked. |
||||
|
Fill |
Enter the MID fill character for the associated field name or *PFKEY.
|
Define a trancode definition, consisting of a function key (values specified in the MFS Function Keys example on Example:), and the fields OPTION-PREFIX and NEXT-OPTION. If the end user enters no values in these two fields, the literal UPDTMENU transmits in the MID.
IMS DC target
Screen Painter feature
Change the MID/MOD order in which the I/O fields from your screen appear in the generated Working-Storage. Do so to meet any site standards that require transmittal of screen data in a particular order.
To change the order in which your I/O fields appear in the generated Working-Storage, follow these steps.
Reorder the fields in the first screen. The second screen sequences ERR-MSG after PAGING in the Working-Storage Section. The third screen shows the result.



Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Batch environments
Specify the report mock-up name in your report program.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 MOCK mockupname
Mockupname is the name entered in the Reports field associated with your program in the Application Painter and painted in the Report Painter.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
RED STOCK-REPORT
CONTROLS ARE FINAL WS-LOCATION-CODE
PAGE LIMIT IS 50
FIRST DETAIL 10
LAST DETAIL 40
FOOTING 47.
MOCK STCKPRT
01 TYPE IS REPORT HEADING NEXT GROUP
NEXT PAGE LINE 20.
MOCKUP LINES 1 THRU 6
SOURCE WS-DATE Report Writer statement (see Report Writer Structures and the APS User's Guide chapter Create Reports with Report Writer.)
Batch environments
In your report program, specify the line numbers in the report mock-up that correspond to the detail lines, headers, and footers.
MOCKUP|M LINE|LINES linenumber1 [THRU linenumberN]
Specify that lines 1 through 8 in the report mock-up contain the heading text.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
01 TYPE IS REPORT HEADING LINE 20 NEXT GROUP
NEXT PAGE.
MOCKUP LINES 1 THRU 8 APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Mock-Up Report contains a representation of a report mock-up as painted in the Report Painter. When produced from the Report Generator, the report includes line numbers. This report documents a key aspect of an application for end users to review or for developers to use when maintaining or enhancing the application.
The Report Options screen displays. Specify y(es) to print line numbers or n(o) if you do not want to print them.
REPORT CODE: REPT APS ENTITY REPORT FACILITY PAGE 1
CLSAPS.CLS2 01/18/92 15:01
REPORT CRITERIA: 2
ALL MEMBERS OF LIBRARY TYPE : RP
*********************************************************************************************
LIBRARY ENTITY
TYPE NAME STATUS REMARKS
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RP COSTRPT REPORTED
RP MERPT REPORTED
REPORT CODE: RP01 APS APPLICATION PAINTER PAGE 1
APPLICATION DEFINITION REPORT 01/18/92 15:01
CLSAPS.CLS2
SELECTION CRITERIA: COSTRPT
*******************************************************************************************
REPORT: COSTRPT CREATED: 07/27/90
AUTHOR: CLSONE UPDATED: 07/27/90
*************************************************************************************************
USER MANUFACTURING COMPANY
EXPENDITURES REPORT AS OF XXXXXXXX
NO CUMULATIVE
MONTH DAY DEPT PURCHASES ITEM COST COST
XXXXXXXXX EXPENDITURES
XXXXXXXXX XX XXX 2Z9 X ZZ9.99
TOTAL COSTS FOR W/E XXXXXXXXX XX Z,ZZ9.88 ZZ,ZZ9.99
TOTAL COSTS FOR XXXXXXXXX ZZ,ZZ9.99
TOTAL EXPENDITURES FOR YEAR-TO-DATE ZZZ,ZZ9.99
PAGE ZZZ9
END OF REPORT
REPORT CODE:RP01 APS APPLICATION PAINTER PAGE 1
APPLICATION DEFINITION REPORT 01/18/92 15:01
CLSAPS.CLS2
SELECTION CRITERIA: MERPT
*******************************************************************************************
REPORT: MERPT CREATED: 08/24/90
AUTHOR: CLSTRA UPDATED: 08/24/90
*************************************************************************************************
USER MANUFACTURING COMPANY
EXPENDITURES REPORT AS OF XXXXXXXX
NO CUMULATIVE
MONTH DAY DEPT PURCHASES ITEM COST COST
XXXXXXXX EXPENDITURES
XXXXXXXX XX XXX 2Z9 X ZZ9.99
TOTAL COSTS FOR W/E XXXXXXXX XX Z,ZZ9.99 ZZ,ZZ9.99
TOTAL COSTS FOR XXXXXXXX ZZ,ZZ9.99
TOTAL EXPENDITURES FOR YEAR-TO-DATE ZZZ,ZZ9.99
PAGE ZZZ9
END OF REPORT Under normal screen processing, the MDT (Modified Data Tag) attribute must be turned on for each field when you use Field Edits with an updateable program. This causes the end user workstation or terminal to always send all field modified or unmodified data to the program.
Transmission of data is more efficient if MDT is turned off, but then only the data modified by the end user is returned to the program, and the unmodified data is lost, which is of course, undesirable. To turn off the MDT tag and not lose unmodified data, follow these steps.
$TP-MDTOFF-READQ-TS-ERROR
$TP-MDTOFF-WRITEQ-TS-ERROR
$TP-MDTOFF-DELETEQ-TS-ERROR
As shipped, these macros generate a CICS-SEND-TEXT call to display appropriate error messages, and a TERM to terminate the program. You can change these macros to conform to your shop standards.
