Program Painter and Specification Editor keyword (see Keywords)
Redefine the TP-USERAREA field of the Commarea. To pass data between programs, see TP-COMMAREA.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 CA datastructure
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 CA05 COBOLdatastructure
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 CADS datastructurename
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
IO INPUT-FILE ASSIGN TO UT-S-INPUT
IO OUTPUT-FILE ASSIGN TO UT-S-OUTPUT
FD INPUT-FILE
LABEL RECORDS ARE STANDARD
BLOCK CONTAINS 0 RECORDS
01 INPUT-REC PIC X(80).
DS01 INPUTREC
FD OUTPUT-FILE
LABEL RECORDS ARE STANDARD
BLOCK CONTAINS 0 RECORDS
REC OUTPUT-REC X80
01 OUTPUT-REC-R REDEFINES OUTPUT-REC.
...COPY OUTREC.
CA CA-INPUT-REC
CA-IN-PART-NO N8
CA-IN-DESC X50
CA-IN-BASE-PRICE N6V2
CADS CAOUTREC IMS DB target
Use CCODE to include additional IMS command codes in DB-OBTAIN, DB-MODIFY, DB-PROCESS, and DB-STORE.
Valid IMS CCODEs are:
|
P |
Establish parentage at this level. |
|
Q |
Enqueue the segment. |
|
U |
Maintain current position at this level. |
|
- |
Null command code. |
APS generates the following IMS CCODEs; do not code them yourself.
|
D |
Put segment in I/O area (generated by REC). |
|
F |
Locate first occurrence (generated by FIRST). |
|
L |
Locate last occurrence (generated by LAST). |
|
N |
Do not replace segment (generated by REF). |
|
V |
Maintain current position at this level (generated by CURRENT). |
For more information, refer to the applicable IMS manuals.
Retrieve and enqueue RECORD-A and make it unavailable to other processing until the program terminates or explicitly frees the record with a checkpoint call.
DB-OBTAIN REC RECORD-A ... WHERE KEY-A = WS-KEY-A CCODE 'Q' ... REC RECORD-B ... WHERE KEY-B = WS-KEY-B ... VIEW PCBNAME RESET
ENDEVOR Interface feature
Add to or update the ENDEVOR library with an APS component from an APS Project Group. Alternatively, sign in a component at check in, without adding to or updating the ENDEVOR library. To retrieve a member from the library, see Checkout.
From the APS/ENDEVOR Version Control Menu, select option 1, Checkin. Alternatively, enter CI in the Command field on any APS screen.
Specify requirements on the Checkin screen, as follows.
|
Field |
Description
and Values |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Entity Type |
Entity type of the APS component to check in. Valid values are: |
|
|
|
ap |
Application Painter component in APSAPPL plus its related component in APRAPPL |
|
|
cn |
Scenario Painter component in APSCNIO |
|
|
ds |
Data Structure Painter component in APSDATA |
|
|
ox |
Online Express component in APSEXPS |
|
|
pg |
Program Painter component in APSPROG plus its related component in APRPROG |
|
|
rp |
Report Mock-up Painter component in APSREPT |
|
|
sc |
Screen Painter component in APSSCRN |
|
|
For other APS component types in your Project.Group, specify a data set name, such as USERMACS and DDISYMB. |
|
|
Member |
Component name to check in, or leave the Member field blank to select from a member list. |
|
|
System |
ENDEVOR System name, if it differs from the default System name for your current APS Project.Group. |
|
|
Subsystem |
ENDEVOR Subsystem name, if it differs from the default Subsystem name for your current APS Project.Group. |
|
|
Comment |
Text comment for the check in. |
|
|
CCID |
ENDEVOR CCID for the check in. |
|
|
Bypass Gen Processor |
Specify yes to bypass the associated ENDEVOR Generate Processor. |
|
|
Delete Input Source |
Specify yes to delete the component from the APS Project.Group. |
|
|
Processor Group |
Name of the ENDEVOR Processor Group. |
|
|
Override Signout |
Specify yes to override an existing signout. You must have authority to do so. |
|
|
Signin Only |
Specify yes to Signin only, releasing a previous signout of the component issued with your user ID; the Add or Update action is not executed. |
|
|
Stage |
ENDEVOR Stage number for signin. |
|
|
Component Parts |
For checking in AP and PG component type components. Valid values are: |
|
|
|
none |
Default. Process only the component specified in the Member field. |
|
|
all |
Process the component specified in the Member field and all its associated component parts, or components. |
|
|
list |
Display the Component Types Selection screen, to select the associated component types for processing. |
|
|
APS submits a batch job to perform the check in when some or all component parts are checked in with the component specified in the Member field. |
|
ENDEVOR Interface feature
Retrieve and, by default, sign out a revision from a controlled member of the ENDEVOR library to an APS Project Group so that you can modify it. To add or update the library, see Checkin.
