Creating a Custom Data Type
- On the
Tools menu, click
Custom Data Types.
The Custom Data Types tab is displayed.
- To define a new data type, click
New.
The Custom Data Type dialog box is displayed.
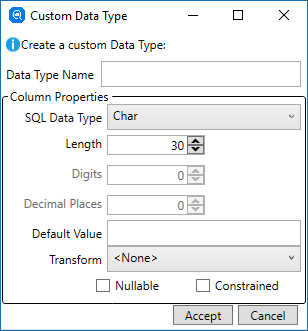
- In the Data Type Name field, type a descriptive name for this user data type.
- In the SQL Data Type field, click Char and select the required data type.
- Depending on the data type selected, complete the following options when enabled:
- Length - the maximum number of characters for the length of the column value.
- Digits - the number of decimal digits in the column value.
- Decimal Places - the number of decimal digits to the right of the decimal point in the column value.
- If required, in the
Default Value field, specify the default column value.
The default value is used for columns of this type when, for example, a column value is not specified in an SQL INSERT statement.
- In the
Transform field, click
<None> and select the required transform.
The value <None> indicates that no column transform is desired, but an item transform may be associated with the data item upon which columns of this user data type are based.
- Select the Nullable tick-box if the user data type allows the column to be set to null.
- Select the Constrained tick-box if the user data type constrains the column value to one of the true values of an 88-level condition-name associated with the data item upon which the column is based.
- Click Accept to add the new user data type.
- Click Save to Catalog.