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
IMS DC and ISPF Prototyping targets
Send a data or a message to the specified program trancode or subprogram.
[TP-]MSG-SW trancode|programname|dataname [errorpara] ... [screenname|recordname] ... [keyword[+keyword]...]
[TP-]MSG-SW trancode|programname|dataname [errorpara] ... [screenname]
Send messages to another program; perform error routine when error occurs.
MSG-SW trancode PROCESS-ERRORS
Send messages and pass a screen record. Note that the asterisk (*) replaces the positional parameter errorpara.
MSG-SW trancode * SCRA
Send messages and pass a COBOL record.
MSG-SW trancode * WS-CUSTOMER RECORD
Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Generate a program template that fully defines all parts of your program except for the procedural code that you supply.
NTRY generates a program template that defines:
In CICS programs, NTRY also generates code to:
In ISPF Dialog programs, NTRY also generates code to display screens.
In IMS programs, NTRY also generates code to:
NTRY|ENTR screenname(mapsetname)] ... [errorpara] ... [RETRY|NORETRY]
Format 1:
NTRY|ENTR
Format 2:
NTRY|ENTR screenname ... [errorpara] ... [RETRY|NORETRY]
Format 3:
NTRY|ENTR recordname ... [errorpara] ... [RETRY|NORETRY] ... *RECORD
NTRY|ENTR screenname ... [errorpara] ... [RETRY|NORETRY] ... [CANCEL|RETURN] ... [dataareas]
NTRY|ENTR screenname ... [RETRY|NORETRY] ... [CANCEL|RETURN] ... [dataareas]
|
CANCEL |
Default. Generate CONTROL ERRORS CANCEL (return control to ISPF when dialog error of return code 12 or higher). |
|
dataareas |
Generate the PROCEDURE DIVISION USING statement. List user-defined data areas only, not records defined by TP-COMMAREA, TP-LINKAGE, and SCRNLIST, which automatically generate other data areas. APS generates data areas in the following order. Data areas listed with NTRY.
|
|
errorpara |
User-defined error routine to perform when an abnormal condition occurs. Errorpara is positional; if omitted, code an asterisk (*) in its place. |
|
mapsetname |
Mapset containing the screen(s) the program receives; must be a literal (maximum 7 characters). See also Comments: for CICS below. |
|
NORETRY |
Accept invalid data in screen fields with assigned edits. See also Comments: below. |
|
*RECORD |
Code when using recordname instead of screenname as input. |
|
recordname |
User-defined I/O area in Working-Storage, long enough for any input message that can be received. The area receives the data returned from the GU to the program control block. For a conversational program, the program reads the ASPA with a GU, and the input message with a GN. It does not expect a multisegment input message. PF keys are not generated; you must code them. |
|
RETRY |
Default. Accept only valid data in screen fields with assigned edits; otherwise, return screen to the terminal user for correction. See also "Comments" below. |
|
RETURN |
Generate CONTROL ERRORS RETURN to return control to program when dialog error occurs. See also Comments: below. |
|
screenname |
Screen name; value must be literal (maximum 8 characters). |
Code an NTRY, PROC, or OPT statement for each program.
It is possible, however, to accept screens with data that does not pass editing. When NORETRY is coded, the application logic executes regardless. A set of runtime flags allow application logic to determine the success or failure of editing.
|
APS-EDITS-PASSED |
88-level flag set to true when data for all edited fields is valid. Code IF APS-EDITS-PASSED to test whether the edit is OK. |
|
screenname-fieldname-FLAG |
Indicator flag set to spaces when data for a specified field valid. Code IF screenname-fieldname-FLAG = SPACES to test whether the data is valid. |
|
screenname-fieldname-INPT |
APS-generated data field; contains data exactly as entered if the field failed to pass editing. |
|
APS-MSG-IO-ERROR |
Applies to IMS DC only. 88-level flag set to true when a program sends a user-defined I/O error message. Code IF APS-MSG-IO-ERROR to test if message sent. |
|
APS-MSG-EDIT-ERROR |
88-level flag set to true when a program sends a user-defined edit error message. Code IF APS-MSG-EDIT-ERROR to test if the message is sent. |
| Screen Name Length |
Generated
Mapset Name |
|---|---|
|
4 characters |
screennameSET |
|
5 characters |
screenname$ |
|
6 characters |
screenname$ |
|
7 characters |
Last character of screenname changes to $ |
|
8 characters |
Truncates eighth character of screenname; seventh character changes to $ |
| User Macro Name |
Where
Included |
|---|---|
|
TP-ENTRY-EXIT-1 |
Bottom of APS-HOUSEKEEPING-PARA |
|
TP-ENTRY-EXIT-2 |
After APS-HOUSEKEEPING-PARA |
It is possible, however, to accept screens with data that does not pass editing. When NORETRY is coded, the application logic executes regardless. A set of runtime flags allow application logic to determine the success or failure of editing.
|
APS-EDITS-PASSED |
88-level flag set to true when data for all edited fields is valid. Code IF APS-EDITS-PASSED to test whether the edit is OK. |
|
screenname-fieldname-FLAG |
Indicator flag set to spaces when data for a specified field valid. Code IF screenname-fieldname-FLAG = SPACES to test whether the data is valid. |
|
screenname-fieldname-INPT |
APS-generated data field; contains data exactly as entered if the field failed to pass editing. |
|
APS-MSG-IO-ERROR |
Applies to IMS DC only. 88-level flag set to true when a program sends a user-defined I/O error message. Code IF APS-MSG-IO-ERROR to test if message sent. |
|
APS-MSG-EDIT-ERROR |
88-level flag set to true when a program sends a user-defined edit error message. Code IF APS-MSG-EDIT-ERROR to test whether if message sent. |
The APS/IMS DC Generator creates programs consistent with this practice. Termination DC calls (SEND, MSG-SW, TERM) do not terminate a program, but instead return control to NTRY-generated logic to receive a new input message.