From the APS/ENDEVOR Version Control Menu, select option 2, Checkout. Alternatively, enter CO in the Command field on any APS screen.
Specify requirements on the Checkout screen, as follows.
|
Field |
Description
and Values |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Entity Type |
Component Type of the component to check out. Valid values same as for Checkin. |
|
|
Member |
Member name to check out, or leave the Member field blank to select from a member list. |
|
|
System |
ENDEVOR System name, if it differs from the default System name for your current APS project.group. |
|
|
Subsystem |
ENDEVOR Subsystem name, if it differs from the default Subsystem name for your current APS Project.Group. |
|
|
Stage |
ENDEVOR Stage number of the member to check out. |
|
|
Version |
Default to the current revision. You can optionally override this value with another version number. |
|
|
Level |
Default to the current level. You can optionally override this value with another level number. |
|
|
Comment |
Text comment for the check out. |
|
|
CCID |
ENDEVOR CCID to associate with the check out. |
|
|
No Signout |
Specify yes to check out and browse the member without signing it out to your user ID. |
|
|
Replace Member |
Specify yes to overlay an existing member in the APS project.group. |
|
|
Override Signout |
Specify yes to override an existing Signout by another user. You must have authority to do so. |
|
|
Component Parts |
For checking out AP and PG component type components. Valid values are: |
|
|
|
none |
Default. Process only the component specified in the Member field. |
|
|
all |
Process the component specified in the Member field and all its associated component parts, or components. |
|
|
list |
Display the Component Types Selection screen, to select the associated component types for processing. |
|
|
APS submits a batch job to perform the check in when some or all component parts are checked in with the component specified in the Member field. |
|
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Use with the TP-LINKAGE call (TP-LINKAGE) to access CICS storage areas.
CIC-ADDRESS option(linkdataname) [option(linkdataname) ...]
|
option |
CWA |
Common Work Area |
|
|
TCTUA |
Terminal Control Table User Area |
|
|
TWA |
Transaction Work Area |
|
|
CSA |
Common Storage Area (z/OS target only) |
|
|
EIB |
Execute Interface Block (z/OS target only) |
|
linkdataname |
01-level Linkage Section data area identical to the linkdataname in the associated TP-LINKAGE call. |
|
Pass information to the application program. Set the Linkage Section data area (LK-CWA) in the current program to the address of the CWA for access.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 SYLK TP-LINKAGE LK-CWA LK01 LK-CWA PIC X(200). NTRY CIC-ADDRESS CWA(LK-CWA)
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Obtain values outside the program and assign them to a Working-Storage data area in the current program.
CIC-ASSIGN CICSoption(dataarea) [CICSoption(dataarea)....] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
|
Valid CICS option. See your CICS reference manual for more information. |
|
|
(dataarea) |
COBOL data name containing the result of the call. |
|
(errorpara) |
User-defined error routine to perform when an abnormal condition occurs. |
Obtain a value outside the application program and assign it to a user-defined area.
CIC-ASSIGN APPLID(WS-APPLID) ... ERROR(ERROR-PARA)
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Cancel a previously issued CIC-DELAY (See CIC-DELAY) or CIC-START (See CIC-START).
CIC-CANCEL [REQID(name)] ... [TRANSID(name)] ... [SYSID(name)] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Cancel an activity invoked by a CIC-START.
CIC-CANCEL TRANSID('TRAN') ERROR(ERROR-PARA)Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Suspend task processing for a prescribed time interval.
CIC-DELAY [ REQID(name)] ... [INTERVAL(hhmmss)|TIME(hhmmss)] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Suspend task processing for a 5-minute interval; let another task cancel this activity (UNIQCOM command).
CIC-DELAY INTERVAL(500) ERROR(ERROR-PARA) REQID('UNIQCOM')
Suspend task processing until 1:30 a.m.
CIC-DELAY TIME(013000) ERROR(ERROR-PARA) REQID('UNIQCOM') Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Delete all transient data associated with a predefined transient data queue.
CIC-DELETEQ-TD QUEUE(name) ... [SYSID(name)] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Delete all the intrapartition transient data stored in storage queue 'TDAQ'.
CIC-DELETEQ-TD QUEUE('TDAQ') ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Delete all temporary data and free all storage associated with a temporary storage queue.
CIC-DELETEQ-TS QUEUE(name) ... [SYSID(name)] ... [ERROR(erropara)]
Delete all the data stored in temporary storage queue 'TSAQ'.
CIC-DELETEQ-TS QUEUE('TSAQ') ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Release storage previously acquired by a CIC-GETMAIN (See CIC-GETMAIN).
CIC-FREEMAIN DATA(linkdataname)
|
linkdataname |
01-level Linkage Section data area identical to the linkdataname in the associated TP-LINKAGE call. |
Release the main storage of LK-STORAGE-AREA.
CIC-FREEMAIN DATA(LK-STORAGE-AREA)
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Obtain and initialize main storage. To release storage, see CIC-FREEMAIN.
CIC-GETMAIN SET(linkdataname) ... LENGTH(value)|FLENGTH(value) ... [INITIMG(value)] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Obtain an area of main storage of the length specified in the Working-Storage data area (WS-LENGTH). Specify initialization value (WS-BLANK) for the acquired main storage.
CIC-GETMAIN SET(STORAGE-AREA) ... LENGTH(WS-LENGTH) ... INITIMG(WS-BLANK) ... ERROR(ERROR-PARA)
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Load specified programs, tables, or maps from a library to main storage; to delete these, see CIC-RELEASE.
CIC-LOAD PROGRAM(name) [SET(linkdataname)] ... [LENGTH(dataarea)]|[FLENGTH(dataarea)] ... [ENTRY(pointref)] ... [HOLD] [ERROR(errorpara)]
Load table TAXTAB into main storage; perform user-defined error routine ERROR-PARA when an error occurs; store the address at which the module was loaded in Linkage Section data area TAX-TABLE-AREA; and store the length of the loaded module in Working-Storage data area TAX-LEN.
CIC-LOAD PROGRAM('TAXTAB')
... SET(TAX-TABLE-AREA) LENGTH(TAX-LEN)
... ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Read transient data from a predefined data queue.
CIC-READQ-TD QUEUE(name) ... INTO(dataarea)|SET(linkdataname) ... [LENGTH(dataarea)] [SYSID(name)] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Read a record from a transient data queue `TDAQ' into data area WS-TD-REC.
CIC-READQ-TD QUEUE('TDAQ') INTO(WS-TD-REC)
... LENGTH(WS-TD-LEN)
... ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Retrieve data from a temporary storage queue in main or auxiliary storage.
CIC-READQ-TS QUEUE(name) ... INTO(dataarea)|SET(linkdataname) ... LENGTH(dataarea) NUMITEMS(dataarea) ... [ITEM(value)|next] ... [SYSID(name)] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Read the next (or only) record from temporary storage queue `TSAQ' into data area WS-TD-RECORD.
CIC-READQ-TS QUEUE('TSAQ')
... INTO(WS-TD-RECORD) LENGTH(WS-TD-RECLEN)
... ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target in the z/OS environment
Delete program, table, or map, previously loaded with a CIC-LOAD call (See CIC-LOAD), from main storage.
CIC-RELEASE PROGRAM(name) ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
|
ERROR(errorpara) |
User-defined error routine to perform when an abnormal condition occurs |
|
PROGRAM(name) |
Main storage module to be deleted; can be a literal or COBOL data name (maximum 8 characters) |
Delete program PROG5.
CIC-RELEASE PROGRAM('PROG5')
... ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS targets
Code and pass through native CICS calls.
CICS command
Retrieve the system time of day.
CICS ASKTIME
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS and IMS DB targets
Schedule the PSB in the program, if not currently scheduled; to terminate it, see CIC-TERM-PSB. APS automatically generates these calls when you specify a PSB in the Application Painter.
CIC-SCHEDULE-PSB
To define a PSB in your application definition, see the APS User's Guide chapter Paint the Application Definition.
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Format output data without mapping and transmit to a terminal or line printer.
CIC-SEND-TEXT FROM(dataarea) ... LENGTH(value) [CICSoptions] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Use CIC-SEND-TEXT prior to a TERM (See TERM) from a main program in order to clear the screen and unlock the keyboard.
CIC-SEND-TEXT outputs data block TEXT-STRING, to be formatted without being mapped.