Because a program may process multiple messages in a single execution, you program should perform any Working-Storage initialization in the Procedure Division, rather than in Working-Storage using the VALUE clause. You can still use the VALUE clause to initialize Working-Storage constants that are never changed during execution.
| User Macro Name |
Where
Included |
|---|---|
|
TP-ENTRY-EXIT-1 |
Bottom of APS-HOUSEKEEPING-PARA |
|
TP-ENTRY-EXIT-2 |
After APS-HOUSEKEEPING-PARA |
|
TP-ENTRY-EXIT-2S |
After screen message is sent |
|
TP-ENTRY-EXIT-3 |
At end of $TP-ENTRY macro |
It is possible, however, to accept screens with data that does not pass editing. When NORETRY is coded, the application logic executes regardless. A set of runtime flags allow application logic to determine the success or failure of editing.
|
APS-EDITS-PASSED |
88-level flag set to true when data for all edited fields is valid. Code IF APS-EDITS-PASSED to test whether the edit is OK. |
|
screenname-fieldname-FLAG |
Indicator flag set to spaces when data for a specified field valid. Code IF screenname-fieldname-FLAG = SPACES to test whether the data is valid. |
|
screenname-fieldname-INPT |
APS-generated data field; contains data exactly as entered if the field failed to pass editing. |
|
APS-MSG-IO-ERROR |
Applies to IMS DC only. 88-level flag set to true when a program sends a user-defined I/O error message. Code IF APS-MSG-IO-ERROR to test if message sent. |
|
APS-MSG-EDIT-ERROR |
88-level flag set to true when a program sends a user-defined edit error message. Code IF APS-MSG-EDIT-ERROR to test whether if message sent. |
Generate code to receive screen SCRA when the program is screen-invoked. Specify that the program can receive a screen that contains invalid data. Omit the error paragraph.
-KYWD- 12--*--20---*----30----*---40---*----50---*----60 NTRY SCRA * NORETRY
Receive multiple screens and include an error routine. Note that when you use SCRNLIST, you do not specify any screens in the NTRY statement.
-KYWD- 12--*--20---*----30----*---40---*----50---*----60 SYM1 SCRNLIST C1ORDR C2ORDR C3ORDR NTRY * PROCESS-ERRORS
Generate code to receive screen CUSTORDR in mapset CUSTOR$ for a screen-invoked program. Perform MAP-ERROR-PARA when an exceptional condition occurs on the RECEIVE MAP.
-KYWD- 12--*--20---*----30----*---40---*----50---*----60 NTRY CUSTODR(CUSTOR$) MAP-ERROR-PARA
Receive a message into a COBOL record I/O area.
-KYWD- 12--*--20---*----30----*---40---*----50---*----60 NTRY WS-CUSTOMER * *RECORD
Generate code to display screen SCRA. Perform PROCESS-ISPF-ERRORS when return codes from services are greater than 12. Generate CONTROL ERRORS RETURN code so the program can control all error processing.
-KYWD- 12--*--20---*----30----*---40---*----50---*----60 NTRY SCRA PROCESS-ISPF-ERRORS RETURN
Generate code to display screen SCRA. Perform PROCESS-ISPF-ERRORS when return codes from services are greater than 12. Generate CONTROL ERRORS RETURN code so the program can control all error processing.
-KYWD- 12--*--20---*----30----*---40---*----50---*----60 NTRY SCRA PROCESS-ISPF-ERRORS RETURN
SQL target
Use a null indicator variable to indicate whether the associated host variable has been assigned a null value.
APS/SQL generates a null indicator variable in Working-Storage, defined as follows.
01 IND-cursorname|IND-recordname
05 IND-column
Data Structure Painter construct (see Data Structures)
Code OCCURS clauses in your data structures.
dataname(OCCURSclause) [TIMES] [... DO|ODO dataname] [... IX|IB|IXB|IXBY dataname] [... ASCENDING KEY IS dataname] [... DESCENDING KEY IS dataname] ... PICformat
Shorthand syntax for the dimensions of a table in an OCCURS clause.
|
OCCURS Format |
Generated
Code |
|---|---|
|
(number) |
OCCURS number |
|
(number) TIMES |
OCCURS number TIMES |
|
(number1-number2) |
OCCURS number1 TO number2 |
|
(number1 TO number2) |
OCCURS number1 TO number2 |
|
(&variable) |
OCCURS &variable |
|
(&variable1 TO &variable2) |
OCCURS &variable1 TO &variable2 |
|
DO|ODO |
Generates DEPENDING ON |
|
... IX|IXB|IXBY|IB |
Generates INDEXED BY |
Always code an INDEXED BY clause on a continuation line.
Data Structure Painter format:
-LINE- ------- Data Structure Painter -------- 000001 EXDS-TABLE 000002 EXDS-TABLE-3 (1-99) 000003 ... ODO EXDS-TABLE-3-SIZE 000004 ... IXB EXDS-INDEX 000005 ... X20
Generated COBOL code:
01 EXDS-TABLE.
05 EXDS-TABLE-3 OCCURS 1 TO 99
DEPENDING ON
EXDS-TABLE-3-SIZE
INDEXED BY EXDS-INDEX
PIC X(20).
Data Structure Painter format:
-LINE- ------- Data Structure Painter -------- 000001 TYPE-DESC-RATE-CONSTANTS X90 000002 TYPE-DESC-RATE-TABLE-REDEF R 000003 TYPE-DESC-RATE-TABLE (30) 000004 ... ASCENDING KEY IS TYPE-CODE 000005 ... IXB DATA-INDEX 000006 TYPE-CODE X 000007 DESC-CODE X 000008 RATE-CODE X
Generated COBOL code:
01 TYPE-DESC-RATE-CONSTANTS PIC X(90).
01 TYPE-DESC-RATE-TABLE-REDEF REDEFINES
TYPE-DESC-RATE-CONSTANTS.
05 TYPE-DESC-RATE-TABLE OCCURS 30
ASCENDING KEY IS TYPE-CODE
INDEXED BY DATA-INDEX.
10 TYPE-CODE PIC X.
10 DESC-CODE PIC X.
10 RATE-CODE PIC X.
Data Structure Painter format:
-LINE- ------- Data Structure Painter -------- 000001 LOAN-RATE-TABLE 000002 LOAN-RATE-ROW OCCURS 10 TIMES 000003 ... ASCENDING KEY IS TYPE-CODE 000004 ... IXB DATA-INDEX 000005 TYPE-CODE PIC X(05)
Generated COBOL code:
01 LOAN-RATE-TABLE.
05 LOAN-RATE-ROW OCCURS 10 TIMES
ASCENDING KEY IS TYPE-CODE
INDEXED BY DATA-INDEX.
10 TYPE-CODE PIC X(05). Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Programs created in Program Painter
Suppress the mainline program section generated by the NTRY or PROC keyword, in order to supply your own screen and program invocation logic. Use OPT only in programs with screens.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 NTRY| PROC OPT PROG
Report Writer statement (see Report Writer Structures and the APS User's Guide chapter Create Reports with Report Writer)
Batch environments
Print one line on top of the other without advancing the line printer. Use this feature to create bold text or to underscore text.
OVERPRINT|O WHEN 'characterstring' AT COLUMN integer
|
characterstring |
Line or text to be overprinted; must be identical to characterstring in mock-up; delimit with single or double quotation marks. |
|
integer |
Starting column number of characterstring on the mock-up. |
In the mock-up, the two lines of text that print on one line of the page must be consecutive. On the first line enter a text string. On the second line enter the text that prints over the first line, and to the right of this text enter a unique characterstring to identify the line. When the report prints, blanks replace characterstring in the mock-up.
Underscore text within a page heading. Below are lines 7 and 8 of a mock-up. The identifying character string, NO ADVANCING, begins in column 70 of the second line.
XXXXXXX _______ NO ADVANCING
The OVERPRINT clause:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
01 TYPE IS PAGE HEADING.
MOCKUP LINES 7 THRU 9
OVERPRINT WHEN 'NO ADVANCING' AT COLUMN 70
The printed result:
XXXXXXX
Print text within the report heading of a mock-up twice, to appear as bold type. The identifying character string begins in column 70.
WIDGETS WIDGETS DITTO
The OVERPRINT statement:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
01 TYPE IS REPORT HEADING LINE 20 NEXT GROUP NEXT PAGE.
MOCKUP LINES 1 THRU 6
OVERPRINT WHEN 'DITTO' AT COLUMN 70
The printed result:
WIDGETS
Report Writer clause (see Report Writer Structures and the APS User's Guide chapter Create Reports with Report Writer)
Batch environments
Define the page length and the vertical subdivisions of a printed page.
PAGE LIMIT IS|ARE number [LINE|LINES]
[FIRST DETAIL linenumber]
[LAST DETAIL linenumber]
[FOOTING linenumber] [.]
|
number LINE|LINES |
Number of lines on each report page. Number cannot exceed 3 digits and must be greater than or equal to the FOOTING linenumber. |
|
FIRST DETAIL linenumber |
First detail line. Print control break heading and report body detail lines beginning on linenumber. Print REPORT and PAGE HEADING groups before linenumber. |
|
LAST DETAIL linenumber |
Line number of the last report body detail line. Print CONTROL FOOTING, PAGE FOOTING, and REPORT FOOTING lines after this number. Linenumber must be greater than FIRST DETAIL linenumber. |
|
FOOTING linenumber |
Last line number of the last control footing report group. Print PAGE FOOTING and REPORT FOOTING lines after this number. Linenumber must be greater than or equal to LAST DETAIL linenumber. |
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
RED STOCK-REPORT
CONTROLS ARE FINAL WS-LOCATION-CODE
PAGE LIMIT IS 50
FIRST DETAIL 10
LAST DETAIL 40
FOOTING 47. ISPF Dialog target
Screen Painter feature
Generate native panel definition statements.