CIC-SEND-TEXT FROM(TEXT-STRING) ... LENGTH(100) ERASE FREEKB ... ERROR(ERROR-PARA)
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Establish addressability to a data area in the Linkage Section following an address change in the BLL cell.
CIC-SERVICE-RELOAD linkdataname
|
linkdataname |
01-level Linkage Section data area identical to the linkdataname in the associated TP-LINKAGE call. |
SERVICE-RELOAD is an OS/VS COBOL statement; do not use with COBOL II, because the compiler treats this call as a CONTINUE statement.
Establish addressability to Linkage area LINK-AREA-1 after an address change.
MOVE PASSED-ADDRESS TO LINK-AREA-1-PNTR CIC-SERVICE-RELOAD LINK-AREA-1
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Start a task on a local or remote system at a specified time.
CIC-START TRANSID(name) ... [INTERVAL(hhmmss)|TIME(hhmmss)] [CICSoptions] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Start a specific task (not associated with a terminal) in one hour.
CIC-START TRANSID('TRNL') INTERVAL(10000)
... ERROR(ERROR-PARA)
Initiate task TRN2 associated with terminal STA3; begin the task at 5:30 P.M.
CIC-START TRANSID('TRN2') TIME(173000)
... TERMID('STA3') ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Terminate the currently scheduled PSB (See CIC-SCHEDULE-PSB). You normally use this call before transferring to another program.
CIC-TERM-PSB
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Write transient data to a predefined data queue.
CIC-WRITEQ-TD QUEUE(name) FROM(dataarea) ... [LENGTH(value)] [SYSID(name)] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Write data to predefined transient data queue 'TRDQ'.
CIC-WRITEQ-TD QUEUE('TRDQ') FROM(WS-MESSAGE)
... LENGTH(WS-TD-LEN)
... ERROR(ERROR-PARA) Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS target
Write or rewrite temporary data records to a temporary storage queue.
CIC-WRITEQ-TS QUEUE(name) FROM(dataarea) ... LENGTH(value) [SYSID(name)] ... [ITEM(dataarea) [REWRITE] [CICSoptions] ... [NOSUSPEND] ... [ERROR(errorpara)]
Write a record to a temporary storage queue in auxiliary storage, where the queue name is in QUEUE-NAME.
CIC-WRITE-TS QUEUE(QUEUE-NAME) ... FROM(WS-TS-RECORD) ... LENGTH(WS-TS-LENGTH) ... ITEM(WS-TS-ITEM-NO) ... ERROR(ERROR-PARA)
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS, IMS DC, and ISPF Dialog targets
Move spaces or low-values to all fields in a specified screen.
[TP-|SC-]CLEAR screenname
This call does not alter the field attributes.
Move spaces to all fields on screen SCRA.
CLEAR SCRA
Data communication call (see Data Communication Calls)
CICS, IMS DC, and ISPF Dialog targets
Reset all screen field attributes to their original painted values.
[TP-]CLEAR-ATTRS screenname
The screen field contents do not change.
Reset all field attributes to their original values for screen SCRA.
CLEAR-ATTRS SCRA
Code program logic in both the Program Painter and Specification Editor using COBOL/2 structures.
Under APS COBOL/2 support, you can:
You can turn COBOL/2 support on and off by setting the Generate COBOL/2 field on the Generation Options screen.
When programming in the Program Painter or Specification Editor, you can code in COBOL/2 as follows.
000001 IF OK-TO-PROCEED 000002 MOVE A TO B 000003 IF D = E 000004 MOVE F TO G 000005 ELSE 000006 MOVE H TO I
When compiling and generating the above code, APS will not know which IF statement lines 005 and 006 belong to.
This truncation only occurs on a keyword line, and in fairly unusual circumstances, such as a PARA keyword followed by a long string of arguments with the last argument ending in column 72. If it happens, edit the member, fix the line, and save the file with COBOL/2 support turned on.
Report Writer clause (see Report Writer Structures and the APS User's Guide chapter Create Reports with Report Writer)
Batch environments
Specify a two-character literal placed at the beginning of each report line. It is useful when writing multiple reports to one file.
CODE literal
|
literal |
A two-character, non-numeric name inserted as the first two bytes of each report record or print line |
If your report does not have a File Description, the APS default record length of 250 includes the extra two bytes the CODE clause needs.
See the APS User's Guide chapter Create Reports with Report Writer.
Enter comments in your program. To write comments in the Identification Division, see REM.