To generate native panel definition statements, follow these steps.
| Field |
Description and Values |
|---|---|
|
Command Field |
Enter screen field name for the panel command field that allows end users to enter ISPF commands and prevents truncation errors when they use PF keys. Default is the first unprotected I/O field on the screen. This option generates the native )BODY CMD(variable) statement. |
|
Long Message Short Message |
Enter sysmsg, if specified on Screen Generation Parameters screen, or a screen field name for the panel long and short message fields. These fields allow the program to move literal messages to the screen. These options generate the native )BODY LMSG(variable) statement for the long message and the )BODY SMSG(variable) statement for the short message. |
|
Help Panel |
Enter the name of the panel to display, if the end user requests help. This option generates the HELP = panelname statement. |
|
Pfkey Option |
P Program controls PF key processing. APS saves the end user's original PF key values and replaces them with literals not recognized by ISPF, so that you can control the PF key usage. When the program terminates, the original PF key values are restored. See PF Key Values. I Default. ISPF controls PF key processing. |
Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Indicate a paragraph in your program code. A paragraph is a Procedure Division routine that you write and perform specifically for one program. Use paragraphs to perform the following, depending on which APS tool you use.
|
Use paragraphs in... |
To
perform... |
|---|---|
|
Online Express |
Custom actions for events; Custom routines at window events |
|
Specification Editor |
Custom routines in the Procedure Division |
|
Program Painter |
Custom routines in the Procedure Division |
Format 1:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
PARA paragraphname [SECTION.]
paragraphcode
Format 2:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60--
.
.
.
PERFORM paragraphname [(arguments)]
.
.
.
PARA paragraphname [(+|-arguments)]
statement
.
.
.
PERFORM subparagraphname [(arguments)]
PARA subparagraphname [(+|-arguments)]
statement
.
.
.
WS
01 group-level-data-item
05 elementary-data-item
.
.
.
Rules for coding paragraphs in Online Express:
Rules for coding paragraphs in the Specification Editor and Program Painter:
Anywhere in the program, use APS Data Division keywords to define any data items that the paragraphs reference.
S-COBOL structure (see S-COBOL Structures)
Depart from the normal program execution sequence to execute a particular paragraph or section and then return control to the statement immediately following the PERFORM statement.
Format 1, perform a paragraph:
PERFORM paragraphname
Format 2, perform a paragraph and pass arguments:
PERFORM paragraphname (actualargument1[[,]
... actualargument2[,] ... actualargumentN])
.
.
PARA paragraphname ([+|-]formalargument1[[,]
... [+|-]formalargument2[,] ... [+|-]formalargumentN])
|
+|- |
A plus (+) or minus (-) sign preceding a formalargument passes values between actual arguments and formal arguments, as follows.
|
|
actualargument |
Values you send to or receive from a formalargument in the paragraph; can be literals, identifiers, arithmetic expressions, variables, or index names. |
|
formalargument |
Values you receive from or send to an actualargument in the PERFORM statement. |
|
paragraphname |
Name of paragraph to perform. |
PERFORM PARA-1( 'ABC', ABC-FLD, RESULT)
.
.
.
PARA-1( +ARG1, +ARG2, -'Y')
Generates:
MOVE 'ABC' TO ARG-1
MOVE ABC-FLD TO ARG2
PERFORM PARA-1 THRU .......
MOVE 'Y' TO RESULT
Perform GET-SALARY (line 5010); pass the literal 20 to HOURS-WORKED and the value of HOURLY-RATE to PAY-RATE before calculating TOT-PAY (line 5020). After the GET-SALARY paragraph executes, pass the value of PAY-RATE to HOURLY-RATE and the value of TOT-PAY to WEEKLY-PAY.
-LINE- -KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*-- 000100 NTRY . . . 003010 IF CLASS = 'HALF-TIME' 003020 PERFORM GET-SALARY( 20, 003021 ... HOURLY-RATE, WEEKLY-PAY) 003030 ELSE 003040 PERFORM GET-SALARY( 40, 003041 ... HOURLY-RATE, WEEKLY-PAY) 003050 WEEKLY-PAY = WEEKLY-PAY * TAX 003060 COMPUTE MEDICAL-DEDUC = 003061 ... HOURLY-RATE * 1.50 . . . 005010 PARA GET-SALARY( +HOURS-WORKED, 005011 ... PAY-RATE,-TOT-PAY) 005020 TOT-PAY = HOURS-WORKED * PAY-RATE . . .
Data communications feature (see also Data Communication Calls)
CICS, IMS DC, and ISPF Dialog targets
Use the PF key 88-levels generated by APS.
PFKEY-FIELD PIC X(01).
88 ENTER-KEY VALUE '''. (single quotation mark)
88 CLEAR-KEY VALUE '_'.
88 PEN VALUE '='.
88 OPID VALUE 'W'.
88 MSRE VALUE 'X'.
88 STRF VALUE 'H'.
88 TRIG VALUE '"'. (double quotation mark)
88 PA1 VALUE '%'.
88 PA2 VALUE '>'.
88 PA3 VALUE ','.
88 PF0 VALUE '''. (single quotation mark)
88 PF00 VALUE '''. (single quotation mark)
88 PF1 VALUE '1'.
88 PF2 VALUE '2'.
88 PF3 VALUE '3'.
88 PF4 VALUE '4'.
88 PF5 VALUE '5'.
88 PF6 VALUE '6'.
88 PF7 VALUE '7'.
88 PF8 VALUE '8'.
88 PF9 VALUE '9'.
88 PF1 VALUE ':'.
88 PF11 VALUE '#'.
88 PF12 VALUE '@'.
88 PF13 VALUE 'A'.
88 PF14 VALUE 'B'.
88 PF15 VALUE 'C'.
88 PF16 VALUE 'D'.
88 PF17 VALUE 'E'.
88 PF18 VALUE 'F'.
88 PF19 VALUE 'G'.
88 PF20 VALUE 'H'.
88 PF21 VALUE 'I'.
88 PF22 VALUE '['.
88 PF23 VALUE '.'.
88 PF24 VALUE '<'.
APS assigns character values for the 24 PF keys and the ENTER key to APS-painted screens. NTRY generates logic to place this portion of the input message in a field with 88-level condition names to facilitate program testing for PF and ENTER keys.
TP-PF-KEY PIC X(132).
88 PF0 VALUE ' '.
88 PF00 VALUE ' '.
88 PF1 VALUE '1'.
88 PF01 VALUE '1'.
88 PF2 VALUE '2'.
88 PF02 VALUE '2'.
88 PF3 VALUE '3'.
88 PF03 VALUE '3'.
88 PF4 VALUE '4'.
88 PF04 VALUE '4'.
88 PF5 VALUE '5'.
88 PF05 VALUE '5'.
88 PF6 VALUE '6'.
88 PF06 VALUE '6'.
88 PF7 VALUE '7'.
88 PF07 VALUE '7'.
88 PF8 VALUE '8'.
88 PF08 VALUE '8'.
88 PF9 VALUE '9'.
88 PF09 VALUE '9'.
88 PF10 VALUE 'A'.
88 PF11 VALUE 'B'.
88 PF12 VALUE 'C'.
88 PF13 VALUE 'D'.
88 PF14 VALUE 'E'.
88 PF15 VALUE 'F'.
88 PF16 VALUE 'G'.
88 PF17 VALUE 'H'.
88 PF18 VALUE 'I'.
88 PF19 VALUE 'J'.
88 PF20 VALUE 'K'.
88 PF21 VALUE 'L'.
88 PF22 VALUE 'M'.
88 PF23 VALUE 'N'.
88 PF24 VALUE 'O'.
88 ENTER-KEY VALUE ' '.
88 NO-KEY-USED VALUE LOW-VALUES.
During screen painting, if you paint PF key values or use a PF key to supply all or part of the trancode value, you cannot use the above facility for PF key testing.
TP-PF-KEY PIC X(04).
88 ENTER-KEY VALUE ' '.
88 PF1 VALUE 'PF01'.
88 PF01 VALUE 'PF01'.
88 PF2 VALUE 'PF02'.
88 PF02 VALUE 'PF02'.
88 PF3 VALUE 'PF03'.
88 PF03 VALUE 'PF03'.
88 PF4 VALUE 'PF04'.
88 PF04 VALUE 'PF04'.
88 PF5 VALUE 'PF05'.
88 PF05 VALUE 'PF05'.
88 PF6 VALUE 'PF06'.
88 PF06 VALUE 'PF06'.
88 PF7 VALUE 'PF07'.
88 PF07 VALUE 'PF07'.
88 PF8 VALUE 'PF08'.
88 PF08 VALUE 'PF08'.
88 PF9 VALUE 'PF09'.
88 PF09 VALUE 'PF09'.
88 PF10 VALUE 'PF10'.
88 PF11 VALUE 'PF11'.
88 PF12 VALUE 'PF12'.
88 PF13 VALUE 'PF13'.
88 PF14 VALUE 'PF14'.
88 PF15 VALUE 'PF15'.
88 PF16 VALUE 'PF16'.
88 PF17 VALUE 'PF17'.
88 PF18 VALUE 'PF18'.
88 PF19 VALUE 'PF19'.
88 PF20 VALUE 'PF20'.
88 PF21 VALUE 'PF21'.
88 PF22 VALUE 'PF22'.
88 PF23 VALUE 'PF23'.
88 PF24 VALUE 'PF24'.
To let your program control PF key values, specify P(rogram controlled) in the PFKEY Option field on the ISPF Panel Options screen. See Panel Options, ISPF Dialog.
Application generation
Define variations and special features for program precompilation.
| Option |
Description and Values |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Apost |
Override Quote.
|
||||||||
|
Quote |
Override Apost.
|
||||||||
|
SCBtrace |
|
||||||||
|
RWT |
Note: For very large Report Writer programs, enter rwt=bigrwt in the APS Parm field on the Generator Options screen. |
||||||||
|
Lang |
Indicate which type of source to process and which columns to process.
|
||||||||
|
XLATE |
Specify which processing step(s) that APS performs. You can stop processing at any of the steps listed below to help isolate the step at which errors occur. The steps are listed in the order in which APS executes them. All options except ALL are mutually exclusive.
|
||||||||
|
MockupFMP |
|
||||||||
|
SUBR |
|
||||||||
|
Narrow |
|
||||||||
|
Evalmess |
|
||||||||
|
Seq |
Specifiy the type of sequence numbers that APS generates. See also, Genident, Spaceident, Ident.
|
||||||||
|
Syntax |
Specify which compiler to use.
|
||||||||
|
Emark |
Generate a three-character string marking error and warning messages in the message report.
|
||||||||
|
Genseq |
Override Spaceseq.
|
||||||||
|
Spaceseq |
Override Genseq.
|
||||||||
|
Genident |
See also, Spaceident, Ident, Seq.
|
||||||||
|
Spaceident |
See also, Genident, Ident, Seq.
|
||||||||
|
Main |
Specify location of the main input source.
|
||||||||
|
Ident |
See also, Genident, Spaceident, Seq.