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60 /* commentline
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
/*commentline
-KYWD- 12-*----20---*----30---*----40---*----50---*----60
Program code /*comment
%* comment
* comment /* comment %* comment
Note: You cannot code comments within database calls, data communication calls, or Data Structure Painter constructs.
In the Program Painter:
-LINE- -KYWD- 12--*--20---*----30----*---40---*----50---*----60 002000 /* S-COBOL COMMENT LINE 002010 /* COBOL COMMENT LINE 002020 PARA MAIN-PARA /* S-COBOL COMMENT
In the Data Structure Painter:
-LINE- -------- DATA STRUCTURE PAINTER ------- 000001 /* WORK FIELD 1 RECORD 000002 WRK1-FIELD-1 X(5) 000003 88 OPEN-VAL V'OPEN' 000004 88 CLOSED-VAL V'CLOSE'
Generated COBOL code:
000001 */* WORK FIELD 1 RECORD 000002 01 WRK1-FIELD-1 PIC X(5). 000003 88 OPEN-VAL VALUE 'OPEN'. 000004 88 CLOSED-VAL VALUE 'CLOSE'.
APS-generated report (see Application Reports)
The Component List Report catalogs all of the components created for an application within a specific Project andGroup.
The report lists components by painter in six columns - one each for applications, programs, screens, report mock-ups, data structures, and scenarios. Within each column, the report lists components in alphabetical order. The bottom of the report totals the number of components listed for each painter. You can produce a report listing application components of one or more types.
REPORT CODE: MS01 APS APPLICATION DICTIONARY PAGE 1
COMPONENT LIST 05/17/92 09:13
MKTAPS.MKT2
SELECTION CRITERIA: ALL
*********************************************************************************************
APPLICATIONS PROGRAMS SCREENS REPORTS DATA STRUCTURES SCENARIOS
------------ -------- ------- ------- --------------- ---------
CICSJSS ADEMO ADEMO $APSCMR APCOMM APDEMO
CICSVSAM AW02PGM ADEMOKB MANUFAC AWO3 APSDEMO
CUSTORDR AW03PGM ADEMO1 MWPART BANK2 APSDEMO2
DEMOKEB XXXPGM ADEMO1J REPORT1 COMAREA2 APSDEMO3
DEMO1803 ANNER1 ADEMO1X VNDROPD DLGAPPL DEMO4
DLXVAPPL DLGINQ ADEMO3D CPFDATAB CBIS
DLX2APPL LGMNU ADEMO3J DB2DEMO DL2APPL
DMVAPPL DLXVINQ A2CASE MARIA DEMO###
LEVEL30 DLX2UPD CMKTEMP QSSGLOBL ISR00007
MVS20SCR DMOMNU CMK1 QSS9 MVS21
PTSUNLD PMINFOT1 DLGU SSS2
PXAPPL PMINFOT2 DMOM TEST
QSSAPPL PMINFO3 KEB
SSKTEST PMINFO4 KEBDEMO1
TDDEMO PMUDS1 KEB1
TESTQSS PMXXXXT2 MEAD1
USRDEMO PMXXXXT3 P22604
PM1SVKEY REWDEMO
PTSUNLD TDCS
PXCUSTM TDDDH
PXMENU TDDST
PXORDRM TDFIRN
PXORDRS TDJH
PXPARTL TDME
PXVCUSTM TDOJ
PXVMENU TDOM
PXVORDRM TDOT
PXVORDRS TDOU
PXVPARTL TDPF
.
.
TDCM
TDCS
TDME
TDOJ
TDOM
TDOT
TDOU
TDPF
TDPL
TDPM
APPLICATIONS - 28
PROGRAMS - 60
SCREENS - 50
REPORTS - 6
DATA STRUCTURES - 13
SCENARIOS - 18 Report Writer clause (see Report Writer Structures and the APS User's Guide chapter Create Reports with Report Writer)
Batch environments
Identify control data items (controls), which are tested for a change each time a detail line is printed. Create a control hierarchy for the report control headings and footings (control breaks).
CONTROL [IS] [FINAL] dataname
CONTROLS [ARE] [FINAL] dataname1 ... datanameN
|
dataname |
Data item that causes a control break when it changes. |
|
FINAL |
Inclusive report control group not associated with a control dataname. It represents the highest level of control. |
See the APS User's Guide chapter Create Reports with Report Writer.
Use APS control file variables to control certain functions. Each control file contains documentation on its variables. Look in the APS CNTL PDS or library for these files.
|
APS CNTL File |
Environment or Function Controlled |
|
APCICSIN |
CICS |
|
APSDBDC |
Database and data communication calls |
|
APFEIN |
Field edits |
|
APDLGIN |
ISPF Dialog |
|
APIMSIN |
IMS DB and DC |
|
APDB2IN |
SQL |
|
APVSAMIN |
VSAM |
|
APHLPIN |
User Help Facility database |
File APCICSIN controls:
Note: Changing APSDBDC file parameter values affects the entire installation. To override values only for a specific Project, set the variables in the CNTL file APSPROJ.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Suppress blank lines from appearing in the output. Override with % SET BLANK. |
|
|
Define the characters used as evaluation brackets. Important: Overriding this parameter is not recommended because it will affect the Customization Facility macros. |
|
|
Limit the APSMACS (APS macros) and USERMACS (user macros) Customization Facility loop structures to a maximum of 500 loops. Override with another number, 6 digits maximum. Note: Loop limit flags for DB-PROCESS loops are in the target-specific APS CNTL files. |
|
|
Allows COBOL comments to appear in generated source. Override with 0. |
|
|
Customization Facility parameter. An error trace mechanism that identifies the line of source that caused the error, the active % INCLUDE statement(s), the macro(s) currently invoked and not yet ended, and the number of loops completed at the time of error (if applicable). The severity codes of errors traced are F (Fatal), E (Error), W (Warning), and I (Information) messages. To eliminate Information message traces, append a space and the keyword NOINFO to the trace statement. To turn off the trace in selected portions of a program, code % SET NOTRACE. |
|
|
Prevent APS-generated IMS DB-OBTAIN calls from HOLDing a record for update except when HOLD is specified in the DB-OBTAIN call. Override with "procopt", which does HOLD a record automatically, assuming the subschema or PSB specifies that the program can update the record. |
|
|
"Yes" specifies that a VSAM program is a prototype, enabling you to code DB calls without accessing a VSAM file. All subschema validation at program generation is still performed. NO means prototype mode is inactive. |
|
|
Deactivate the prototype mode for an IMS program. "Yes" specifies that an IMS program is a prototype, enabling you to code DB calls without accessing a data base. All subschema validation at program generation is still performed. |
|
|
Disable the APS-supplied IMS database error routine macros from calling the IMS-supplied error display module, DFS0AER. All database errors are resolved using only the APS-supplied status flags. To enable use of DSF0AER and the APS-supplied flags, set to 1. If your installation does not use DFS0AER, leave this flag set to 0. See Error Handling. |
|
|
IMS DB parameter. If your top-level copylib records begin with the level number 01 positioned in column 8, use the flag default of 0. If they don't, override with 1. When writing DDI statements for copylibs that don't begin with 01-level records, see instructions in the topic "Writing DDI Statements for IMS" in the APS User's Guide. Note: For VSAM, an equivalent flag exists in the APS CNTL file APVSAMIN. |
|
|
% &IM-SUPPRESS-COPYLIB = 0 and % &VS-SUPPRESS-COPYLIB = 0 |
Override with 1 to suppress a copylib described in your DDI statements. &IM is for IMS; &VS is for VSAM. |
|
Use a supplied Assembler routine to move data between record I/O areas and IMS concatenated segment I/O areas in APS-generated programs. This method is recommended because it's more efficient and doesn't require redefining the record I/O areas. Note: Because this module is linked during generation of COBOL code, setting this variable to 1 might interfere with transportablilty of the generated code. Overriding with 0 causes APS-generated programs to block and unblock IMS concatenated I/O areas using a byte-level loop in the generated code. Setting to 0 also causes APS to automatically redefine all record I/O areas as an array of bytes Note: Setting to 0 is incompatible with copylib members containing a COBOL OCCURS DEPENDING ON clause or multiple record declarations in a single member. |
|
|
Specifies that copylib members are placed in Working-Storage. |
|
|
Set the parameter RETRY as the default parameter for the NTRY call. Override with 0 to set the default to NORETRY. You can also override on a program-by-program basis by coding RETRY or NORETRY in the NTRY call. See NTRY for more information. |
|
|
Generate CALL 'CBLTDLI' syntax. Override with 1 to generate EXEC DL/I syntax. |
|
|
Set to 1, the Double Byte Character Set flag, for KANJI support. |
Use the IMS control file, APIMSIN, to control these functions:
Use the ISPF Dialog contol file, APDLGIN, to control these functions:
Use the DB2 control file, APDB2IN, to control these functions:
Use the VSAM control file, APVSAMIN, to control these functions:
Use the APS User Help Facility control file, APHLPIN, to control these functions for generating the User Help database:
Online Express feature
Write and execute custom processing logic to supplement or override the default logic that Online Express generates. Execute this logic at any of the APS-provided locations in your program, known as program control points.