|
||||||||
|
FMP |
|
||||||||
|
Source |
|
||||||||
|
Gendirect |
|
||||||||
|
Gencomment |
|
||||||||
|
Usernames |
Note: To generate any other prefix, enter the following in the APS Parm field on this screen. usernames=prefix |
||||||||
|
APS Parm |
Display all Precompiler options whose default values you override. These values also display in the APS Parm field on the Generator Options screen. APS saves the values you change on the APS Parm field on the Precompiler Option screen. APS does not save values that you change in the APS Parm field on the Generator Options screen. |
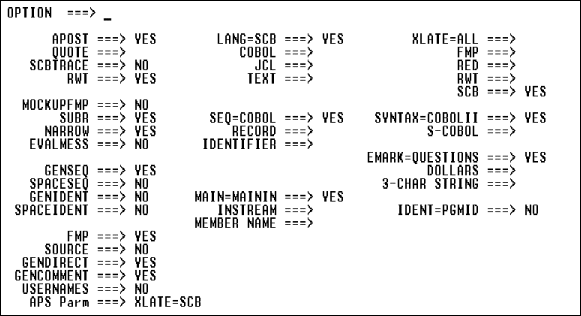
GENIDENT ===> YES SEQ=RECORD ===> YES
The generated lines are:
| Input |
S-COBOL |
|---|---|
|
00000100 |
00000002 |
|
00000200 |
00000004 |
|
00000300 |
00000006 |
Generate sequence numbers in columns 73-80, with 00 in columns 73-74.
GENIDENT ===> YES SEQ=IDENTIFIER ===> YES
The generated lines are:
| Input |
S-COBOL |
|---|---|
|
00000001 |
00000001 |
|
00000002 |
00000002 |
|
00000003 |
00000003 |
XLATE=RED ===> YES
Process S-COBOL, and report mock-ups but do not process the APS macros or user-defined Customization Facility macros.
XLATE=RED ===> YES FMP ===> NO
Process only the APS macros and user-defined Customization Facility macros, columns 1-80. You must supply your own JCL to support this override.
XLATE=FMP ===> YES LANG=TEXT ===> YES
MAIN=MEMBER NAME ===> XYZ
USERNAMES ===> YES
Generate the prefix xyz- for all APS-generated paragraphs, rather than the default prefix G--.
APS Parm ===> USERNAMES=XYZ-
QUOTE ===> YES NARROW ===> NO
Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Non-IMS batch programs
Generate the batch program template, including a PROCEDURE DIVISION USING clause that enables a called program to receive data from the calling program.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 PROC [variablename1 variablename2 ... variablenameN]
Program Painter code:
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 PROC REC-2 REC-2 REC-3
Generated COBOL code:
PROCEDURE DIVISION USING REC-2 REC-2 REC-3
Data communication feature (see also Data Communication Calls)
IMS DC target
APS generates an IO PCB with the following format in the Linkage Section.
LINKAGE SECTION.
01 IO-PCB.
05 IO-PCB-LTERM PIC X(8).
05 FILLER PIC X(2).
05 IO-PCB-STATUS PIC X(2).
05 IO-PCB-INPUT-PREF.
10 IO-PCB-DATE PIC S9(7) COMP-3.
10 IO-PCB-TIME PIC S9(7) COMP-3.
10 IO-PCB-MSG-SEQ PIC S9(7) COMP.
05 IO-PCB-MOD-NAME PIC X(8).
05 IO-PCB-USER-ID PIC X(8).
In an APS IMS/SQL program, code a PSB with the same name as your DB2 subschema. The PSB must specify an IO PCB (by setting CMPAT=YES in the PSBGEN). If your program uses MSG-SW, the PSB must also specify an alternate IO PCB.
APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Program DB/DC Report includes documentation summaries on the subschemas, PSBs, and screens used by a program. The Program DB/DC Report has a separate section for database views, record I/O areas, and screen I/O areas.
The Database Views section provides the following information.
The Record I/O Areas section provides information on the COBOL I/O areas for the database and file records. Records are listed alphabetically by record name.
The Screen I/O Areas section provides information on COBOL I/O areas for up to 20 screens arranged alphabetically.
Produce the Program DB/DC Report from the Documentation Facility.
REPORT CODE: PG02 APS PROGRAMMER SUBSYSTEM 01/17/92 14:29
PROGRAM DB/DC REPORT
***************************************************************************
PROGRAM: TDOM PSB/SUBSCHEMA: TDDB2
SCREENS: TDOM
***************************************************************************
TABLES/VIEWS: (DB2 RECORDS)
---------------------------
TABLE: TDCUST-REC
TABLE: TDODET-REC
TABLE: TDORDR-REC
TABLE: TDPART-REC
RECORD IO AREAS
---------------
RECORD: TDCUST-REC
****************************************************************
* DCLGEN TABLE : MKTAEA.TDCUST USER: CLSTR1 *
* LIBRARY: CLSAPS.CLS2.COPYLIB *
* MEMBER : TDCUST DATE: 90/11/27 *
* ACTION(REPLACE) TIME 13:11:44 *
* DB2 SYSTEM: DB2B *
********************************************************************
EXEC SQL DECLARE MKTAEA.TDCUST TABLE
(CM_CUSTOMER_NO CHAR(6) NOT NULL,
CM_CUSTOMER_NAME CHAR(20) ,
CM_CUSTOMER_ADDR CHAR(20) ,
CM_CUSTOMER_CITY CHAR(20) ,
CM_CUSTOMER_ZIP CHAR(9) )
END-EXEC.