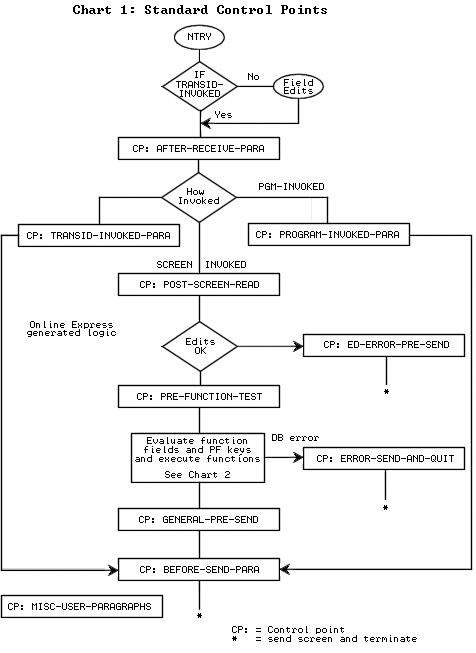
To view the control points in your program, display the Control Points screen or the Database Call Tailoring screen. Or, you can look in your generated program source to see where the control points occur. The complete set of control points is as follows.
|
Control Point |
Location in
Program |
|---|---|
|
After entering a program, regardless of invocation mode. |
|
|
After a screen-invoked program receives its screen. |
|
|
After a transid-invoked program is invoked. |
|
|
When APS displays the screen of a program invoked by the XCTL or MSG-SW function. |
|
|
Before APS terminates the program. |
|
|
After the end user presses the processing key (the Enter key is the default), and before the PRE-FUNCTION-TEST paragraph executes. |
|
|
Before APS evaluates all functions except the Terminate, or Exit, function. |
|
|
Before each MSG-SW, XCTL, or Call function executes. |
|
|
Before APS send a screen whose field edits have failed. |
|
|
After APS checks all functions, and before the TP-SEND call executes, when invocation mode is screen-invoked. |
|
|
Before APS sends the screen, regardless of invocation mode. |
|
|
Before APS performs the MOVE-SCREEN-TO-REC paragraph. |
|
|
After APS performs the MOVE-SCREEN-TO-REC paragraph, and the Update or Add function executes. |
|
|
Before APS performs the MOVE-REC-TO-SCREEN paragraph. |
|
|
After APS performs the MOVE-REC-TO-SCREEN paragraph, and after the Query function executes. |
|
|
Before the Add or Update function executes for a repeated record block row, and before screen fields move to database fields. APS uses the subscript CTR to reference repeated block rows. |
|
|
Before the Add or Update function executes for a repeated record block row, and after screen fields move to database fields. APS uses the subscript CTR to reference repeated block rows. |
|
|
After the Query or Forward function executes for a repeated record block row, and before database fields move to screen fields. APS uses the subscript CTR to reference repeated block rows. |
|
|
After the Query or Forward function executes for a repeated record block row, and after database fields move to screen fields. APS uses the subscipt CTR to reference repeated block rows. |
|
|
When a program terminates abnormally, such as when a database call fails when the Database Call Tailoring screen's Abort On Error parameter is set to Y. |
|
|
A location where you can write and store any number of paragraphs to perform at any control point in the program. Code all your paragraphs in one file in this location. |
|
|
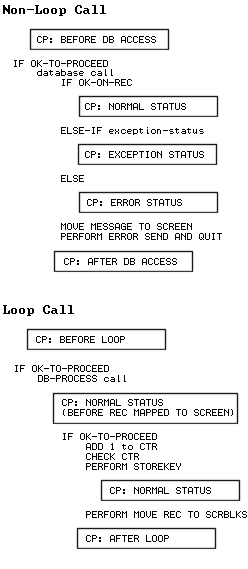
Before a non-loop database call executes |
|
|
Before a loop database call executes |
|
|
Before Online Express maps looped records to the screen |
|
|
Normal Status |
After Online Express maps any records to the screen |
|
After the database call returns a status flag with the Exception status code |
|
|
After the database call returns a status flag with the Error status code |
|
|
After a non-loop database call executes |
|
|
After a loop database call executes |
The following flowcharts illustrate the locations of all control points in APS-generated programs.

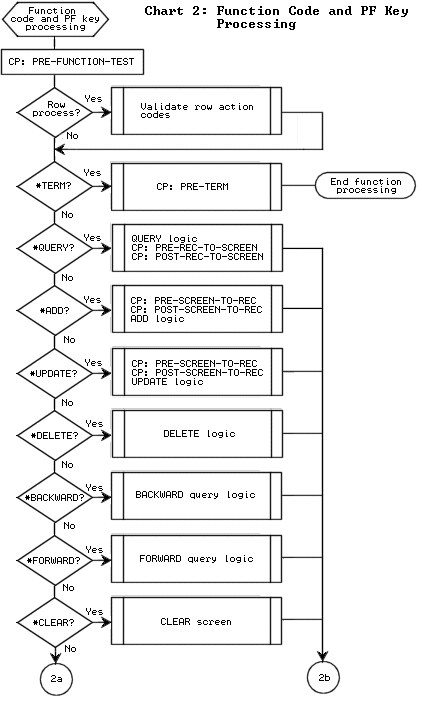
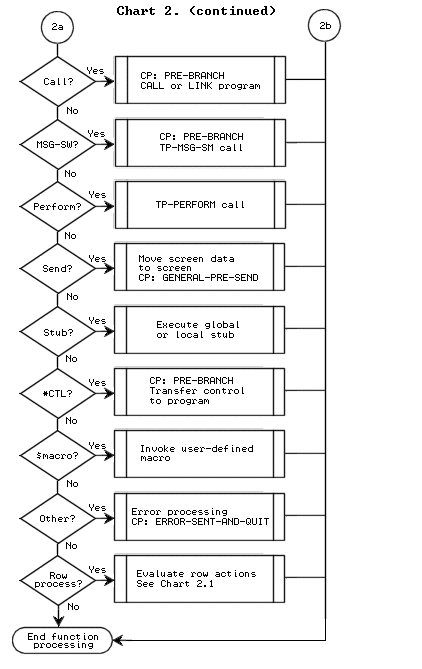
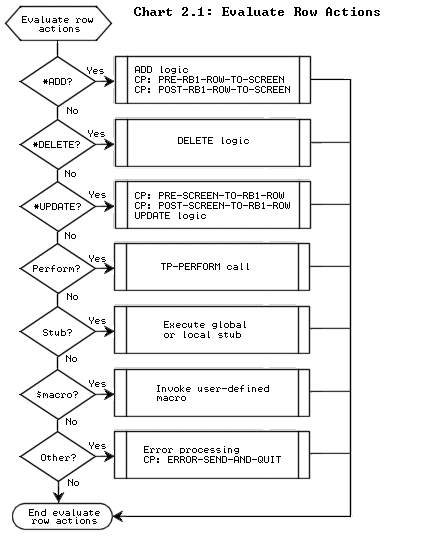
The flowchart below illustrates the location of the database call control points in generated programs.
Map records that show annual sales of $100,000 or more in the Northwest region, and calculate and map the grand total of those records. First define a loop call and qualify it to obtain the records of $100,000 or more. Then tailor the loop call with two local stubs. The first stub checks the records obtained by the loop to allow only records of the Northwest region to be processed further. The second stub calculates the grand total of those records, and maps the total to the screen.
DB-PROCESS REC SALES-RECORD
... WHERE ANNUAL-SALES-TOTAL > 99999
PERFORM CHECK-BEFORE-MAPPING-STUB-PARA
IF OK-TO-PROCEED
ADD 1 TO CTR
PERFORM RECORD-STOREKEY-PARA
MOVE REC-TO-SCREEN-BLK1
PERFORM CHECK-AFTER-MAPPING-STUB-PARA
.
.
.
CHECK-BEFORE-MAPPING-PARA
TRUE OK-TO-PROCEED
IF SALES-REGION NOT = NORTHWEST
FALSE OK-TO-PROCEED
CHECK-AFTER-MAPPING-PARA
calculation and mapping routine for grand totalNote:
Copyright © 2001 Micro
Focus International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the
proprietary marks and names used
herein are protected by international law.
Copyright © 2002 Micro Focus International Limited. All rights reserved.
This document and the proprietary marks and names
used herein are protected by international law.