******************************************************************
* COBOL DECLARATION FOR TABLE MKTAEA.TDCUST *
******************************************************************
01 TDCUST-REC.
10 CM-CUSTOMER-NO PIC X(6).
10 CM-CUSTOMER-NAME PIC X(20).
10 CM-CUSTOMER-ADDR PIC X(20).
10 CM-CUSTOMER-CITY PIC X(20).
10 CM-CUSTOMER-ZIP PIC X(9).
******************************************************************
* THE NUMBER OF COLUMNS DESCRIBED BY THE DECLARATION IS 5 *
**********************************************************************
SCREEN IO AREAS
---------------
SCREEN: TDOM FORMAT (:/D/M )
RULEDLINE:
INITIAL CURSOR (X):: :
COLOR: :: :
UNDERSCORE (U/:):: : :: :
BLINKING (B/:): :: : :: :
REVERSE VIDEO (R/:): : :: : :: :
INTENSITY (B/:/D): : : :: : :: :
PROTECT (P/U): : : : :: : :: :
01 TDOM-RECORD. : : : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-FUNCTION PIC X(1). U B : : : :: X :: :
05 TDOM-ORDER-NO PIC X(6). U B : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-SAVEKEY-1 PIC X(8). P D : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-CUSTOMER-NO PIC X(6). U B : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-CUSTOMER-NAME PIC X(20). U B : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-CUST-ENTRY-DATE PIC X(8). U B : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-ORDER-DEL-DUE-D PIC X(8). U B : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-ORDER-DEL-INSTR PIC X(20). U B : : : :: : :: :
05 TDOM-TABLE-1. : : : : : :: : :: :
10 FILLER OCCURS 5. : : : : : :: : :: :
15 TDOM-ROW-FUNCTION
PIC X(1).
15 TDOM-PART-NO PIC X(8).
15 TDOM-LINE-NO PIC X(4).
15 TDOM-PART-SHORT-DESC
PIC X(14).
15 TDOM-QTY-ORDERED
PIC X(8).
15 TDOM-QTY-BASE-PRICE
PIC X(10).
15 TDOM-TAX-CATEGORY
PIC X(1).
15 TDOM-SAVEKEY-2 PIC X(15).
05 TDOM-MESSAGE PIC X(79). P B : : : :: : :: : APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Program Definition Report produces a listing of the program code you create in the Program Painter. Use this report when you need to review program listings to troubleshoot problems, or when you need to document completed programs in your applications.
Produce the Program Definition Report from the Report Generator, Painter Menu, or Application Painter.
REPORT CODE: PG01 APS APPLICATION PAINTER PAGE 1
PROGRAM DEFINITION REPORT 01/18/92 15:10
CLSAPS.CLS2
SELECTION CRITERIA:
TDCM
*************************************************************************************
PROGRAM: TDCM CREATED: 03/19/90
TITLE :
UPDATED : 12/19/90
*************************************************************************************************
START KYWD STATEMENT LINE NO
COL ---- --------------------------------------------------------------------
8 SYM1 % INCLUDE APSMACS (APXMACS) 00010007
8 NTRY TDCM * NORETRY 00020007
12 /************************************************************ 00030007
12 /************************************************************ 00040007
12 /*** 00050007
12 /*** MAINLINE LOGIC 00060007
12 /*** 00070007
12 /************************************************************ 00080007
12 /************************************************************ 00090007
12 TP-PERFORM PX-INIT-HOUSEKEEPING 00100007
12 /************************************************************ 00110007
12 /* CONTROL POINT: - POST-SCREEN-READ 00120007
12 /************************************************************ 00130007
12 IF SC-ED-ALL-OK 00140007
16 MOVE SPACE TO TDCM-MESSAGE 00150007 CICS and IMS DB targets
When you assign a PSB to a program by naming the PSB in the Application Painter, CICS schedules only one PSB at a time. NTRY schedules the PSB. This PSB is active until the program
To ensure that your PSB remains active when you link or transfer to another program, pass the associated PCBs in the LINK or XCTL call, as shown below.
LINK programname [errorpara] ... [DLIUIB pcbname [pcbname ...]] ... [userparm [userparm]...] XCTL programname [errorpara] ... [DLIUIB pcbname [pcbname ...]]
The invoking program must pass the PCBs in the order that they are coded in the Linkage Section of the invoked program.
When a program invokes a LINK to a subprogram, and passes a scheduled PSB, it expects the PSB to remain scheduled when control returns from the subprogram. To return without terminating the PSB, use TERM because it does not terminate a PSB passed from a higher-level program. To terminate a PSB, use the CIC-TERM-PSB call.
Pass part of a scheduled PSB and two Linkage Section data areas.
LINK PROGRMB * DLIUIB ... ORDERDB-PCB ... ITEMDB-PCB ... USER-LINK-1 ... USER-LINK-2
The PSB remains scheduled at the start of the next program.
Application generation
Identify application project and group location and where you want APS to generate the project and group DDIFILE dataset.
| Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Project |
The name of the project. For example, MYPROJ. Must be 1-8 alphanumeric characters; the first character must be alphabetic. |
|
Group |
The name of the group. For example, mygrp. Must be 1-8 alphanumeric characters; the first character must be alphabetic. |
|
DDIFILE |
The location of the project and group DDIFILE data set; do not specify the name DDIFILE. Default: The project and group path specified above. For example, myproj.group. |
|
Data Element Library Prefix |
Optional. The location of the Data Element Facility APSDE data set; do not specify the name APSDE. For example, APSPG.PROJECT1.GROUP1. |
Copyright © 2002 Micro Focus International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.